|
Thyristor-controlled Reactor
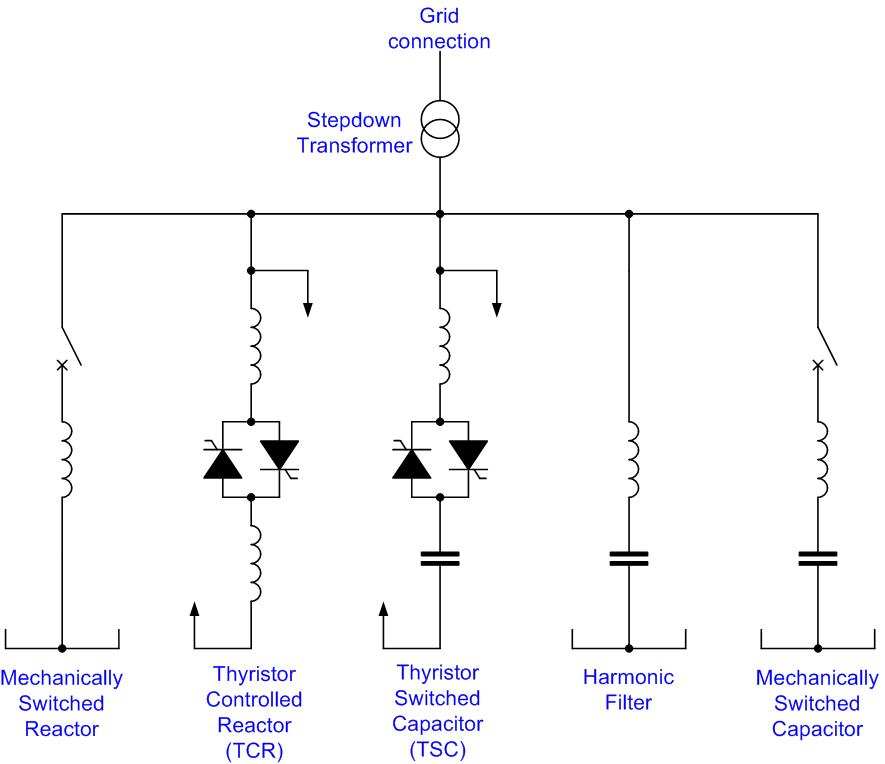
In an electric power transmission system, a thyristor-controlled reactor (TCR) is a reactance connected in series with a bidirectional thyristor valve. The thyristor valve is phase-controlled, which allows the value of delivered reactive power to be adjusted to meet varying system conditions. Thyristor-controlled reactors can be used for limiting voltage rises on lightly loaded transmission lines. Another device which used to be used for this purpose is a magnetically controlled reactor (MCR), a type of magnetic amplifier otherwise known as a transductor. In parallel with series connected reactance and thyristor valve, there may also be a capacitor bank, which may be permanently connected or which may use mechanical or thyristor switching. The combination is called a static VAR compensator. Circuit diagram A thyristor controlled reactor is usually a three-phase assembly, normally connected in a delta arrangement to provide partial cancellation of harmonics. Often the main TCR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Grid
An electrical grid (or electricity network) is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power over long distances, and finally electric power distribution to customers. In that last step, voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage. Power stations are typically built close to energy sources and far from densely populated areas. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the ''power grid''. Grids are nearly always synchronous, meaning all distribution areas operate with three phase alternating current (AC) frequencies synchronized (so that voltage swings occur at almost the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Reactance
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, magnetism is one of two aspects of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminium and oxygen, are weakly attracted to an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor
A thyristor (, from a combination of Greek language ''θύρα'', meaning "door" or "valve", and ''transistor'' ) is a solid-state semiconductor device which can be thought of as being a highly robust and switchable diode, allowing the passage of current in one direction but not the other, often under control of a gate electrode, that is used in high power applications like inverters and radar generators. It usually consists of four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials. It acts as a bistable switch (or a latch). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its gate lead controls the larger current of the anode-to-cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the anode and cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). The thyristor continues conducting until the voltage across the device is reverse-biased or the voltage is removed (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Amplifier
The magnetic amplifier (colloquially known as a "mag amp") is an electromagnetism, electromagnetic device for amplifying electrical signals. The magnetic amplifier was invented early in the 20th century, and was used as an alternative to vacuum tube amplifiers where robustness and high current capacity were required. World War II Germany perfected this type of amplifier, and it was used in the V-2 rocket. The magnetic amplifier was most prominent in power control and low-frequency signal applications from 1947 to about 1957, when the transistor began to supplant it. The magnetic amplifier has now been largely superseded by the transistor-based amplifier, except in a few safety critical, high-reliability or extremely demanding applications. Combinations of transistor and mag-amp techniques are still used. Principle of operation Visually a mag amp device may resemble a transformer, but the operating principle is quite different from a transformer – essentially the mag amp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transductor
A transductor is a type of magnetic amplifier used in power systems for compensating reactive power. It consists of an iron-cored inductor with two windings - a main winding through which an alternating current flows from the power system, and a secondary control winding which carries a small direct current. By varying the direct current, the iron core of the transductor can be arranged to saturate at different levels and thus vary the amount of reactive power absorbed. Transductors were widely used before the advent of solid-state electronics but today have been largely replaced by power electronic devices such as the Static VAR compensator and STATCOM. A formerly common use for Transductors was in CRT displays, to correct a distortion called pincushion distortion, where the side of the picture bowed in at the centre as a result of the geometry of large deflection angles. It would have one set of windings in the horizontal deflection circuit and the other set in the vertical; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static VAR Compensator
In electrical engineering, a static VAR compensator (SVC) is a set of electrical devices for providing fast-acting reactive power on high-voltage electric power transmission, electricity transmission networks. SVCs are part of the flexible AC transmission system (FACTS) device family, regulating voltage, power factor, harmonics and stabilizing the system. A static VAR compensator has no significant moving parts (other than internal switchgear). Prior to the invention of the SVC, power factor compensation was the preserve of large rotating machines such as synchronous condensers or switched capacitor banks. The SVC is an automated impedance matching device, designed to bring the system closer to unity power factor. SVCs are used in two main situations: * Connected to the power system, to regulate the transmission voltage ("transmission SVC") * Connected near large industrial loads, to improve power quality ("industrial SVC") In transmission applications, the SVC is used to regulate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harmonic''; the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Controlled Reactor Circuit
A thyristor (, from a combination of Greek language ''θύρα'', meaning "door" or "valve", and ''transistor'' ) is a solid-state semiconductor device which can be thought of as being a highly robust and switchable diode, allowing the passage of current in one direction but not the other, often under control of a gate electrode, that is used in high power applications like inverters and radar generators. It usually consists of four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials. It acts as a bistable switch (or a latch). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its gate lead controls the larger current of the anode-to-cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the anode and cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). The thyristor continues conducting until the voltage across the device is reverse-biased or the voltage is removed (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
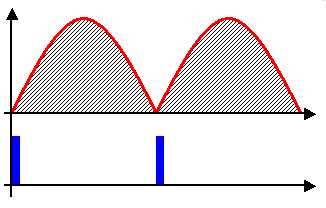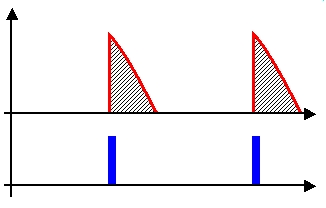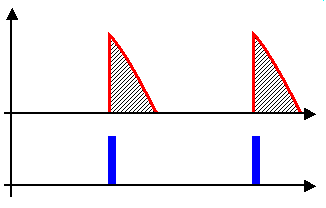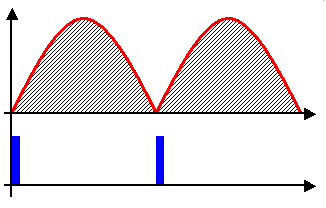
Thyristor Controlled Reactor Waveforms
A thyristor (, from a combination of Greek language ''θύρα'', meaning "door" or "valve", and ''transistor'' ) is a Solid state (electronics), solid-state semiconductor device which can be thought of as being a highly robust and switchable diode, allowing the passage of current in one direction but not the other, often under control of a gate electrode, that is used in high power applications like inverters and radar generators. It usually consists of four layers of alternating P-type semiconductor, P- and N-type semiconductor, N-type materials. It acts as a Flip-flop (electronics), bistable switch (or a latch). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its gate lead controls the larger current of the anode-to-cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the anode and cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). The thyristor continues c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor Controlled Reactor Valve
A thyristor (, from a combination of Greek language ''θύρα'', meaning "door" or "valve", and ''transistor'' ) is a solid-state semiconductor device which can be thought of as being a highly robust and switchable diode, allowing the passage of current in one direction but not the other, often under control of a gate electrode, that is used in high power applications like inverters and radar generators. It usually consists of four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials. It acts as a bistable switch (or a latch). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its gate lead controls the larger current of the anode-to-cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the anode and cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). The thyristor continues conducting until the voltage across the device is reverse-biased or the voltage is removed (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |