|
Thomsen Parameters
A transversely isotropic (also known as polar anisotropic) material is one with physical properties that are symmetry, symmetric about an axis that is normal to a plane of isotropy. This transverse plane has infinite planes of symmetry and thus, within this plane, the material properties are the same in all directions. In geophysics, vertically transverse isotropy (VTI) is also known as radial anisotropy. This type of material exhibits hexagonal symmetry (though technically this ceases to be true for tensors of rank 6 and higher), so the number of independent constants in the (fourth-rank) elasticity tensor are reduced to 5 (from a total of 21 independent constants in the case of a fully Anisotropy, anisotropic solid). The (second-rank) tensors of electrical resistivity, permeability, etc. have two independent constants. Example of transversely isotropic materials An example of a transversely isotropic material is the so-called on-axis unidirectional fiber Composite material, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USA 10052 Grand Canyon Luca Galuzzi 2007
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) describes their capacity to exert attractive or repulsive forces on another charged object. Charged particles exert attractive forces on each other when the sign of their charges are opposite, one being positive while the other is negative, and repel each other when the signs of the charges are the same. Because these forces are exerted mutually, two charges must be present for the forces to take place. These forces are described by Coulomb's law, which says that the greater the magnitude of the charges, the greater the force, and the greater the distance between them, the weaker the force. Informally, the greater the charge of an object, the stronger its electric field. Similarly, an electric field is stronger nearer charged objects and weaker f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (Molecular diffusion, particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
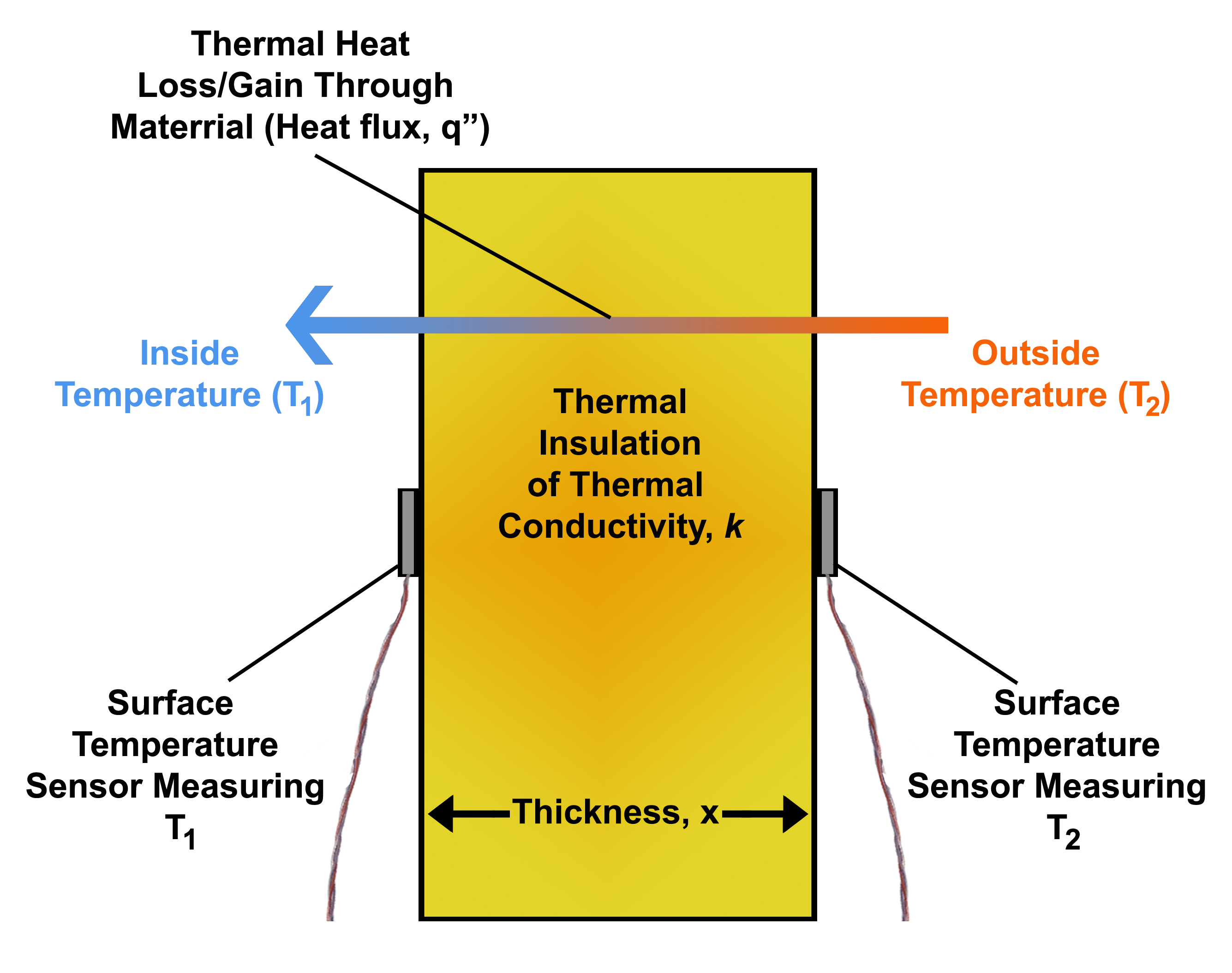
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to heat conduction, conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa and is measured in W·m−1·K−1. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials such as mineral wool or Styrofoam. Metals have this high thermal conductivity due to free electrons facilitating heat transfer. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Gradient
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature spatial gradient is a vector quantity with Dimensional analysis, dimension of temperature difference per unit length. The International System of Units, SI Units of measurement, unit is kelvin per meter (K/m). Temperature gradients in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere are important in the atmospheric sciences (meteorology, climatology and related fields). Mathematical description Assuming that the temperature ''T'' is an intensive quantity, i.e., a single-valued, Continuous function, continuous and Derivative, differentiable Function (mathematics), function of three-dimensional space (often called a scalar field), i.e., that :T=T(x,y,z) where ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' are the Cartesian coordinate system, coordinates of the location of interest, then the temperature gradient is the vector (geometric) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Flux
In physics and engineering, heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as heat flux density, heat-flow density or heat-flow rate intensity, is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time (physics), time. Its SI units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a direction and a magnitude, and so it is a Vector (geometric), vector quantity. To define the heat flux at a certain point in space, one takes the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case where the size of the surface becomes infinitesimally small. Heat flux is often denoted \vec_\mathrm, the subscript specifying ''heat'' flux, as opposed to ''Mass flux, mass'' or Transport phenomena, ''momentum'' flux. Heat conduction#Fourier's law, Fourier's law is an important application of these concepts. Fourier's law For most solids in usual conditions, heat is transported mainly by thermal conduction, conduction and the heat flux is adequately described by Fourier's law. Fourier's law in one dimension \phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conduction
Thermal conduction is the diffusion of thermal energy (heat) within one material or between materials in contact. The higher temperature object has molecules with more kinetic energy; collisions between molecules distributes this kinetic energy until an object has the same kinetic energy throughout. Thermal conductivity, frequently represented by , is a property that relates the rate of heat loss per unit area of a material to its rate of change of temperature. Essentially, it is a value that accounts for any property of the material that could change the way it conducts heat. Heat spontaneously flows along a temperature gradient (i.e. from a hotter body to a colder body). For example, heat is conducted from the hotplate of an electric stove to the bottom of a saucepan in contact with it. In the absence of an opposing external driving energy source, within a body or between bodies, temperature differences decay over time, and thermal equilibrium is approached, temperature becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Permeability
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization produced in a material in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter ''μ''. It is the ratio of the magnetic induction B to the magnetizing field H in a material. The term was coined by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1872, and used alongside permittivity by Oliver Heaviside in 1885. The reciprocal of permeability is magnetic reluctivity. In SI units, permeability is measured in henries per meter (H/m), or equivalently in newtons per ampere squared (N/A2). The permeability constant ''μ''0, also known as the magnetic constant or the permeability of free space, is the proportionality between magnetic induction and magnetizing force when forming a magnetic field in a classical vacuum. A closely related property of materials is magnetic susceptibility, which is a dimensionless proportionality factor that indicates the degree of magnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, electric currents, and electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function (mathematics), function assigning a Euclidean vector, vector to each point of space, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force, electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field. Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faraday's law of induction. Lenz's law describes the direction of the induced field. Faraday's law was later generalized to become the Maxwell–Faraday equation, one of the four Maxwell's equations, Maxwell equations in his theory of electromagnetism. Electromagnetic induction has found many applications, including electrical components such as inductors and transformers, and devices such as electric motors and electric generator, generators. History Electromagnetic induction was discovered by Michael Faraday, published in 1831. It was discovered independently by Joseph Henry in 1832. In Faraday's first experimental demonstration, on August 29, 1831, he wrapped two wires aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, magnetism is one of two aspects of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys. All substances exhibit some type of magnetism. Magnetic materials are classified according to their bulk susceptibility. Ferromagnetism is responsible for most of the effects of magnetism encountered in everyday life, but there are actually several types of magnetism. Paramagnetic substances, such as aluminium and oxygen, are weakly attracted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Permittivity
In electromagnetism, the absolute permittivity, often simply called permittivity and denoted by the Greek letter (epsilon), is a measure of the electric polarizability of a dielectric material. A material with high permittivity polarizes more in response to an applied electric field than a material with low permittivity, thereby storing more energy in the material. In electrostatics, the permittivity plays an important role in determining the capacitance of a capacitor. In the simplest case, the electric displacement field resulting from an applied electric field E is \mathbf = \varepsilon\ \mathbf ~. More generally, the permittivity is a thermodynamic function of state. It can depend on the frequency, magnitude, and direction of the applied field. The SI unit for permittivity is farad per meter (F/m). The permittivity is often represented by the relative permittivity which is the ratio of the absolute permittivity and the vacuum permittivity \kappa = \varepsilon_\mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |