|
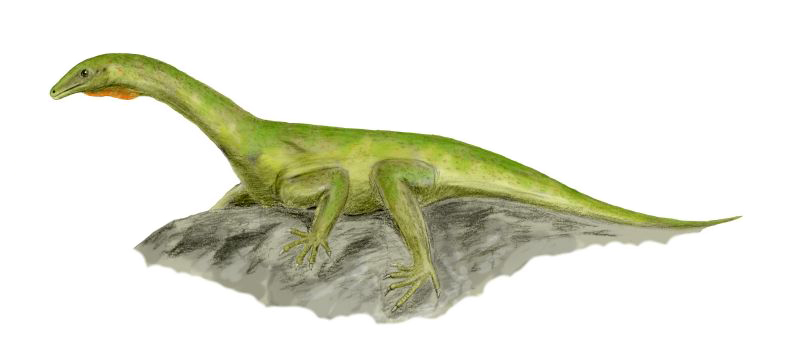
Trachelosaurus Fischeri
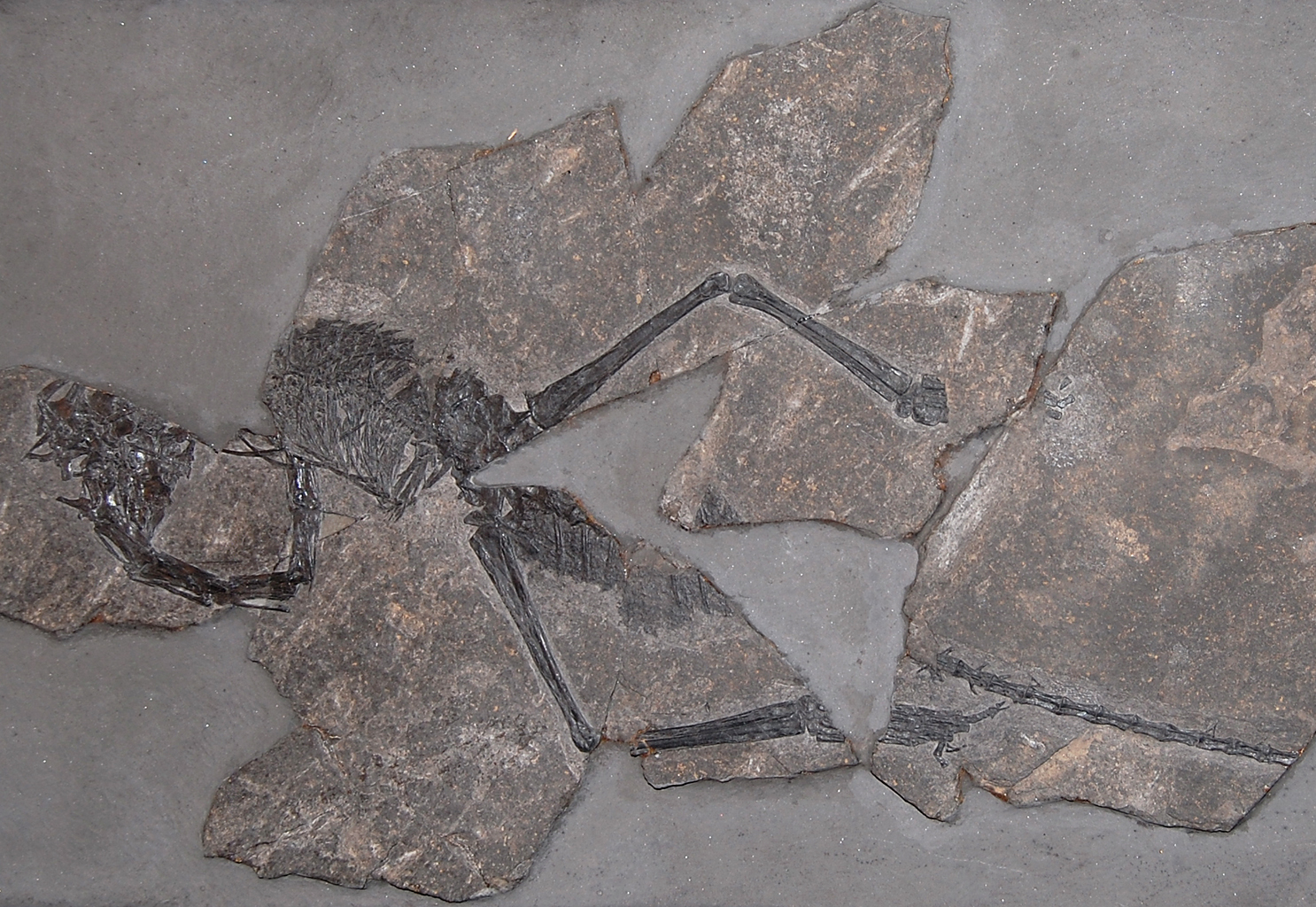
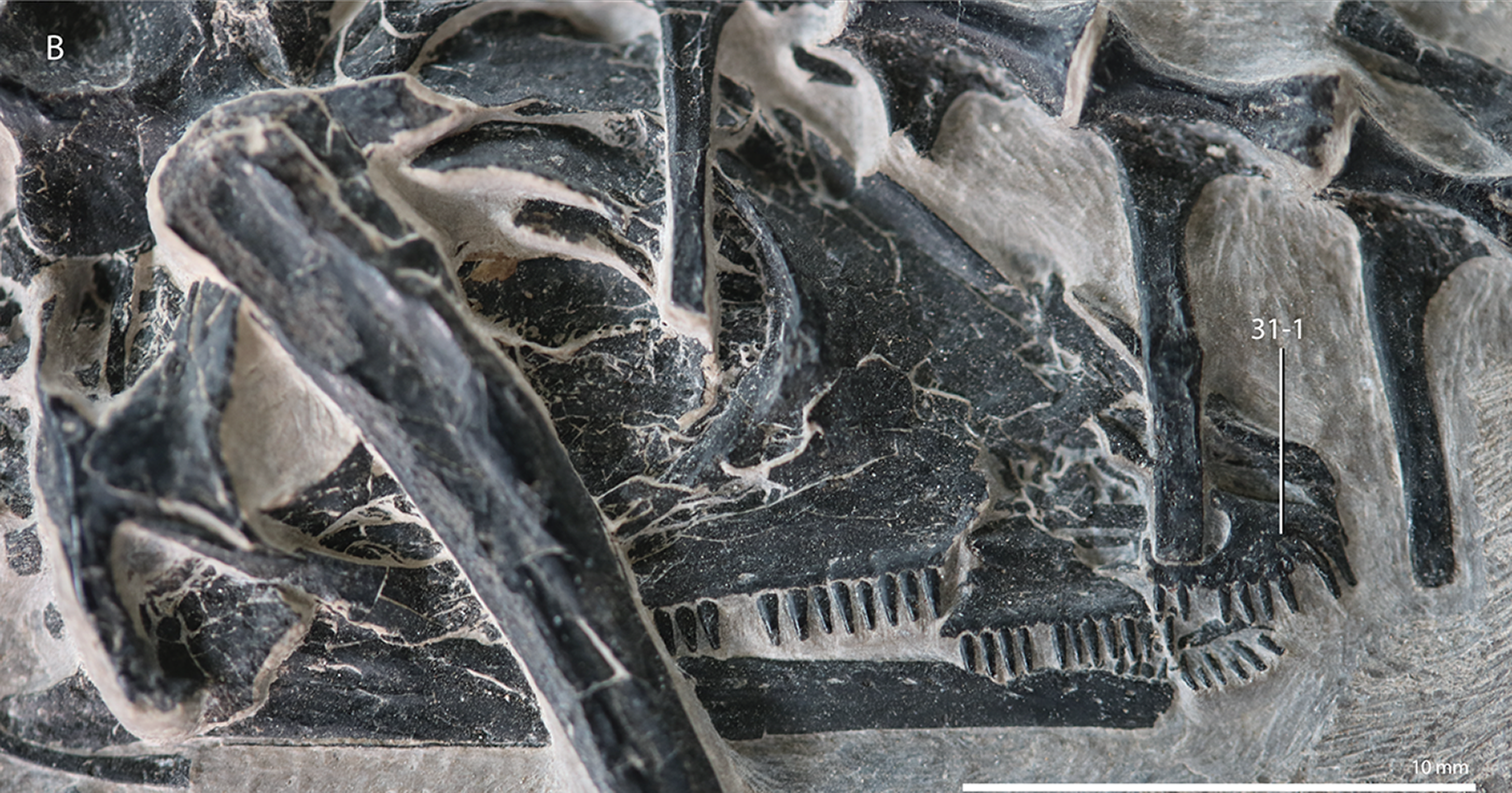
''Trachelosaurus'' is an extinct genus of lizard-like early archosauromorph reptiles in the family Trachelosauridae. It was originally described as a dinosaur until it was redescribed as a "protorosaur" reptile by Robert L. Carroll in 1988. The type species, ''T. fischeri'', was described by F. Broili & E. Fischer in 1917F. Broili and E. Fischer. (1917). ''Trachelosaurus fischeri'' nov. gen. nov. sp. A new dinosaur from the Buntsandstein of Bernburg. ''Jahrbuch der Königlich Preussischen geologischen Landesanstalt zu Berlin'' 37(1):359-414 based on remains found in the Solling Formation (Buntsandstein), Bernburg, Germany.H. H. Ecke. (1986). Palynologie des Zechsteins und Unteren Buntsandsteins im Germanischen Becken. ''Dissertation Georg-August-Universität Göttingen'' 1-117 A 2024 redescription identified ''Trachelosaurus'' as a long-necked and presumably aquatic reptile closely related to ''Dinocephalosaurus'' from the Guanling Formation of China. Classification In their 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Trias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Analyses
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as Computational phylogenetics, phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and Morphology (biology), morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothesis, hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living Taxon, taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in questi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raibliania
''Raibliania'' is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph discovered in the Calcare del Predil Formation in Italy. It lived during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic and it was related to ''Tanystropheus''. ''Raibliania'' is distinct from ''Tanystropheus'' due to some distinct features of the cervical vertebrae and teeth. The type species is ''Raibliania calligarisi'', named in 2020. The holotype (MFSN 27532) consists of a partial post-cranial skeleton, with the known elements including vertebrae ( sacral, cervical and dorsal; sans caudal), a single tooth, several ribs, gastralia and parts of the pelvis ( ilium and pubis). In their 2024 description of ''Dinocephalosaurus'' material, Spiekman ''et al''. suggested that the ''Raibliania'' fossil material may actually be referrable to ''Tanystropheus'', due to notable similarities between skeletons of the two taxa. The results of their phylogenetic analysis, which included both ''Raibliania'' and ''Tanystropheus'' spp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langobardisaurus
''Langobardisaurus'' (, meaning Reptile of Langobardi, in reference to the Long Bearded People, an ancient Central-European civilisation of North Germanic origin) is an extinct genus of Tanystropheidae, tanystropheid Archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile, with one valid species, ''L. pandolfii''. Its fossils have been found in Italy and Austria, and it lived during the Late Triassic period, roughly 228 to 201 million years ago. ''Langobardisaurus'' was initially described in 1994, based on fossils from the Calcare di Zorzino Formation in Northern Italy. Fossils of the genus are also known from the Forni Dolostone of Northern Italy and the Seefeld Formation of Austria. Discovery To date, five specimens of ''Langobardisaurus'' have been found. Calcare di Zorzino specimens The first fossils of the genus were discovered in 1974 at a quarry in Cene, Lombardy exposing the Calcare di Zorzino (Zorzino Limestone). This formation has produced two specimens, both of which are flatten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amotosaurus
''Amotosaurus'' is an extinct genus of tanystropheid protorosaur from the earliest Middle Triassic (early Anisian stage) of Black Forest, southwestern Germany. ''Amotosaurus'' is known from the holotype SMNS 50830, a partial skeleton including left maxilla with teeth, cervical series, pelvic girdle and other postcranial remains. Other specimens include SMNS 90600-90601, SMNS 50691, SMNS 54783a-b and SMNS 54810. It was first described and named by Nicholas C. Fraser and Olivier Rieppel in 2006 and the type species In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ... is ''Amotosaurus rotfeldensis''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4747981 Fossil taxa described in 2006 Tanystropheidae Middle Triassic reptiles of Europe Prehistoric reptile genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocnemus
''Macrocnemus'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile known from the Middle Triassic (Late Anisian to Ladinian) of Europe and China. ''Macrocnemus'' is a member of the Tanystropheidae family and includes three species''. Macrocnemus bassanii'', the first species to be named and described, is known from the Besano Formation and adjacent paleontological sites in the Italian and Swiss Alps. ''Macrocnemus fuyuanensis,'' on the other hand, is known from the Zhuganpo Formation in southern China. A third species, ''Macrocnemus obristi,'' is known from the Prosanto Formation of Switzerland and is characterized by gracile limbs. The name ''Macrocnemus'' is Greek for "long tibia". Description ''Macrocnemus'' is known from multiple specimens, most belonging to ''M. bassanii''. It is a small reptile measuring long. ''Macrocnemus'' possessed at least 52 or 53 caudal vertebrae. Like many other early archosauromorphs, ''Macrocnemus'' had a small and low head on the end of a thin ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxisaurus
''Luxisaurus'' (meaning " Luxi lizard") is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph reptile from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) Guanling Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, ''L. terrestris'', known from an articulated partial skeleton. ''Luxisaurus'' is hypothesized to have lived a more terrestrial lifestyle than many other tanystropheids, which may have been aquatic. Discovery and naming The ''Luxisaurus'' holotype specimen, HFUT SML-21-08-001, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation (Upper Member), dated to the Anisian age ( Pelsonian substage) of the middle Triassic period, near Suomeiluo in Luxi County, Yunnan Province, China. The articulated incomplete specimen consists of most of both forelimbs (missing their proximal ends), most of both hindlimbs (missing part of the right femur), gastralia, elements of the pelvic girdle, part of the last dorsal vertebra, two sacral vertebrae with sacral ribs, and several proximal caudal ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustaburiania
''Augustaburiania'' is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph from the latest Early Triassic (late Olenekian age) of Volgograd Region, western Russia. All specimens were recovered in the right slope of the Don River valley from the Lipovskaya Formation. It was named by Sennikov in 2011 and the type species In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ... is ''Augustaburiania vatagini''. ''Augustaburiania'' is the oldest known tanystropheid. References Tanystropheidae Prehistoric reptile genera Olenekian genera Early Triassic reptiles of Europe Triassic Russia Fossils of Russia Fossil taxa described in 2011 {{triassic-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheidae
Tanystropheidae is an extinct family (biology), family of archosauromorph reptiles that lived throughout the Triassic Period, often considered to be "protorosaurs". They are characterized by their long, stiff necks formed from elongated cervical vertebrae with very long cervical ribs. Members of the group include both terrestrial and aquatic forms. While some tanystropheids were small lizard-like animals, other tanystropheids such as ''Tanystropheus'' were large animals that had necks that were several meters long, longer than the rest of their bodies. Tanystropheids are known from Europe, Asia (Russia, China, and Saudi Arabia), North America and probably South America (Brazil). The presence of tanystropheids in Europe and China indicate that they lived along much of the coastline of the Tethys Ocean. However, species in western North America are found in terrestrial deposits, suggesting that as a group, tanystropheids were ecologically diverse. Relationships among tanystropheid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gracilicollum
''Gracilicollum'' (meaning "slender neck") is an extinct genus of likely tanysaurian archosauromorph from the Middle Triassic (Anisian) Guanling Formation of China. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''G. latens'', known from a skull and partial neck. Discovery and naming The ''Gracilicollum'' holotype specimen, IVPP V 15636, was discovered in sediments of the Guanling Formation (Member II), dated to the Anisian age of the middle Triassic period, near Xinmin Village in Panzhou, Guizhou Province, China. The specimen, preserved on two blocks, consists of a skull preserved in ventral view articulated with a partial cervical vertebral column of at least 17 vertebrae in lateral view. In 2023, Wang et al. Species description, described ''Gracilicollum latens'', a new genus and species of tanystropheid archosauromorphs, based on these fossil remains. The Genus, generic name, "''Gracilicollum''", combines the Latin words "gracilis", meaning "slender", and "collum", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuyuansaurus
''Fuyuansaurus'' is an extinct genus of "protorosaur" reptiles (probably part of Tanystropheidae) known from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian stage) Zhuganpo Formation of southern China. ''Fuyuansaurus'' was first named by Nicholas C. Fraser, Olivier Rieppel and Li Chun in 2013 and the type species is ''Fuyuansaurus acutirostris''. This genus is known from a single partial skeleton, IVPP V17983. This skeleton includes part of the skull, most of the neck, and portions of the trunk, shoulder girdle, and hip. ''Fuyuansaurus'' can be distinguished from other "protorosaurs" by its elongated and slender snout. Like ''Tanystropheus'', it possessed an elongated neck, but it differs from most tanystropheids in the structure of its hip. Nevertheless, Ezcurra and Butler classified it as a tanystropheid in 2018, as did Spiekman et al. in 2021. Description The skull was crushed and incomplete, with the tip of the snout broken off and the middle part of the skull obscured by the part of the ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectodens
''Pectodens'' (meaning "comb tooth") is an extinction, extinct genus of archosauromorpha, archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Middle Triassic in China. The type and only species of the genus is ''P. zhenyuensis'', named by Chun Li and colleagues in 2017. It was a member of the Archosauromorpha, specifically part of the unnatural grouping Protorosauria. However, an unusual combination of traits similar (such as the long neck) and dissimilar (such as the absence of a hook on the fifth metatarsal bones, metatarsal bone) to other protorosaurs initially led to confusion over its evolutionary relationships. In 2021, it was placed in a newly-established group, Dinocephalosauridae, along with its closest relative ''Dinocephalosaurus''. A small, slender animal measuring long, ''Pectodens'' was named after the peculiar comb-like arrangement of long, conical teeth present in its mouth. Unlike ''Dinocephalosaurus'' and the other reptiles that it was preserved with, well-developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |