|
Theory Of Mind
In psychology and philosophy, theory of mind (often abbreviated to ToM) refers to the capacity to understand other individuals by ascribing mental states to them. A theory of mind includes the understanding that others' beliefs, desires, intentions, emotions, and thoughts may be different from one's own. Possessing a functional theory of mind is crucial for success in everyday human social interactions. People utilize a theory of mind when analyzing, Value judgment, judging, and inferring other people's behaviors. Theory of mind was first conceptualized by researchers evaluating the presence of theory of mind in animals. Today, theory of mind research also investigates factors affecting theory of mind in humans, such as whether drug and alcohol consumption, language development, cognitive delays, age, and culture can affect a person's capacity to display theory of mind. It has been proposed that deficits in theory of mind may occur in people with autism, anorexia nervosa, schi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feelings, and motivation, motives. Psychology is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the Natural science, natural and social sciences. Biological psychologists seek an understanding of the Emergence, emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As social scientists, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups.Hockenbury & Hockenbury. Psychology. Worth Publishers, 2010. A professional practitioner or researcher involved in the discipline is called a psychologist. Some psychologists can also be classified as Behavioural sciences, behavioral or Cognitive science, cognitive scientists. Some psychologists attempt to understand the role of mental functions in i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia () is a mental disorder characterized variously by hallucinations (typically, Auditory hallucination#Schizophrenia, hearing voices), delusions, thought disorder, disorganized thinking and behavior, and Reduced affect display, flat or inappropriate affect. Symptoms Prodrome, develop gradually and typically begin during young adulthood and rarely resolve. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a psychiatric history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. For a diagnosis of schizophrenia, the described symptoms need to have been present for at least six months (according to the DSM-5) or one month (according to the ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially mood disorder, mood, anxiety disorder, anxiety, and substance use disorders, substance use disorders, as well as obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). About 0.3% to 0.7% of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Temporal Sulcus
The superior temporal sulcus (STS) is the sulcus separating the superior temporal gyrus from the middle temporal gyrus, in the temporal lobe of the mammalian brain. A sulcus (plural sulci) is a deep groove that curves into the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum, and a gyrus (plural gyri) is a ridge that curves outward of the cerebrum. The STS is located under the lateral fissure, which is the fissure that separates the temporal lobe, parietal lobe, and frontal lobe. The STS has an asymmetric structure between the left and right hemisphere, with the STS being longer in the left hemisphere, but deeper in the right hemisphere. This asymmetrical structural organization between hemispheres has only been found to occur in the STS of the human brain. The STS has been shown to produce strong responses when subjects perceive stimuli in research areas that include theory of mind, biological motion, faces, voices, and language. Language processing Spoken language processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
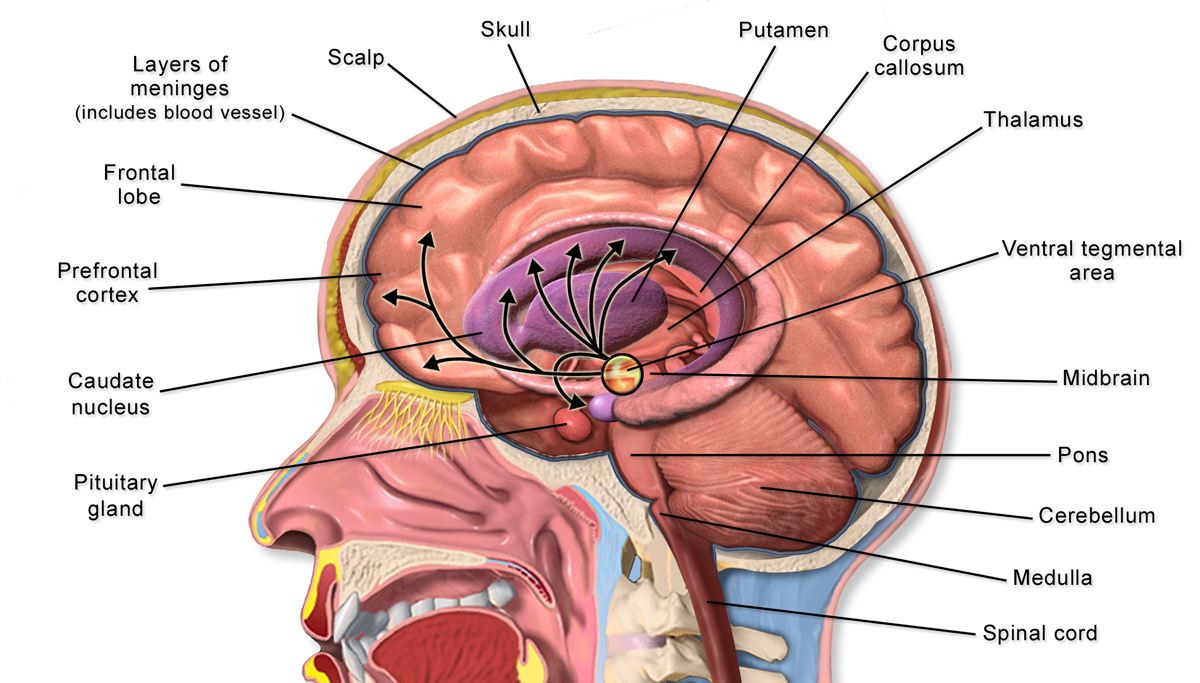
Prefrontal Cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. It is the association cortex in the frontal lobe. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47. This brain region is involved in a wide range of higher-order cognitive functions, including speech formation (Broca's area), gaze ( frontal eye fields), working memory ( dorsolateral prefrontal cortex), and risk processing (e.g. ventromedial prefrontal cortex). The basic activity of this brain region is considered to be orchestration of thoughts and actions in accordance with internal goals. Many authors have indicated an integral link between a person's will to live, personality, and the functions of the prefrontal cortex. This brain region has been implicated in executive functions, such as planning, decision making, working memory, personality expression, moderating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the neuroanatomy, structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology. Neuroradiology is a medical specialty that uses non-statistical brain imaging in a clinical setting, practiced by radiologists who are medical practitioners. Neuroradiology primarily focuses on recognizing brain lesions, such as vascular diseases, strokes, tumors, and inflammatory diseases. In contrast to neuroimaging, neuroradiology is qualitative (based on subjective impressions and extensive clinical training) but sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPIE
SPIE (formerly the Society of Photographic Instrumentation Engineers, later the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers) is an international not-for-profit professional society for optics and photonics technology, founded in 1955. It organizes technical conferences, trade exhibitions, and continuing education programs for researchers and developers in the light-based fields of physics, including: optics, photonics, and imaging engineering. The society publishes peer-reviewed scientific journals, conference proceedings, monographs, tutorial texts, field guides, and reference volumes in print and online. SPIE is especially well-known for Photonics West, one of the laser and photonics industry's largest combined conferences and tradeshows which is held annually in San Francisco. SPIE also participates as partners in leading educational initiatives, and in 2020, for example, provided more than $5.8 million in support of optics education and outreach programs around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurophotonics
''Neurophotonics'' is a quarterly, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering optical technology applicable to study of the brain and their impact on basic and clinical neuroscience applications, published by SPIE. The editor-in-chief is Anna Devor (Boston University, USA). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * PubMed * PubMed Central * Science Citation Index Expanded * Inspec * Scopus * Embase * Ei/Compendex According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 3.593. References External links * Optics journals SPIE academic journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 2014 {{neuroscience-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiley-Blackwell
Wiley-Blackwell is an international scientific, technical, medical, and scholarly publishing business of John Wiley & Sons. It was formed by the merger of John Wiley & Sons Global Scientific, Technical, and Medical business with Blackwell Publishing in 2007. Wiley-Blackwell is now an imprint that publishes a diverse range of academic and professional fields, including biology, medicine, physical sciences, technology, social science, and the humanities. Blackwell Publishing history Blackwell Publishing was formed by the 2001 merger of two Oxford-based academic publishing companies, Blackwell Science, founded in 1939 as Blackwell Scientific Publishing, and Blackwell Publishers, founded in 1922 as Basil Blackwell & Mott. Blackwell Publishers, founded in 1926, had its origins in the 19th century Blackwell's family bookshop and publishing business. The merger between the two publishing companies created the world's leading learned society publisher. The group then acquired BMJ Boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addiction (journal)
''Addiction'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal established in 1903 by the Society for the Study of Addiction to Alcohol and other Drugs as the ''British Journal of Inebriety''. It was renamed ''British Journal of Addiction to Alcohol & Other Drugs'' in 1947, then renamed to ''British Journal of Addiction'' in 1980, before finally obtaining its current name in 1993. It covers research relating to the abuse of alcohol, illicit drugs, and tobacco, as well as behavioural addictions. The editor-in-chief is John Marsden (King's College London). Article types The journal publishes research reports, reviews, commentaries, and letters to the editor relating to all aspects of addictive behaviours. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2019 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol's Neurotoxicity
The long-term impact of alcohol on the brain encompasses a wide range of effects, varying by drinking patterns, age, genetics, and other health factors. Among the many organs alcohol affects, the brain is particularly vulnerable. Heavy drinking causes alcohol-related brain damage, with alcohol acting as a direct neurotoxin to nerve cells, while low levels of alcohol consumption can cause decreases in brain volume, regional gray matter volume, and white matter microstructure. Low-to-moderate alcohol intake may be associated with certain cognitive benefits or neuroprotection in older adults. Social and psychological factors can offer minor protective effects. The overall relationship between alcohol use and brain health is complex, reflecting the balance between alcohol's neurotoxic effects and potential modulatory influences. Classification The neurological consequences of long-term alcohol use can be broadly classified into harmful outcomes (e.g., brain atrophy, cognitive dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Damage
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage. A common category with the greatest number of injuries is traumatic brain injury (TBI) following physical trauma or head injury from an outside source, and the term acquired brain injury (ABI) is used in appropriate circles to differentiate brain injuries occurring after birth from injury, from a genetic disorder (GBI), or from a congenital disorder (CBI). Primary and secondary brain injuries identify the processes involved, while focal and diffuse brain injury describe the severity and localization. Impaired function of affected areas can be compensated through neuroplasticity by forming new neural connections. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of brain injuries vary based on the severity of the injury or how much of the brain is affected. The fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutgers University
Rutgers University ( ), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of three campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's College and was affiliated with the Reformed Church in America, Dutch Reformed Church. It is the eighth-oldest college in the United States, the second-oldest in New Jersey (after Princeton University), and one of nine colonial colleges that were chartered before the American Revolution.Stoeckel, Althea"Presidents, professors, and politics: the colonial colleges and the American revolution", ''Conspectus of History'' (1976) 1(3):45–56. In 1825, Queen's College was renamed Rutgers College in honor of Colonel Henry Rutgers, whose substantial gift to the school had stabilized its finances during a period of uncertainty. For most of its existence, Rutgers was a Private university, private liberal arts college. It has evolved into a Mixed-sex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |