|
Thermal Oxidation
In microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide (usually silicon dioxide) on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The rate of oxide growth is often predicted by the Deal–Grove model. Thermal oxidation may be applied to different materials, but most commonly involves the oxidation of silicon substrates to produce silicon dioxide. The chemical reaction Thermal oxidation of silicon is usually performed at a temperature between 800 and 1200 °C, resulting in a so-called High Temperature Oxide layer (HTO). It may use either water vapor (usually UHP steam) or molecular oxygen as the oxidant; it is consequently called either ''wet'' or ''dry'' oxidation. The reaction is one of the following: :\rm Si + 2H_2O \rightarrow SiO_2 + 2H_ :\rm Si + O_2 \rightarrow SiO_2 \, The oxidizing ambient may also contain several percent of hydrochloric acid (HCl). The chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dangling Bond
In chemistry, a dangling bond is an unsatisfied Valence (chemistry), valence on an immobilized atom. An atom with a dangling bond is also referred to as an immobilized free radical or an immobilized radical, a reference to its structural and chemical similarity to a free radical. When speaking of a dangling bond, one is generally referring to the state described above, containing one electron and thus leading to a neutrally charged atom. There are also dangling bond defects containing two or no electrons. These are negatively and positively charged respectively. Dangling bonds with two electrons have an energy close to the Valence and conduction bands, valence band of the material and those with none have an energy that is closer to the Valence and conduction bands, conduction band. Properties In order to gain enough electrons to fill their valence shells (see also octet rule), many atoms will form covalent bonds with other atoms. In the simplest case, that of a single bond, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvation
Solvations describes the interaction of a solvent with dissolved molecules. Both ionized and uncharged molecules interact strongly with a solvent, and the strength and nature of this interaction influence many properties of the solute, including solubility, reactivity, and color, as well as influencing the properties of the solvent such as its viscosity and density. If the attractive forces between the solvent and solute particles are greater than the attractive forces holding the solute particles together, the solvent particles pull the solute particles apart and surround them. The surrounded solute particles then move away from the solid solute and out into the solution. Ions are surrounded by a concentric shell of solvent. Solvation is the process of reorganizing solvent and solute molecules into solvation complexes and involves bond formation, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. Solvation of a solute by water is called hydration. Solubility of solid compounds dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
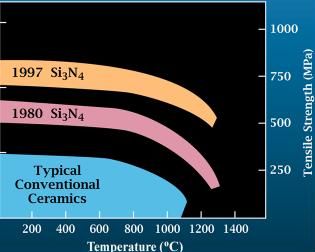
Silicon Nitride
Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. (''Trisilicon tetranitride'') is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term ″''Silicon nitride''″ commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot . It is very hard (8.5 on the mohs scale). It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications. Production Silicon nitride is prepared by heating powdered silicon between 1300 °C and 1400 °C in a nitrogen atmosphere: :3 Si + 2 → The silicon sample weight increases progressively due to the chemical combination of silicon and nitrogen. Without an iron catalyst, the reaction is complete after several hours (~7), when no further weight increase due to nitrogen absorption (per gram of silicon) is detected. In addition to , several other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LOCOS
''Locos: A Comedy of Gestures'' is the first novel of Spanish-born American writer Felipe Alfau (1902–1999), written in 1928 and published in 1936. The metafictional novel remained out of print until 1988 when it was reprinted by Dalkey Archive Press; its positive reception then led to the publication of Alfau's second novel '' Chromos'' in 1990, which he had written in 1948. Synopsis The book consists of eight independent but interrelated short stories that the author states can be read in any order. In the introduction, Alfau thanks his characters "for their anarchic collaboration"—in the stories the characters and narrator often interact. Contents # "Identity" # "A Character" # "The Beggar" # "Fingerprints" # "The Wallet" # "Chinelato" #: I "The Ogre" #: II "The Black Mandarin" #: III "Tia Mariquita" # "The Necrophil" # "A Romance of Dogs" #: I "Students" #: II "Spring" Background Felipe Alfau was born and grew up in Spain. In 1916, the 14-year-old Alfau moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichloroethylene
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is an organochloride with the formula C2HCl3, commonly used as an industrial metal-degreasing solvent. It is a clear, colourless, non-flammable, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like pleasant mild smell and sweet taste.Trichloroethylene (TCE) on ATSDR Its name is trichloroethene. Trichloroethylene has been sold under a variety of trade names. Industrial abbreviations include trichlor, Trike, Tricky and tri. Under the trade names Trimar and Trilene, it was used as a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl. Reactions Hydrogen chloride is a diatomic molecule, consisting of a hydrogen atom H and a chlorine atom Cl connected by a Polar-covalent bond, polar covalent bond. The chlorine atom is much more Electronegativity, electronegative than the hydrogen atom, which makes this bond polar. Consequently, the molecule has a large Molecular dipole moment, dipole moment with a negative partial charge (δ−) at the chlorine atom and a positive partial charge (δ+) at the hydrogen atom. In part because of its high polarity, HCl is very soluble in water (and in other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and curing (food preservation), food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further Chemical synthesis, chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the Abundance of elements in Earth's crust, sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been Leaching (chemistry), leached by the action of water from the Earth, Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in Soap, soap manufac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale. In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, MOS FET, or MOS transistor) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The term ''metal–insulator–semiconductor field-effect transistor'' (''MISFET'') is almost synonymous with ''MOSFET''. Another near-synonym is ''insulated-gate field-effect transistor'' (''IGFET''). The main advantage of a MOSFET is that it requires almost no input current to control the load current under steady-state or low-frequency conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polythiazyl, polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |