|
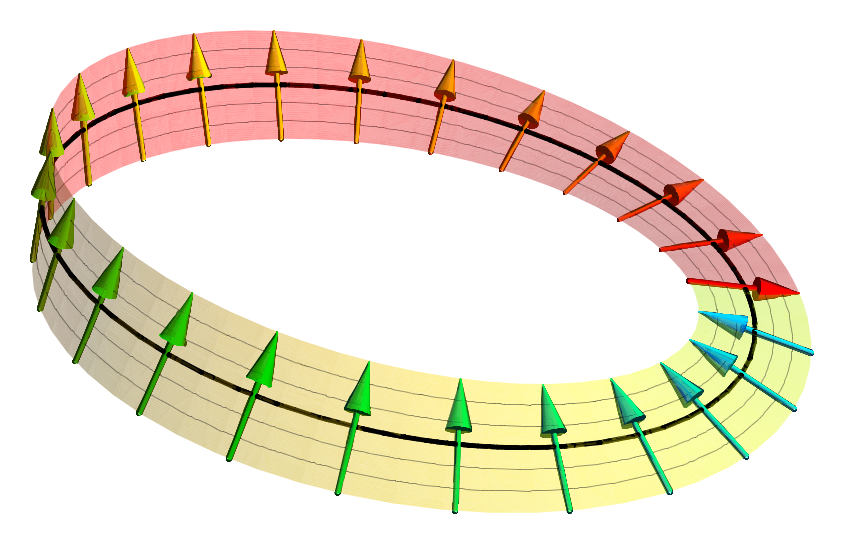
Torsion Field (pseudoscience)
A torsion field (also called axion field, spin field, spinor field, and microlepton field) is a reoccurring feature of many pseudoscience, pseudoscientific proposals. It posits that the Spin (physics), quantum spin of particles can be used to cause emanations to carry information through vacuum orders of magnitude faster than the speed of light. History The first torsion field proposals were proposed in the late Soviet Union by a group of physicists in the 1980s who loosely based their ideas on Einstein–Cartan theory and some variant solutions of Maxwell's equations that do not have a solid grounding in scientific fact. The group, led by Anatoly Akimov and Gennady Shipov, began the research as the state-sponsored Center for Nontraditional Technologies. They disbanded in 1991 when their research was exposed by physicist Eugene Alexandrov as a fraud and an embezzlement of government funding. Akimov and Shipov received financing for torsion field research from the Russian Ministry o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, Electrical network, electric and Magnetic circuit, magnetic circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar, etc. They describe how electric field, electric and magnetic fields are generated by electric charge, charges, electric current, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity, and as Einstein's theory of gravity, is the differential geometry, geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General theory of relativity, relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time in physics, time, or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ''curvature of spacetime'' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever is present, including matter and radiation. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second-order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes gravity in classical mechanics, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion Tensor
In differential geometry, the torsion tensor is a tensor that is associated to any affine connection. The torsion tensor is a bilinear map of two input vectors X,Y, that produces an output vector T(X,Y) representing the displacement within a tangent space when the tangent space is developed (or "rolled") along an infinitesimal parallelogram whose sides are X,Y. It is skew symmetric in its inputs, because developing over the parallelogram in the opposite sense produces the opposite displacement, similarly to how a screw moves in opposite ways when it is twisted in two directions. Torsion is particularly useful in the study of the geometry of geodesics. Given a system of parametrized geodesics, one can specify a class of affine connections having those geodesics, but differing by their torsions. There is a unique connection which ''absorbs the torsion'', generalizing the Levi-Civita connection to other, possibly non-metric situations (such as Finsler geometry). The difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy Stress Tensor
In continuum mechanics, the Cauchy stress tensor (symbol \boldsymbol\sigma, named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy), also called true stress tensor or simply stress tensor, completely defines the state of stress at a point inside a material in the deformed state, placement, or configuration. The second order tensor consists of nine components \sigma_ and relates a unit-length direction vector e to the ''traction vector'' T(e) across an imaginary surface perpendicular to e: :\mathbf^ = \mathbf e \cdot\boldsymbol\quad \text \quad T_^= \sum_\sigma_e_i. The SI base units of both stress tensor and traction vector are newton per square metre (N/m2) or pascal (Pa), corresponding to the stress scalar. The unit vector is dimensionless. The Cauchy stress tensor obeys the tensor transformation law under a change in the system of coordinates. A graphical representation of this transformation law is the Mohr's circle for stress. The Cauchy stress tensor is used for stress analysis of mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarization (waves)
, or , is a property of transverse waves which specifies the geometrical orientation of the oscillations. In a transverse wave, the direction of the oscillation is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the wave. One example of a polarized transverse wave is vibrations traveling along a taut string, for example, in a musical instrument like a guitar string. Depending on how the string is plucked, the vibrations can be in a vertical direction, horizontal direction, or at any angle perpendicular to the string. In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves, and transverse sound waves ( shear waves) in solids. An electromagnetic wave such as light consists of a coupled oscillating el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ranging from radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. All forms of EMR travel at the speed of light in a vacuum and exhibit wave–particle duality, behaving both as waves and as discrete particles called photons. Electromagnetic radiation is produced by accelerating charged particles such as from the Sun and other celestial bodies or artificially generated for various applications. Its interaction with matter depends on wavelength, influencing its uses in communication, medicine, industry, and scientific research. Radio waves enable broadcasting and wireless communication, infrared is used in thermal imaging, visible light is essential for vision, and higher-energy radiation, such as X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion (other)
Torsion may refer to: Science * Torsion (mechanics), the twisting of an object due to an applied torque * Torsion of spacetime, the field used in Einstein–Cartan theory and ** Alternatives to general relativity * Torsion angle, in chemistry Biology and medicine * Torsion fracture or spiral fracture, a bone fracture when torque is applied * Organ torsion, twisting that interrupts the blood supply to that organ: ** Splenic torsion, causing splenic infarction ** Ovarian torsion ** Testicular torsion * Penile torsion, a congenital condition * Torsion of the digestive tract in some domestic animals: ** Torsion, a type of horse colic ** Gastric torsion, or gastric dilatation volvulus * Torsion (gastropod), a developmental feature of all gastropods Mathematics * Torsion of a curve * Torsion tensor, in differential geometry * Torsion (algebra), in ring theory * Torsion group, in group theory and arithmetic geometry * Tor functor, the derived functors of the tensor product of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinor
In geometry and physics, spinors (pronounced "spinner" IPA ) are elements of a complex numbers, complex vector space that can be associated with Euclidean space. A spinor transforms linearly when the Euclidean space is subjected to a slight (infinitesimal transformation, infinitesimal) rotation, but unlike Euclidean vector, geometric vectors and tensors, a spinor transforms to its negative when the space rotates through 360° (see picture). It takes a rotation of 720° for a spinor to go back to its original state. This property characterizes spinors: spinors can be viewed as the "square roots" of vectors (although this is inaccurate and may be misleading; they are better viewed as "square roots" of Section (fiber bundle), sections of vector bundles – in the case of the exterior algebra bundle of the cotangent bundle, they thus become "square roots" of differential forms). It is also possible to associate a substantially similar notion of spinor to Minkowski space, in which cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensor Field
In mathematics and physics, a tensor field is a function assigning a tensor to each point of a region of a mathematical space (typically a Euclidean space or manifold) or of the physical space. Tensor fields are used in differential geometry, algebraic geometry, general relativity, in the analysis of stress and strain in material object, and in numerous applications in the physical sciences. As a tensor is a generalization of a scalar (a pure number representing a value, for example speed) and a vector (a magnitude and a direction, like velocity), a tensor field is a generalization of a ''scalar field'' and a ''vector field'' that assigns, respectively, a scalar or vector to each point of space. If a tensor is defined on a vector fields set over a module , we call a tensor field on . A tensor field, in common usage, is often referred to in the shorter form "tensor". For example, the ''Riemann curvature tensor'' refers a tensor ''field'', as it associates a tensor to each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (physics)
In science, a field is a physical quantity, represented by a scalar (mathematics), scalar, vector (mathematics and physics), vector, or tensor, that has a value for each Point (geometry), point in Spacetime, space and time. An example of a scalar field is a weather map, with the surface temperature described by assigning a real number, number to each point on the map. A surface wind map, assigning an arrow to each point on a map that describes the wind velocity, speed and direction at that point, is an example of a vector field, i.e. a 1-dimensional (rank-1) tensor field. Field theories, mathematical descriptions of how field values change in space and time, are ubiquitous in physics. For instance, the electric field is another rank-1 tensor field, while electrodynamics can be formulated in terms of Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field, two interacting vector fields at each point in spacetime, or as a Covariant formulation of classical electromagnetism, single-ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |