|
The End Of Alchemy
The End of Alchemy is a book written by Mervyn King, the former Bank of England Governor from 2003-2013, including during the 2008 financial crisis. The book focuses on the history, flaws, and future of money, banking, and financial systems. Alchemy is referring to the money creation process in which banks 'manufacture' the new money supply as debt in the debt-based monetary system, where banks create margin for themselves and invest it as debt, such as mortgages, loans, bonds, treasuries, and other debt-based financial instruments. The leverage created by banks creates the economic bubbles that the Central banks have to pop with deflationary monetary policy that typically causes unemployment to rise. The Gold Standard and the Great Depression In Chapter 3, titled ' ''The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly'' ' King explains how in the 1920s countries tried to reinstate the Gold standard at pre-World War I parities causing deflationary pressures and the Great Contraction through ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mervyn King, Baron King Of Lothbury
Mervyn Allister King, Baron King of Lothbury, (born 30 March 1948), is a British economist and public servant, who was Governor of the Bank of England from 2003 to 2013. Emeritus Professor of the London School of Economics and Chairman of the Philharmonia since 2020, Lord King serves as President of Marylebone Cricket Club for 2024/25. Born in Buckinghamshire, King was educated at Wolverhampton Grammar School, Staffordshire, before going up to read economics at King's College, Cambridge, and Harvard University. Elected a Fellow of St John's College, Cambridge, working as a researcher on the Cambridge Growth Project he then taught at the University of Birmingham, Harvard and MIT, before becoming a Professor of economics at the London School of Economics. He joined the Bank of England in 1990 as a non-executive director, and became the chief economist in 1991. In 1998, he was promoted deputy governor of the Bank and a member of the Group of Thirty. King was appointed as G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Treasury Security
United States Treasury securities, also called Treasuries or Treasurys, are government bond, government debt instruments issued by the United States Department of the Treasury to finance government spending as a supplement to taxation. Since 2012, the U.S. government debt has been managed by the Bureau of the Fiscal Service, succeeding the Bureau of the Public Debt. There are four types of marketable Treasury securities: #Treasury bill, Treasury bills, #Treasury note, Treasury notes, #Treasury bond, Treasury bonds, and #TIPS, Treasury Inflation Protected Securities (TIPS). The government sells these securities in auctions conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, after which they can be traded in secondary markets. Non-marketable securities include savings bonds, issued to individuals; the State and Local Government Series (SLGS), purchaseable only with the proceeds of state and municipal bond sales; and the Government Account Series, purchased by units of the feder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
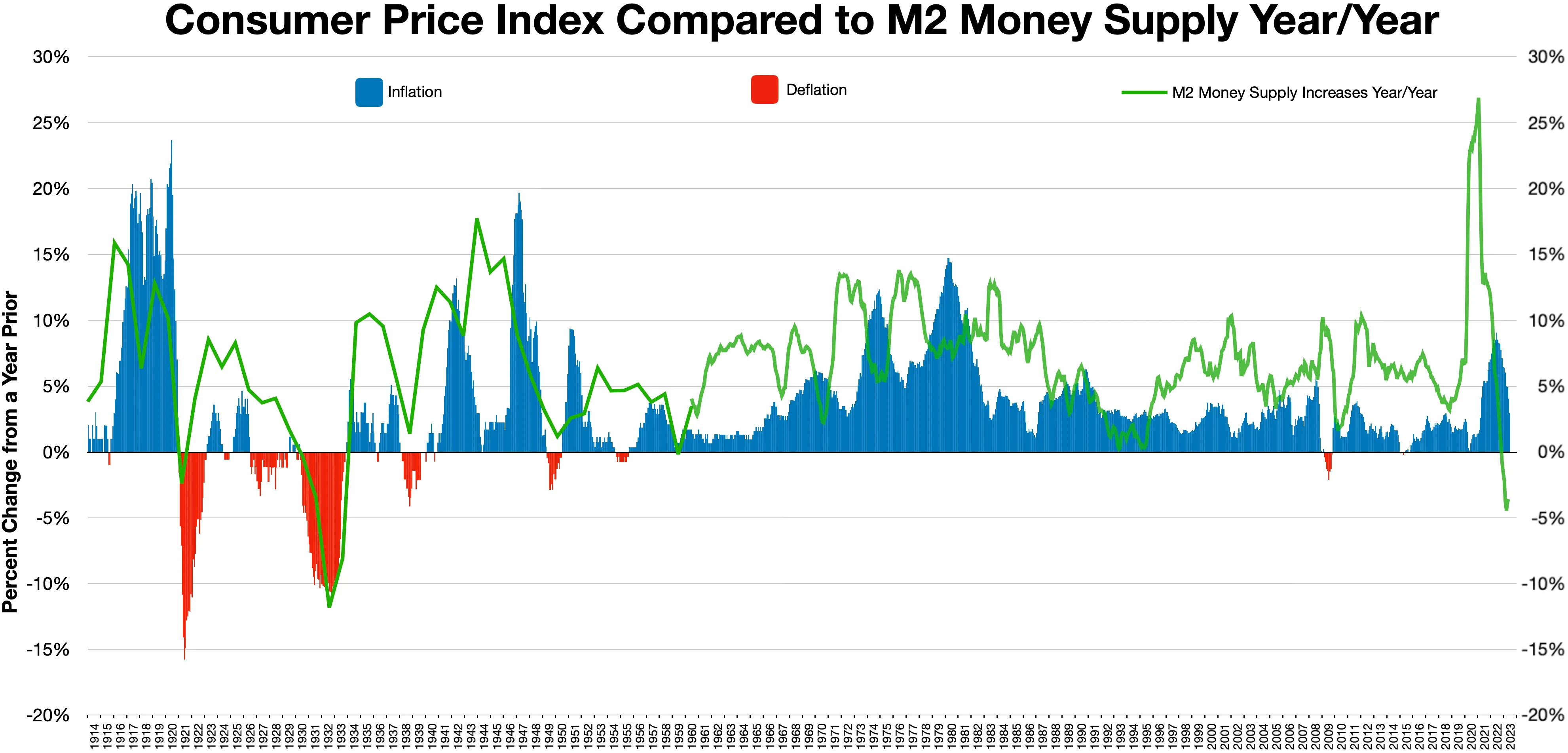
Causes Of The Great Depression
The causes of the Great Depression in the early 20th century in the United States have been extensively discussed by economists and remain a matter of active debate. They are part of the larger debate about economic crises and recessions. Although the major economic events that took place during the Great Depression are widely agreed upon, the finer week-to-week and month-to-month fluctuations are often underexplored in historical literature, as aggregate interpretations tend to align more cleanly with the formal requirements of modern macroeconomic modeling and statistical instrumentation. There was an initial stock market crash that triggered a "panic sell-off" of assets. This was followed by a deflation in asset and commodity prices, dramatic drops in demand and the total quantity of money in the economy, and disruption of trade, ultimately resulting in widespread unemployment (over 13 million people were unemployed by 1932) and impoverishment. However, economists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Tightening
Quantitative tightening (QT) is a contractionary monetary policy tool applied by central banks to decrease the amount of liquidity or money supply in the economy. A central bank implements quantitative tightening by reducing the financial assets it holds on its balance sheet by selling them into the financial markets, which decreases asset prices and raises interest rates. QT is the reverse of quantitative easing (or QE), where the central bank prints money and uses it to buy assets in order to raise asset prices and stimulate the economy. QT is rarely used by central banks, and has only been employed after prolonged periods of Greenspan put-type stimulus, where the creation of too much central banking liquidity has led to a risk of uncontrolled inflation (e.g. 2008, 2018 and 2022). Background Quantitative easing was massively applied by leading central banks to counter the Great Recession that started in 2008. The prime rates were decreased to zero; some rates later went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Contraction
The Great Contraction, as characterized by economist Milton Friedman, was the recessionary period from 1929 until 1933, i.e., the early years of the Great Depression. The phrase was the title of a chapter in the 1963 book '' A Monetary History of the United States'' by Friedman and his fellow monetarist Anna Schwartz. The chapter was later published as a stand-alone book titled ''The Great Contraction, 1929–1933'' in 1965. Both books are still in print from Princeton University Press, and some editions include as an appendix a speech honoring Friedman in which Federal Reserve Governor Ben Bernanke made this statement: Let me end my talk by abusing slightly my status as an official representative of the Federal Reserve. I would like to say to Milton and Anna: Regarding the Great Depression, you're right. We did it. We're very sorry. But thanks to you, we won't do it again. Ben S. Bernanke (Nov. 8, 2002)Federal Reserve Board Speech: "Remarks by Governor Ben S. Bernanke" Conferenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parities
Parity may refer to: Computing * Parity bit in computing, sets the parity of data for the purpose of error detection * Parity flag in computing, indicates if the number of set bits is odd or even in the binary representation of the result of the last operation * Parity file in data processing, created in conjunction with data files and used to check data integrity and assist in data recovery Mathematics * Parity (mathematics), indicates whether a number is even or odd ** Parity of a permutation, indicates whether a permutation has an even or odd number of inversions ** Parity function, a Boolean function whose value is 1 if the input vector has an odd number of ones ** Parity learning, a problem in machine learning ** Parity of even and odd functions Other uses * Parity (physics), a symmetry property of physical quantities or processes under spatial inversion * Parity (biology), the number of times a female has given birth; gravidity and parity represent pregnancy and viability, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Standard
A gold standard is a backed currency, monetary system in which the standard economics, economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was the basis for the international monetary system from the 1870s to the early 1920s, and from the late 1920s to 1932 as well as from 1944 until 1971 when the United States unilaterally terminated convertibility of the US dollar to gold, effectively ending the Bretton Woods system. Many states nonetheless hold substantial gold reserves. Historically, the silver standard and bimetallism have been more common than the gold standard. The shift to an international monetary system based on a gold standard reflected accident, network externalities, and path dependence. Great Britain accidentally adopted a ''de facto'' gold standard in 1717 when Isaac Newton, then-master of the Royal Mint, set the exchange rate of silver to gold too low, thus causing silver coins to go out of circulation. As Great Britain became the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, which is the number of people who are unemployed as a percentage of the labour force (the total number of people employed added to those unemployed). Unemployment can have many sources, such as the following: * the status of the economy, which can be influenced by a recession * competition caused by globalization and international trade * new technologies and inventions * policies of the government * regulation and market * war, civil disorder, and natural disasters Unemployment and the status of the economy can be influenced by a country through, for example, fiscal policy. Furthermore, the monetary authority of a country, such as the central bank, can in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rate of inflation). Further purposes of a monetary policy may be to contribute to economic stability or to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies. Today most central banks in developed countries conduct their monetary policy within an inflation targeting framework, whereas the monetary policies of most developing countries' central banks target some kind of a fixed exchange rate system. A third monetary policy strategy, targeting the money supply, was widely followed during the 1980s, but has diminished in popularity since then, though it is still the official strategy in a number of emerging economies. The tools of monetary policy vary from central bank to central bank, depending on the country's stage of development, inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deflationary
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Bank
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the monetary base. Many central banks also have supervisory or regulatory powers to ensure the stability of commercial banks in their jurisdiction, to prevent bank runs, and, in some cases, to enforce policies on financial consumer protection, and against bank fraud, money laundering, or terrorism financing. Central banks play a crucial role in macroeconomic forecasting, which is essential for guiding monetary policy decisions, especially during times of economic turbulence. Central banks in most developed nations are usually set up to be institutionally independent from political interference, even though governments typically have governance rights over them, legislative bodies exercise scrutiny, and central banks frequently do show resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |