|
Tataviam Language
The Tataviam language is an extinct Uto-Aztecan language formerly spoken by the Tataviam people of the upper Santa Clara River basin, Santa Susana Mountains, and Sierra Pelona Mountains in southern California. It had become extinct by 1916 and is known only from a few early records, notably a few words recorded by Alfred L. Kroeber and John P. Harrington in the early decades of the 20th century. These word lists were not from native speakers, but from the children of the last speakers who remembered a few words and phrases. Language family Uto-Aztecan Scholars have recognized Tataviam as belonging to the Uto-Aztecan language family, specifically the putative Takic branch. Based on the most thorough and most recent analysis, it is part of the Serran group along with Kitanemuk and Serrano (Munro and Johnson, 2001). Chumashan An earlier alternative suggestion by some scholars is that Tataviam was a Chumashan language, from the Ventureño language and others, of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern California
Southern California (commonly shortened to SoCal) is a geographic and Cultural area, cultural List of regions of California, region that generally comprises the southern portion of the U.S. state of California. Its densely populated coastal region includes Greater Los Angeles (the second-most populous urban agglomeration in the United States) and San Diego County (the second-most populous county in California). The region generally contains ten of California's 58 counties: Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles, San Diego County, California, San Diego, Orange County, California, Orange, Riverside County, California, Riverside, San Bernardino County, California, San Bernardino, Kern County, California, Kern, Ventura County, California, Ventura, Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara, San Luis Obispo County, California, San Luis Obispo, and Imperial County, California, Imperial counties. Although geographically smaller than Northern California in land area, Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumashan Languages
Chumashan is an extinct and revitalizing family of languages that were spoken on the southern California West Coast of the United States, coast by Native Americans in the United States, Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo, California, San Luis Obispo to Malibu, California, Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and canyons east to bordering the San Joaquin Valley, to three adjacent Channel Islands of California, Channel Islands: San Miguel Island, San Miguel, Santa Rosa Island, California, Santa Rosa, and Santa Cruz Island, Santa Cruz. The Chumashan languages may be, along with Yukian languages, Yukian and perhaps languages of southern Baja California such as Waikuri language, Waikuri, one of the oldest language families established in California, before the arrival of speakers of Penutian, Uto-Aztecan, and perhaps even Hokan languages. Chumashan, Yukian, and southern Baja languages are spoken in areas with lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
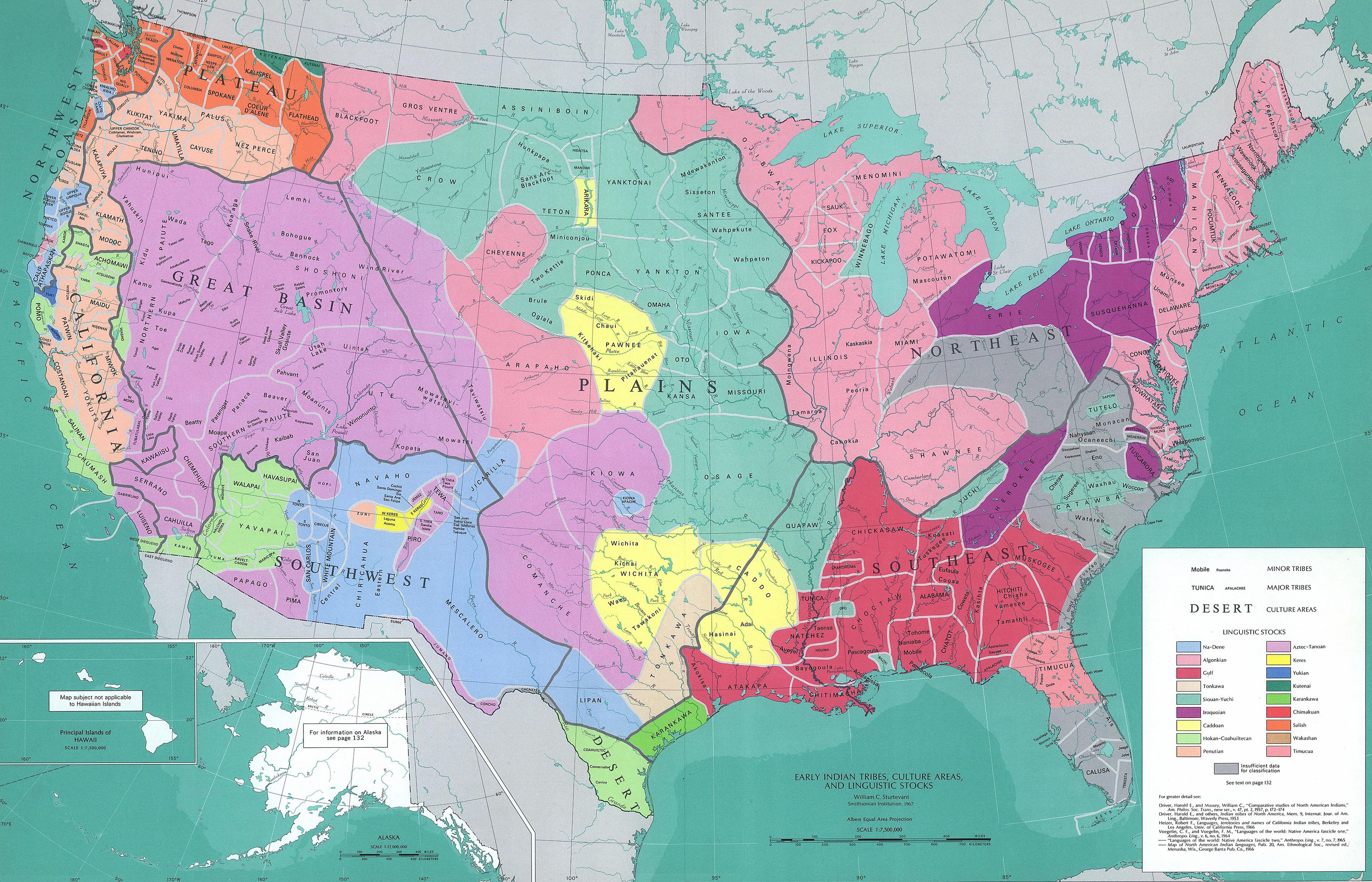
Handbook Of North American Indians
The ''Handbook of North American Indians'' is a series of edited scholarly and reference volumes in Native American studies, published by the Smithsonian Institution beginning in 1978. Planning for the handbook series began in the late 1960s and work was initiated following a special congressional appropriation in fiscal year 1971. To date, 16 volumes have been published. Each volume addresses a subtopic of Americanist research and contains a number of articles or chapters by individual specialists in the field coordinated and edited by a volume editor. The overall series of 20 volumes is planned and coordinated by a general or series editor. Until the series was suspended, mainly due to lack of funds, the series editor was William C. Sturtevant, who died in 2007. This work documents information about all Indigenous peoples of the Americas north of Mexico, including cultural and physical aspects of the people, language family, history, and worldviews. This series is a reference w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leanne Hinton
Leanne Hinton (born 28 September 1941) is an American linguist and emerita professor of linguistics at the University of California at Berkeley. Education and career Hinton received her PhD in 1977 from UC San Diego, with a dissertation entitled " Havasupai songs: a linguistic perspective," written under the supervision of Margaret Langdon. After joining the Berkeley faculty in 1978, Hinton began working with California languages. Hinton specializes in American Indian languages, sociolinguistics, and language revitalization. She has been described as "an authority on how and why languages are being lost, the significance of language diversity, and the ways in which indigenous tongues can be revitalized before it's too late." "She first worked with Native American groups on bilingual education, orthographic design and literature development. Hinton is a director of the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages The Survey of California and Other Indian Languages (origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ives Goddard
Robert Hale Ives Goddard III (born 1941) is a linguist and a curator emeritus in the Department of Anthropology of the National Museum of Natural History at the Smithsonian Institution. He is widely considered the leading expert on the Algonquian languages and the larger Algic language family. Early life and education Goddard received his B.A. from Harvard College in 1963 and his Ph.D. from Harvard University in 1969. From 1966–1969 he was a junior fellow of the Harvard Society of Fellows. Career After earning his doctorate, Goddard taught for several years at Harvard as a junior professor. In 1975, he moved to the Smithsonian Institution. His own field research in linguistics has concentrated on the Delaware languages and Meskwaki (Fox). He is also known for work on the Algonquian Massachusett language, and the history of the Cheyenne language. He has also published on the history of the Arapahoan branch of Algonquian: its two current lines that are extant are Arapaho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bright
William Oliver Bright (August 13, 1928 – October 15, 2006) was an American linguist and toponymist who specialized in Native American and South Asian languages and descriptive linguistics. Biography Bright earned a bachelor's degree in linguistics in 1949 and a doctorate in the same field in 1955, both from the University of California, Berkeley. He was a professor of linguistics and anthropology at UCLA from 1959 to 1988. He then moved to the University of Colorado at Boulder, where he remained on the faculty until his death. Bright was an authority on the native languages and cultures of California, and was especially known for his work on Karuk, a Native American language from northwestern California. His study of the language was the first carried out under the auspices of the Survey of California and Other Indian Languages. He was made an honorary member of the Karuk tribe—the first outsider to be so honored—in recognition of his efforts to document and preserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Narratives (Native California)
The traditional narratives of Native Indigenous Californians are the folklore and mythology of the native people of California. In California, most of the native peoples can be categorized into three large groups, Penutian, Hokan and Uto-Aztecan. For many historic nations of California, there is only a fragmentary record of their traditions. Spanish missions in California from the 18th century Christianized many of these traditions, and the remaining groups were mostly assimilated to US culture by the early 20th century. Due to assimilation many native groups lost the original folklore and mythology that was integrated into their culture and traditions, resulting in the blurred and changed stories that are known today. While there are sparse records from the 18th century, most material was collected during the 19th and the early 20th centuries. In California, most of the native peoples can be categorized into three large groups, Penutian, Hokan and Uto-Aztecan. Of these tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
Historically, classification of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas is based upon cultural regions, geography, and linguistics. Anthropologists have named various cultural regions, with fluid boundaries, that are generally agreed upon with some variation. These cultural regions are broadly based upon the locations of the Indigenous peoples of the Americas from early European and African contact beginning in the late 15th century. When Indigenous peoples have been forcibly removed by nation-states, they retain their original geographic classification. Some groups span multiple cultural regions. Peoples can also be classified by genetics, technology, and social structure. Canada, Greenland, United States, and northern Mexico In the United States and Canada, ethnographers commonly classify Indigenous peoples into ten geographical regions with shared cultural traits, called cultural areas. Greenland is part of the Arctic region. Some scholars combine the Plateau and Great Basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Native American History Of California
*The history of the Indigenous peoples of California. ::::*For individual tribal histories, see articles & tribal subcategories in: : Native American tribes in California ---- ::*Individual indigenous people of California (historical & contemporary) are in the category for their relevant tribe/people, found in: : Native American tribes in California. ::*Indigenous Californian languages (historical & contemporary) are in: : Indigenous languages of California. ::*California Indian reservations (historical & contemporary) are in: : American Indian reservations in California. ::*California tribes (historical & contemporary) are in: : Native American tribes in California. ::*Ongoing topics (contemporary or not only historical) are in: : Indigenous peoples of California topics. ::::*''Labeled map (external link)Map of Native Tribes, Groups, Language Families, and Dialects of California region in 1770'. External links * History History California California () is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Peabody Harrington
John Peabody Harrington (April 29, 1884 – October 21, 1961) was an American linguist and ethnologist and a specialist in the indigenous peoples of California. Harrington is noted for the massive volume of his documentary output, most of which remains unpublished: the shelf space in the National Anthropological Archives dedicated to his work spans nearly 700 feet. Early life and education Born in Waltham, Massachusetts, Harrington moved to California as a child. From 1902 to 1905, Harrington studied anthropology and classical languages at Stanford University. Harrington completed his Stanford undergraduate degree with courses at a summer school at the University of California at Berkeley where he met Alfred Kroeber. He began but did not complete graduate studies in Germany at the University of Leipzig, where he studied under Franz Nikolaus Finck. Like Harrington, Finck was a fieldworker who studied a broad range of languages in situ (especially dialects of Irish and Cauca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survey Of California And Other Indian Languages
The Survey of California and Other Indian Languages (originally the Survey of California Indian Languages) at the University of California at Berkeley documents, catalogs, and archives the indigenous languages of the Americas. The survey also hosts events related to language revitalization and preservation. Origins The Survey was started as a pilot project by Berkeley linguistics professor Murray Emeneau and Mary Haas in 1953. It was established with an official budget on January 1, 1953. Haas was a particular influence on the early working culture of the Survey. One student, Brent D. Galloway, recalled how several of Haas' students had used a Natchez greeting, ''wanhetahnú·ʼis'', and that "the tradition had apparently continued for over twenty years." (Haas' first publication had been on Natchez.) The first project was a study of the Karuk language by William Bright, then a graduate student. Since its founding 80 doctoral dissertations have been written under the auspices ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Indigenous Languages Of California
*Languages of the Indigenous peoples of California.—Of tribes belonging to indigenous California cultures as defined by ethnographers: see Classification of indigenous peoples of California and Native American tribes in California.—The area of this culture does not necessarily correspond with the State of California. See also * * LinksCaliforniaprehistory.com: Map of Native Tribes, Groups, Language Families, and Dialects of the California region in 1770 Languages L01 California California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ... .California Languages of California L01 {{CatAutoTOC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |