|
Thou Shalt Not Kill
Thou shalt not kill ( LXX, KJV; ), You shall not murder ( NIV, ) or Do not murder ( CSB), is a moral imperative included as one of the Ten Commandments in the Torah. The imperative not to kill is in the context of ''unlawful'' killing resulting in bloodguilt. Hebrew Bible Retzach The commandment against murder can be viewed as a legal matter governing human relationships, noting that the first four commandments relate strongly to man's duty to God and that the latter six commandments describe duties toward humans. The commandment against murder can also be viewed as based in respect for God himself. "The voice of your brother's blood is crying to me from the ground. And now you are cursed from the ground, which has opened its mouth to receive your brother's blood from your hand." (ESV) The Genesis narrative also portrays the prohibition of shedding innocent blood as an important aspect of God's covenant with Noah. The Torah portrays murder as a capital crime and descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Commandment (Temple Church, London)
The Sixth Commandment of the Ten Commandments could refer to: * " Thou shalt not murder", under the Philonic division used by Hellenistic Jews, Greek Orthodox and Protestants except Lutherans, or the Talmudic division of the third-century Jewish Talmud * " Thou shalt not commit adultery", under the Augustinian division used by Roman Catholics and Lutherans * ''The Sixth Commandment'' (TV series), a true-life crime drama first shown on BBC in 2023 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sefer Hamitzvot
''Sefer Hamitzvot'' ("Book of Commandments", ; ) is a work by the 12th-century rabbi, philosopher, and physician, Moses Maimonides. While there are various other works titled similarly, the title "''Sefer Hamitzvot''" without a modifier refers to Maimonides' work. It is a listing of all the commandments of the Torah, with a brief description for each. It originally appeared in Judaeo-Arabic under the title "Kitab al-Farai'd", and was translated into Hebrew by the Provençal rabbi Moses ibn Tibbon (first printed 1497) as well as by ibn Hasdai, in the 13th century. A new Hebrew translation from the original Judaeo-Arabic was made by the noted Yemenite scholar, Rabbi Yosef Qafih. Premise In the work, Maimonides lists all the 613 mitzvot traditionally contained in the Torah (Pentateuch). He describes the following fourteen principles (Hebrew: ) to guide his selection. (For each rule, Maimonides cites many illustrative examples. We present only one or two examples for eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yehareg Ve'al Ya'avor
Self-sacrifice is required in Jewish law for rare yet specifically defined circumstances, in which a Jew is expected to sacrifice their own life rather than violate a religious prohibition. The core principle of self-sacrifice, ''yehareg ve'al ya'avor'' ("let him be killed rather than transgress"), is enunciated in a Talmudic sugya (pericope) at Sanhedrin 74a-b and thereafter typically discussed in terms of three cardinal or exceptional prohibitions. One of these prohibitions is that no life should be taken, including one's own. Many more ritual prohibitions exist as well, which means that under limited circumstances a Jew has to self-sacrifice when the greater good calls for breaking a more minor dictate. This practice reflects the practical and perhaps malleable nature of Judaic law. Overview In general, a Jew must violate biblically mandated, and certainly rabbinically mandated, religious laws of Judaism in order to preserve human life. This principle is known as ''ya'avor v' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism (), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, Rabbanite Judaism, or Talmudic Judaism, is rooted in the many forms of Judaism that coexisted and together formed Second Temple Judaism in the land of Israel, giving birth to classical rabbinic Judaism, which flourished from the 1st century CE to the final redaction of the Babylonian Talmud in c. 600. Mainly developing after the destruction of the Jerusalem Temple (70 CE), it eventually became the normative form of Judaism. Rabbinic Judaism has been an orthodox form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Babylonian Talmud. It has its roots in the Pharisaic school of Second Temple Judaism and is based on the belief that Moses at Mount Sinai received both the Written Torah (''Torah she-be-Khetav'') and the Oral Torah (''Torah she-be-al Peh'') from God. The Oral Torah explains the Written Torah, and it was the rabbis claimed that it was them who possessed this memorized and orally transmitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuteronomy
Deuteronomy (; ) is the fifth book of the Torah (in Judaism), where it is called () which makes it the fifth book of the Hebrew Bible and Christian Old Testament. Chapters 1–30 of the book consist of three sermons or speeches delivered to the Israelites by Moses on the Plains of Moab, shortly before they enter the Promised Land. The first sermon recounts the Moses#The years in the wilderness, forty years of wilderness wanderings which had led to that moment and ends with an exhortation to observe the law. The second sermon reminds the Israelites of the need to follow Yahweh and the laws (or teachings) he has given them, on which their possession of the land depends. The third sermon offers the comfort that, even should the nation of Israel prove unfaithful and so lose the land, with repentance all can be restored. The final four chapters (31–34) contain the Song of Moses, the Blessing of Moses, and the narratives recounting the passing of the mantle of leadership from Mose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promised Land
In the Abrahamic religions, the "Promised Land" ( ) refers to a swath of territory in the Levant that was bestowed upon Abraham and his descendants by God in Abrahamic religions, God. In the context of the Bible, these descendants are originally understood to have been the Israelites, whose forefather was Jacob, who was a son of Abraham's son Isaac. The concept of the Promised Land largely overlaps with the Land of Israel (Zion) or the Holy Land in a biblical/religious sense and with Canaan or Palestine (region), Palestine in a secular/geographic sense. Although the Book of Numbers provides some definition for the Promised Land's boundaries, they are not delineated with precision, but it is universally accepted that the core areas lie in and around Jerusalem. According to the biblical account, the Promised Land was not inherited until the Conquest of Canaan, Israelite conquest of Canaan, which took place shortly after the Exodus. Biblical narrative The concept of the Promised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
613 Mitzvot
According to Jewish tradition, the Torah contains 613 commandments (). Although the number 613 is mentioned in the Talmud, its real significance increased in later medieval rabbinic literature, including many works listing or arranged by the . The most famous of these was an enumeration of the 613 commandments by Maimonides. While the total number of commandments is 613, no individual can perform all of them. Many can only be observed at the Temple in Jerusalem, which no longer stands. According to one standard reckoning, there are 77 positive and 194 negative commandments that can be observed today, of which there are 26 commandments that apply only within the Land of Israel. In addition, some commandments only apply to certain categories of Jews: some are only observed by '' kohanim'', and others only by men or by women. Symbolism of 613 Rav Hamnuna sourced the count of 613 in the verse ("Moses commanded us the Torah..."). The Talmud notes that the Hebrew numerical value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloodguilt
{{disambig ...
Blood guilt or Bloodguilt may refer to: *any unlawful killing, see manslaughter **murder *any crime severe enough to be punished by the death penalty **crimes falling under high justice in feudal Europe See also * Kin punishment, a form of collective punishment against the family members of one accused of committing a crime *Weregild (blood money), paid in atonement for blood guilt * Blood court (''Blutgericht''), legal term for "high justice" in the Holy Roman Empire *Homicide *Bloodguilt in the Hebrew Bible Thou shalt not kill (LXX, KJV; ), You shall not murder (New International Version, NIV, ) or Do not murder (Christian Standard Bible, CSB), is a moral imperative included as one of the Ten Commandments in the Torah. The imperative not to kill i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yahweh
Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Israel, and the king of the gods, head of the Pantheon (religion), pantheon of the Polytheism, polytheistic Yahwism, Israelite religion. Although there is no clear consensus regarding the geographical origins of the deity, scholars generally hold that Yahweh was associated with Mount Seir, Seir, Edom, Desert of Paran, Paran, and Teman (Edom), Teman, and later with Canaan. The worship of the deity reaches back to at least the early Iron Age, and likely to the late Bronze Age, if not somewhat earlier. In the oldest Bible, biblical texts, Yahweh possesses attributes that were typically ascribed to deities of weather and war, fructifying the Land of Israel and leading a Heavenly host#Hebrew Bible, heavenly army against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
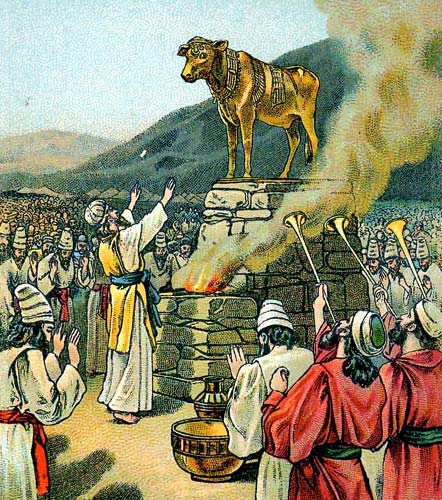
Golden Calf
According to the Torah, the Bible, and the Quran, the golden calf () was a cult image made by the Israelites when Moses went up to Mount Sinai (bible), Mount Sinai. In Hebrew, the incident is known as "the sin of the calf" (). It is first mentioned in the Book of Exodus. Sacred bull, Bull worship was common in many cultures. In Ancient Egypt, Egypt, whence according to the Exodus narrative, the Israelites had recently come, the bull-god Apis (deity), Apis was a comparable object of worship, which some believe the Hebrews were reviving in the wilderness. Alternatively, some believe Yahweh, the national god of the Israelites, was associated with or pictured as a sacred bull through the process of religious assimilation and syncretism. Among the Canaan, Canaanites, some of whom would become the Israelites, the bull was widely worshipped as the sacred bull and the creature of El (deity), El. Biblical narrative When Moses went up Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai to receive the Ten C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortune-telling
Fortune telling is the spiritual practice of predicting information about a person's life. Melton, J. Gordon. (2008). ''The Encyclopedia of Religious Phenomena''. Visible Ink Press. pp. 115–116. The scope of fortune telling is in principle identical with the practice of divination. The difference is that divination is the term used for predictions considered part of a religious ritual, invoking deities or spirits, while the term fortune telling implies a less serious or formal setting, even one of popular culture, where belief in occult workings behind the prediction is less prominent than the concept of suggestion, spiritual or practical advisory or affirmation. Historically, Pliny the Elder describes use of the crystal ball in the 1st century CE by soothsayers (''"crystallum orbis"'', later written in Medieval Latin by scribes as ''orbuculum''). Contemporary Western images of fortune telling grow out of folkloristic reception of Renaissance magic, specifically ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |