|
Toxic Security
A toxic asset is a financial asset that has fallen in value significantly and for which there is no longer a functioning market. Such assets cannot be sold at a price satisfactory to the holder. Because assets are offset against liabilities and frequently leveraged, this decline in price may be quite dangerous to the holder. The term became common during the 2008 financial crisis, in which toxic assets played a major role. When the market for toxic assets ceases to function, it is described as "frozen". Markets for some toxic assets froze in 2007, and the problem grew much worse in the second half of 2008. Several factors contributed to the freezing of toxic asset markets. The value of the assets was very sensitive to economic conditions, and increased uncertainty in these conditions made it difficult to estimate the value of the assets. Banks and other major financial institutions were unwilling to sell the assets at significantly reduced prices, since lower prices would force them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Asset
A financial asset is a non-physical asset whose value is derived from a contractual claim, such as deposit (finance), bank deposits, bond (finance), bonds, and participations in companies' share capital. Financial assets are usually more market liquidity, liquid than tangible property, tangible assets, such as commodities or real estate. The opposite of financial assets is Non-financial asset, non-financial assets, which include both tangible property (sometimes also called real assets) such as land, real estate or commodities, and Intangible asset, intangible assets such as intellectual property, including copyrights, patents, trademarks and data. Types According to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), a financial asset can be: * Cash or cash equivalent, * Equity (finance), Equity instruments of another entity, * Contractual right to receive cash or another financial asset from another entity or to exchange financial assets or financial liabilities with anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt Overhang
Debt overhang is the condition of an organization (for example, a business, government, or family) that has existing debt so great that it cannot easily borrow more money, even when that new borrowing is actually a good investment that would more than pay for itself. This problem emerges, for example, if a company has a new investment project with positive net present value (NPV), but cannot capture the investment opportunity due to an existing debt position, i.e., the face value of the existing debt is bigger than the expected payoff. Hence, the equity holders will be reluctant to invest in such a project because most of the benefits will be reaped by the debt holders. In addition, debt holders will not finance the firm if the company cannot convince the debt holders that the project will not fail. The situation emerges if existing debtholders of a company can be expected to lay claim to (part of) the profits of the new project, and this renders the NPV of the project (when under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collateralized Debt Obligation
A collateralized debt obligation (CDO) is a type of structured finance, structured asset-backed security (ABS). Originally developed as instruments for the corporate debt markets, after 2002 CDOs became vehicles for refinancing Mortgage-backed security, mortgage-backed securities (MBS).Lepke, Lins and Pi card, ''Mortgage-Backed Securities'', §5:15 (Thomson West, 2014). Like other private label securities backed by assets, a CDO can be thought of as a promise to pay investors in a prescribed sequence, based on the cash flow the CDO collects from the pool of bonds or other assets it owns. Distinctively, CDO credit risk is typically assessed based on a probability of default (PD) derived from ratings on those bonds or assets. The CDO is "sliced" into sections known as tranche, "tranches", which "catch" the cash flow of interest and principal payments in sequence based on seniority. If some loans default and the cash collected by the CDO is insufficient to pay all of its investors, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CBC News
CBC News is the division of the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation responsible for the news gathering and production of news programs on the corporation's English-language operations, namely CBC Television, CBC Radio, CBC News Network, and CBC.ca. Founded in 1941 by the public broadcaster, CBC News is the largest news broadcaster in Canada and has local, regional, and national broadcasts and stations. It frequently collaborates with its organizationally separate French-language counterpart, Radio-Canada Info. History The first CBC newscast was a bilingual radio report on November 2, 1936. The CBC News Service was inaugurated during World War II on January 1, 1941, when Dan McArthur, chief news editor, had Wells Ritchie prepare for the announcer Charles Jennings a national report at 8:00 pm. Previously, CBC relied on The Canadian Press to provide it with wire copy for its news bulletins. Readers who followed Jennings were Lorne Greene, Frank Herbert and Earl Cameron. '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Economic Stabilization Act Of 2008
The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008, also known as the "bank bailout of 2008" or the "Wall Street bailout", was a United States federal law enacted during the Great Recession, which created federal programs to "bail out" failing financial institutions and banks. The Bill (law), bill was proposed by United States Secretary of the Treasury, Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson, passed by the 110th United States Congress, and was signed into law by President George W. Bush. It became law as part of Public Law 110-343 on October 3, 2008. It created the $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) whose funds would purchase toxic assets from failing banks. The funds were mostly directed to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions as the United States Department of the Treasury, Treasury continued to review the effectiveness of targeted asset-purchases. The 2008 financial crisis developed partly due to the subprime mortgage crisis, causing the failure o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheila Bair
Sheila Colleen Bair (born April 3, 1954) is an American former government official who was the 19th Chair of the U.S. Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) from 2006 to 2011, during which time she shortly after taking charge of the FDIC in June 2006 began warning of the potential systemic risks posed by the growing trend of subprime-mortgage-backed bonds, and then later assumed a prominent role in the government's response to the 2008 financial crisis. She was appointed to the post for a five-year term on June 26, 2006, by George W. Bush through July 8, 2011. She was subsequently the List of presidents of Washington College, 28th president of Washington College in Chestertown, MD, the first female head of the college in its 234-year history, a position she held from 2015 until her resignation in 2017. Early life Bair is a native of Independence, Kansas, Independence, Kansas. Born to a Lutheran Christian family, her father Albert (1916–2008), who was of German descent, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
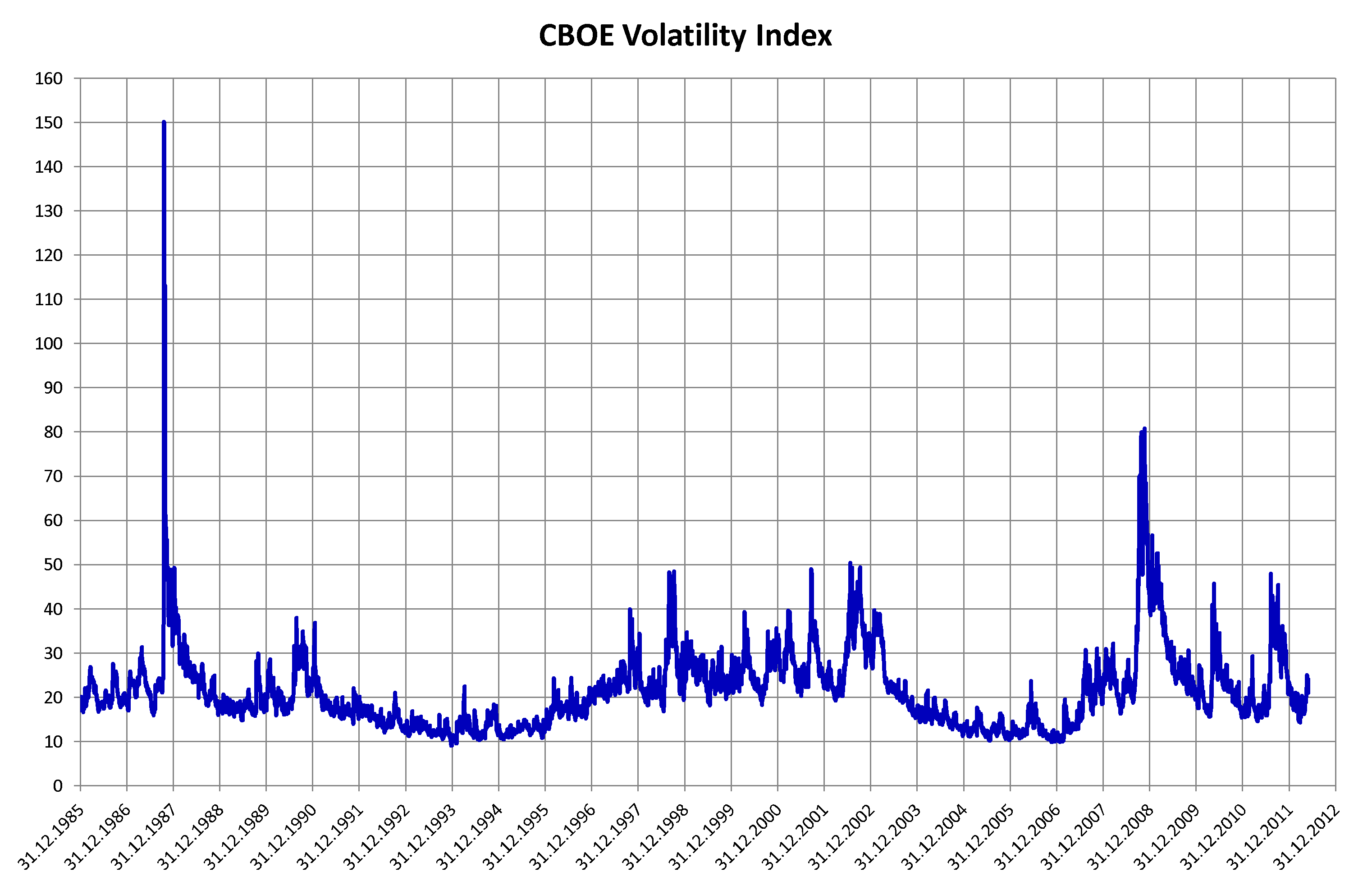
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call Option
In finance, a call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a contract between the buyer and the seller of the call Option (finance), option to exchange a Security (finance), security at a set price. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation, to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument (the underlying) from the seller of the option at or before a certain time (the Expiration (options), expiration date) for a certain price (the strike price). This effectively gives the buyer a Long (finance), ''long'' position in the given asset. The seller (or "writer") is obliged to sell the commodity or financial instrument to the buyer if the buyer so decides. This effectively gives the seller a Short (finance), ''short'' position in the given asset. The buyer pays a fee (called a Insurance, premium) for this right. The term "call" comes from the fact that the owner has the right to "call the stock away" from the seller. Price of opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American New Keynesian economics, New Keynesian economist who is the Distinguished Professor of Economics at the CUNY Graduate Center, Graduate Center of the City University of New York. He was a columnist for ''The New York Times'' from 2000 to 2024. In 2008, Krugman was the sole winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to New Trade Theory, new trade theory and New Economic Geography, new economic geography. The Prize Committee cited Krugman's work explaining the patterns of international trade and the geographic distribution of economic activity, by examining the effects of Economy of scale, economies of scale and of consumer preferences for diverse goods and services. Krugman was previously a professor of economics at MIT, and, later, at Princeton University which he retired from in June 2015, holding the title of Emeritus, professor emeritus there ever since. He also holds the title o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Term Asset Lending Facility
Term may refer to: Language *Terminology, context-specific nouns or compound words **Technical term (or ''term of art''), used by specialists in a field *** Scientific terminology, used by scientists *Term (argumentation), part of an argument in debate theory Law and finance *Contractual term, a provision in a contract **Credit repayment terms **Payment terms, "net ''D''" on a trade invoice **Purchase order, invoice terms more generally * Term life insurance Lengths of time *Academic term, part of a year at school or university *Term of office, a set period a person serves in an elected office *Term of patent, the period of enforcement of patent rights *Term of a pregnancy *Prison sentence Mathematics and physics *Term (logic), a component of a logical or mathematical expression (not to be confused with term logic, or Aristotelian logic) **Ground term, a term with no variables *Term (arithmetic), or addend, an operand to the addition operator **Term of a summation, a polynomial, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troubled Asset Relief Program
The Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) is a program of the United States government to purchase toxic assets and equity from financial institutions to strengthen its financial sector that was passed by Congress and signed into law by U.S. President, President George W. Bush. It was a component of the government's measures in 2009 to address the subprime mortgage crisis. The TARP originally authorized expenditures of $700 billion. The Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 created the TARP. The Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, signed into law in 2010, reduced the amount authorized to $475 billion (approximately $ in ). By October 11, 2012, the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) stated that total disbursements would be $431 billion, and estimated the total cost, including grants for mortgage programs that have not yet been made, would be $24 billion. On December 19, 2014, the U.S. Treasury sold its remaining holdings of Ally Financial, essentially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |