|
Test Data
Test data are sets of inputs or information used to verify the correctness, performance, and reliability of software systems. Test data encompass various types, such as positive and negative scenarios, edge cases, and realistic user scenarios, and aims to exercise different aspects of the software to uncover bugs and validate its behavior. Test data is also used in regression testing to verify that new code changes or enhancements do not introduce unintended side effects or break existing functionalities. Background Test data may be used to verify that a given set of inputs to a function produces an expected result. Alternatively, data can be used to challenge the program's ability to handle unusual, extreme, exceptional, or unexpected inputs. Test data can be produced in a focused or systematic manner, as is typically the case in domain testing, or through less focused approaches, such as high-volume randomized automated tests. Test data can be generated by the tester or by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression Testing
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regression''. Changes that may require regression testing include bug fixes, software enhancements, configuration changes, and even substitution of electronic components ( hardware). As regression test suites tend to grow with each found defect, test automation is frequently involved. Sometimes a change impact analysis is performed to determine an appropriate subset of tests (''non-regression analysis''). Background As software is updated or changed, or reused on a modified target, emergence of new faults and/or re-emergence of old faults is quite common. Sometimes re-emergence occurs because a fix gets lost through poor revision control practices (or simple human error in revision control). Often, a fix for a problem will be " fragil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
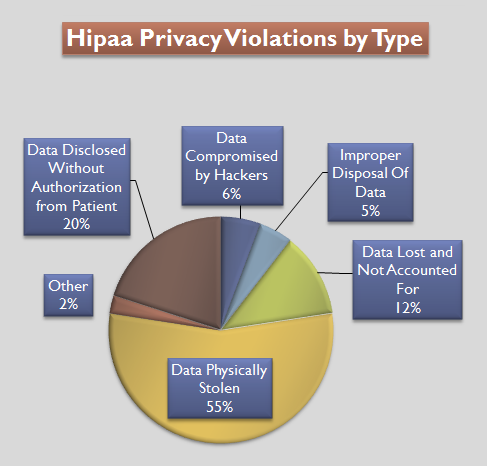
Health Insurance Portability And Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Ted Kennedy, Kennedy–Nancy Kassebaum, Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It aimed to alter the transfer of healthcare information, stipulated the guidelines by which personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on Health insurance in the United States, healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits Health professional, healthcare providers and businesses called covered entities from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. The bill does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves (with limited exceptions). Furthermore, it does not proh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Test
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the integration or system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Mercury project, where individual units developed by different programmes underwent "unit tests" before being integrated together. In 1969, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Plan
A test plan is a document detailing the objectives, resources, and processes for a specific test session for a software or hardware product. The plan typically contains a detailed understanding of the eventual workflow. Test plans A test plan documents the strategy that will be used to verify and ensure that a product or system meets its design specifications and other requirements. A test plan is usually prepared by or with significant input from test engineers. Depending on the product and the responsibility of the organization to which the test plan applies, a test plan may include a strategy for one or more of the following: * Design verification or compliance test – to be performed during the development or approval stages of the product, typically on a small sample of units. * Manufacturing test or production test – to be performed during preparation or assembly of the product in an ongoing manner for purposes of performance verification and quality control. * Acceptanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Suite
In software development, a test suite, less commonly known as a validation suite, is a collection of test cases that are intended to be used to test a software program to show that it has some specified set of behaviors. A test suite often contains detailed instructions or goals for each collection of test cases and information on the system configuration to be used during testing. A group of test cases may also contain prerequisite states or steps and descriptions of the following tests. Collections of test cases are sometimes termed a test plan, a test script, or even a test scenario. Types Occasionally, test suites are used to group similar test cases together. A system might have a smoke test suite that consists only of smoke tests or a test suite for some specific functionality in the system. It may also contain all tests and signify if a test should be used as a smoke test or for some specific functionality. In model-based testing, one distinguishes between ''abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scenario Test
Scenario testing is a software testing activity that uses scenarios: hypothetical stories to help the tester work through a complex problem or test system. The ideal scenario test is a credible, complex, compelling or motivating story; the outcome of which is easy to evaluate. These tests are usually different from test cases in that test cases are single steps whereas scenarios cover a number of steps. History Cem Kaner coined the phrase scenario test by October 2003. He commented that one of the most difficult aspects of testing was maintaining step-by-step test cases along with their expected results. His paper attempted to find a way to reduce the re-work of complicated written tests and incorporate the ease of use cases. A few months later, Hans Buwalda wrote about a similar approach he had been using that he called "soap opera testing". Like television soap operas these tests were both exaggerated in activity and condensed in time. The key to both approaches was to avoid s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Session-based Testing
Session-based testing is a software test method that aims to combine accountability and exploratory testing to provide rapid defect discovery, creative on-the-fly test design, management control and metrics reporting. The method can also be used in conjunction with scenario testing. Session-based testing was developed in 2000 by Jonathan and James Marcus Bach. Session-based testing can be used to introduce measurement and control to an immature test process and can form a foundation for significant improvements in productivity and error detection. Session-based testing can offer benefits when formal requirements are not present, incomplete, or changing rapidly. Elements of session-based testing Mission The mission in Session Based Test Management identifies the purpose of the session, helping to focus the session while still allowing for exploration of the system under test. According to Jon Bach, one of the co-founders of the methodology, the mission explains "what we are te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |