|
Toll-like Receptor 1
Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that form the cornerstone of the innate immune system. TLR1 recognizes bacterial lipoproteins and glycolipids in complex with TLR2. TLR1 is a cell surface receptor. In humans, TLR1 is encoded by the ''TLR1'' gene, which is located on chromosome 4. Function The binding of ligands to TLR1 activates intracellular signaling cascades leading to an inflammatory response and initiation of immune processes. TLR1 cooperates with TLR2 in the recognition of bacterial triacyl lipoproteins. TLR1 has been shown to recognize the outer surface lipoprotein of ''Borrelia burgdorferi''. The important role of TLR1 in recognizing triacyl lipopeptides has been shown in TLR1-deficient mice. Toll-like receptors, including TLR-1, found on the epithelial cell layer that lines the small and large intestine are important players in the management of the gut microbiota and detection of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toll-like Receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from Microorganism, microbes. Once these microbes have reached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13. Humans lack genes for TLR11, TLR12 and TLR13 and mice lack a functional gene for TLR10. The receptors TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell membrane, whereas TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located in Intracellular receptor, intracellular Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles (because they are sensors of nucleic acids). TLRs received their name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins into membrane-bound Vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and Endocytosis, endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. The Golgi apparatus was identified in 1898 by the Italian biologist and pathologist Camillo Golgi. The organelle was later named after him in the 1910s. Discovery Because of its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, such as eosinophil peroxidase, ribonucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Lymphoid Cell
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of Innate immune system, innate immune cells, derived from common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). In response to pathogenic tissue damage, ILCs contribute to immunity via the secretion of Cytokine, signalling molecules, and the regulation of both innate and adaptive immune cells. ILCs are primarily tissue resident cells, found in both Lymphatic system, lymphoid (immune associated), and non- lymphoid tissues, and rarely in the blood. They are particularly abundant at mucosal surfaces, playing a key role in mucosal immunity and homeostasis. Characteristics allowing their differentiation from other immune cells include the regular Lymphocyte, lymphoid morphology, absence of rearranged antigen receptors found on T cell receptor, T cells and B cell receptor, B cells (due to the lack of the recombination-activating gene, RAG gene), and phenotypic markers usually present on Myelocyte, myeloid or dendritic cells. Based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in tissues that are in contact with the body's external environment, such as the skin, and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature and mature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes, where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the '' dendrites,'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance to the dendrites of neurons, these are structures distinct from them. Immature dendr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" and , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to around 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microglia
Microglia are a type of glia, glial cell located throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system (CNS). Microglia account for about around 5–10% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune defense in the CNS. Microglia originate in the yolk sac under tightly regulated molecular conditions. These cells (and other neuroglia including astrocytes) are distributed in large non-overlapping regions throughout the CNS. Microglia are key cells in overall brain maintenancethey are constantly scavenging the CNS for senile plaques, plaques, damaged or unnecessary neurons and synapses, and infectious agents. Since these processes must be efficient to prevent potentially fatal damage, microglia are extremely sensitive to even small pathological changes in the CNS. This sensitivity is achieved in part by the presence of unique potassium channels that respond to even small changes in extracellular pota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
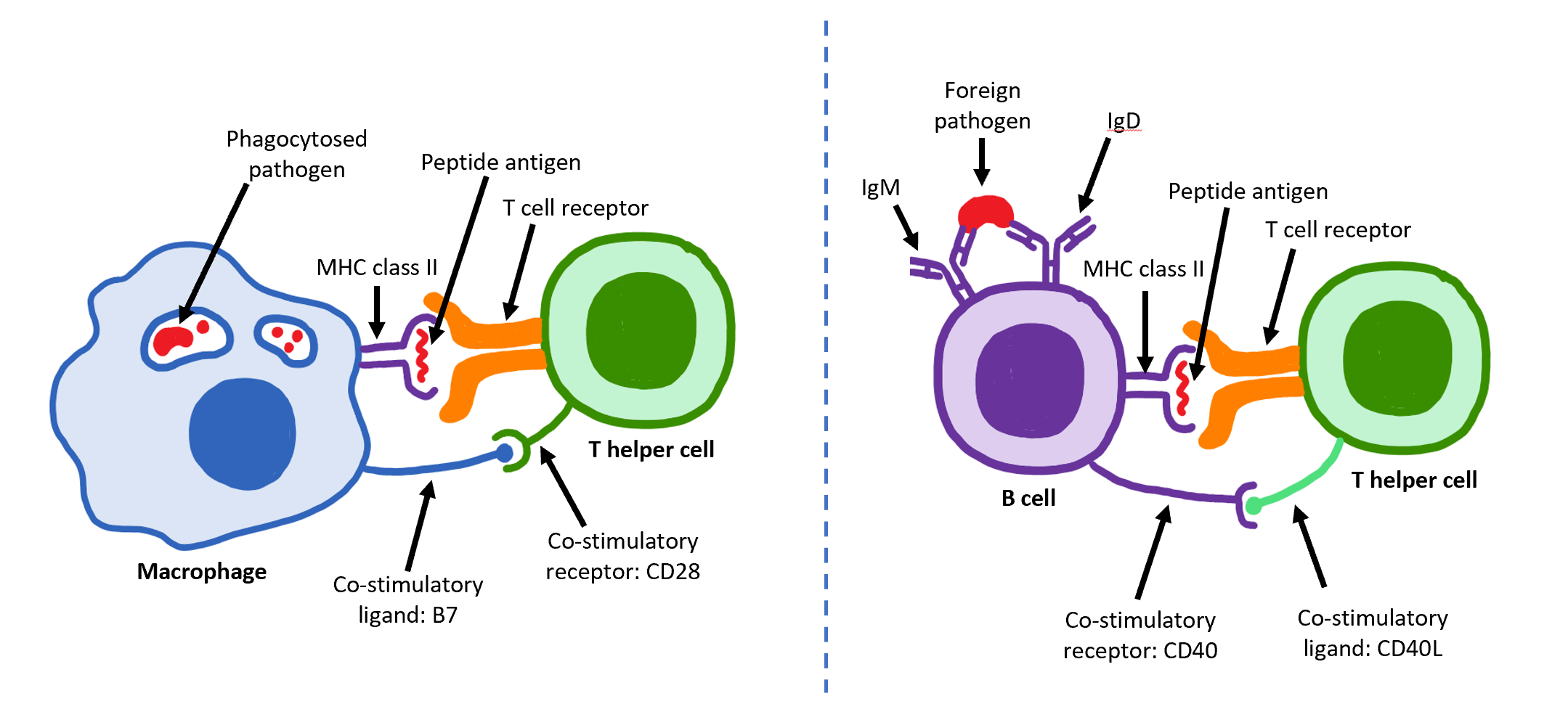
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell Immunoglobulin class switching, antibody class switching, breaking Cross-presentation, cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express Receptor (biochemistry), receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Delta T Cell
Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) are T cells that have a γδ T-cell receptor (TCR) on their surface. Most T cells are αβ (alpha beta) T cells with TCR composed of two glycoprotein chains called α (alpha) and β (beta) TCR chains. In contrast, γδ T cells have a TCR that is made up of one γ (gamma) chain and one δ (delta) chain. This group of T cells is usually less common than αβ T cells. Their highest abundance is in the gut mucosa, within a population of lymphocytes known as intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). The antigenic molecules that activate γδ T cells are largely unknown. γδ T cells are peculiar in that they do not seem to require antigen processing and major-histocompatibility-complex (MHC) presentation of peptide epitopes, although some recognize MHC class Ib molecules. γδ T cells are believed to have a prominent role in lipid antigen recognition. They are of an invariant nature. They may be triggered by alarm signals such as heat shock proteins (HSP) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cells, stressed cells, tumor cells, and other intracellular pathogens based on signals from several activating and inhibitory receptors. Most immune cells detect the antigen presented on MHC class I, major histocompatibility complex I (MHC-I) on infected cell surfaces, but NK cells can recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |