|
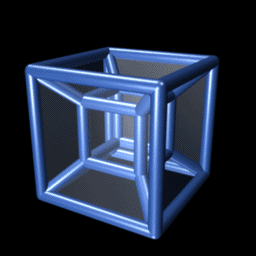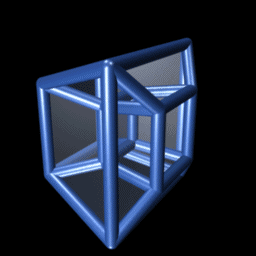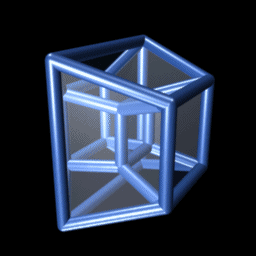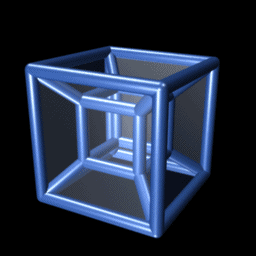
Tesseractic Honeycomb
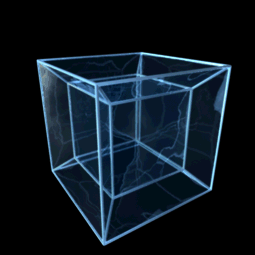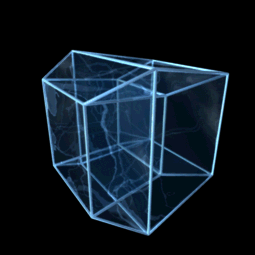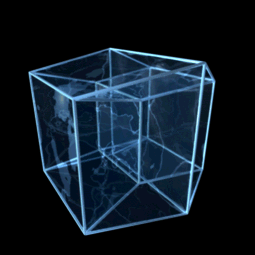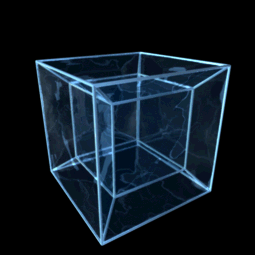
In four-dimensional euclidean geometry, the tesseractic honeycomb is one of the three regular space-filling tessellations (or honeycombs), represented by Schläfli symbol , and consisting of a packing of tesseracts (4-hypercubes). Its vertex figure is a 16-cell. Two tesseracts meet at each cubic cell, four meet at each square face, eight meet on each edge, and sixteen meet at each vertex. It is an analog of the square tiling, , of the plane and the cubic honeycomb, , of 3-space. These are all part of the hypercubic honeycomb family of tessellations of the form . Tessellations in this family are self-dual. Coordinates Vertices of this honeycomb can be positioned in 4-space in all integer coordinates (i,j,k,l). Sphere packing Like all regular hypercubic honeycombs, the tesseractic honeycomb corresponds to a sphere packing of edge-length-diameter spheres centered on each vertex, or (dually) inscribed in each cell instead. In the hypercubic honeycomb of 4 dimensions, vertex- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge-transitive
In geometry, a polytope (for example, a polygon or a polyhedron) or a Tessellation, tiling is isotoxal () or edge-transitive if its Symmetry, symmetries act Transitive group action, transitively on its Edge (geometry), edges. Informally, this means that there is only one type of edge to the object: given two edges, there is a Translation (geometry), translation, Rotation (mathematics), rotation, and/or Reflection (mathematics), reflection that will move one edge to the other while leaving the region occupied by the object unchanged. Isotoxal polygons An isotoxal polygon is an even-sided i.e. equilateral polygon, but not all equilateral polygons are isotoxal. The Duality (mathematics)#Dimension-reversing dualities, duals of isotoxal polygons are isogonal polygons. Isotoxal 4n-gons are Central symmetry, centrally symmetric, thus are also zonogons. In general, a (non-regular) isotoxal 2n-gon has \mathrm_n, (^*nn) dihedral symmetry. For example, a (non-square) rhombus is an isotoxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge (geometry)
In geometry, an edge is a particular type of line segment joining two vertex (geometry), vertices in a polygon, polyhedron, or higher-dimensional polytope. In a polygon, an edge is a line segment on the boundary, and is often called a polygon side. In a polyhedron or more generally a polytope, an edge is a line segment where two Face (geometry), faces (or polyhedron sides) meet. A segment joining two vertices while passing through the interior or exterior is not an edge but instead is called a diagonal. An ''edge'' may also be an infinite line (geometry), line separating two half-planes. The ''sides'' of a plane angle are semi-infinite Half-line (geometry), half-lines (or rays). Relation to edges in graphs In graph theory, an Edge (graph theory), edge is an abstract object connecting two vertex (graph theory), graph vertices, unlike polygon and polyhedron edges which have a concrete geometric representation as a line segment. However, any polyhedron can be represented by its n-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face (geometry)
In solid geometry, a face is a flat surface (a Plane (geometry), planar region (mathematics), region) that forms part of the boundary of a solid object. For example, a cube has six faces in this sense. In more modern treatments of the geometry of polyhedra and higher-dimensional polytopes, a "face" is defined in such a way that it may have any dimension. The vertices, edges, and (2-dimensional) faces of a polyhedron are all faces in this more general sense. Polygonal face In elementary geometry, a face is a polygon on the boundary of a polyhedron. (Here a "polygon" should be viewed as including the 2-dimensional region inside it.) Other names for a polygonal face include polyhedron side and Euclidean plane ''tessellation, tile''. For example, any of the six square (geometry), squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube. Sometimes "face" is also used to refer to the 2-dimensional features of a 4-polytope. With this meaning, the 4-dimensional tesseract has 24 square faces, each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square (geometry)
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degrees, or /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for squaring the circle by compass and straightedge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (geometry)
In solid geometry, a face is a flat surface (a planar region) that forms part of the boundary of a solid object. For example, a cube has six faces in this sense. In more modern treatments of the geometry of polyhedra and higher-dimensional polytopes, a "face" is defined in such a way that it may have any dimension. The vertices, edges, and (2-dimensional) faces of a polyhedron are all faces in this more general sense. Polygonal face In elementary geometry, a face is a polygon on the boundary of a polyhedron. (Here a "polygon" should be viewed as including the 2-dimensional region inside it.) Other names for a polygonal face include polyhedron side and Euclidean plane ''tile''. For example, any of the six squares that bound a cube is a face of the cube. Sometimes "face" is also used to refer to the 2-dimensional features of a 4-polytope. With this meaning, the 4-dimensional tesseract has 24 square faces, each sharing two of 8 cubic cells. Number of polygonal faces of a polyhedr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex Figure
In geometry, a vertex figure, broadly speaking, is the figure exposed when a corner of a general -polytope is sliced off. Definitions Take some corner or Vertex (geometry), vertex of a polyhedron. Mark a point somewhere along each connected edge. Draw lines across the connected faces, joining adjacent points around the face. When done, these lines form a complete circuit, i.e. a polygon, around the vertex. This polygon is the vertex figure. More precise formal definitions can vary quite widely, according to circumstance. For example Coxeter (e.g. 1948, 1954) varies his definition as convenient for the current area of discussion. Most of the following definitions of a vertex figure apply equally well to infinite tessellation, tilings or, by extension, to Honeycomb (geometry), space-filling tessellation with polytope Cell (geometry), cells and other higher-dimensional polytopes. As a flat slice Make a slice through the corner of the polyhedron, cutting through all the edges conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square ( ) and a cube ( ); the special case for is known as a ''tesseract''. It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1- skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions, perpendicular to each other and of the same length. A unit hypercube's longest diagonal in ''n'' dimensions is equal to \sqrt. An ''n''-dimensional hypercube is more commonly referred to as an ''n''-cube or sometimes as an ''n''-dimensional cube. The term measure polytope (originally from Elte, 1912) is also used, notably in the work of H. S. M. Coxeter who also labels the hypercubes the γn polytopes. The hypercube is the special case of a hyperrectangle (also called an ''n-orthotope''). A ''unit hypercube'' is a hypercube whose side has length one unit. Often, the hypercube whose corners (or ''vertices'') are the 2''n'' points in R''n'' with each coordinate equal to 0 or 1 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honeycomb (geometry)
In geometry, a honeycomb is a ''space filling'' or ''close packing'' of polyhedron, polyhedral or higher-dimensional ''cells'', so that there are no gaps. It is an example of the more general mathematical ''tiling'' or ''tessellation'' in any number of dimensions. Its dimension can be clarified as ''n''-honeycomb for a honeycomb of ''n''-dimensional space. Honeycombs are usually constructed in ordinary Euclidean geometry, Euclidean ("flat") space. They may also be constructed in non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean spaces, such as #Hyperbolic honeycombs, hyperbolic honeycombs. Any finite uniform polytope can be projected to its circumsphere to form a uniform honeycomb in spherical space. Classification There are infinitely many honeycombs, which have only been partially classified. The more regular ones have attracted the most interest, while a rich and varied assortment of others continue to be discovered. The simplest honeycombs to build are formed from stacked layers or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include '' regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and '' semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An '' aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern (an aperiodic set of prototiles). A '' tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry, ''Euclid's Elements, Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms (postulates) and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. One of those is the parallel postulate which relates to parallel lines on a Euclidean plane. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated earlier,. Euclid was the first to organize these propositions into a logic, logical system in which each result is ''mathematical proof, proved'' from axioms and previously proved theorems. The ''Elements'' begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school (high school) as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of mathematical proofs. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the ''Elements'' states results of what are now called algebra and number theory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-dimensional Space
Four-dimensional space (4D) is the mathematical extension of the concept of three-dimensional space (3D). Three-dimensional space is the simplest possible abstraction of the observation that one needs only three numbers, called ''dimensions'', to describe the sizes or locations of objects in the everyday world. This concept of ordinary space is called Euclidean space because it corresponds to EuclidEuclidean geometry, 's geometry, which was originally abstracted from the spatial experiences of everyday life. Single locations in Euclidean 4D space can be given as Vector space, vectors or ''n-tuples, 4-tuples'', i.e., as ordered lists of numbers such as . For example, the volume of a rectangular box is found by measuring and multiplying its length, width, and height (often labeled , , and ). It is only when such locations are linked together into more complicated shapes that the full richness and geometric complexity of 4D spaces emerge. A hint of that complexity can be seen in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |