|
Tartu Dialect
The Tartu dialect (Estonian language, Estonian: ') is a dialect of South Estonian spoken in Estonia, near the city of Tartu. It bears similarities to Mulgi dialect, Mulgi, particularly the Tarvastu and Helme varieties. It has historically, along with northern Võro language, Võro, been the basis for the South Estonian literary language. Usage In the 2011 Estonian census, 4109 people were reported to be speaking the Tartu language, and in the 17310 people were reported to have spoken the language. It reached its peak in the 17th century and declined until the 2000s. Its speaker numbers have been increasing ever since, but the majority of speakers are aging, and there is a lack of media in Tartu. Revival movements for Tartu have not been as strong as those for the Seto dialect, Seto, Mulgi dialect, Mulgi and Võro language, Võro languages. Literature Jakob Hurt's collection "Eesti mõtteloo" contains his sermons in the Rõngu dialect of Tartu. In modern literature, Mats T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Languages
The Finnic or Baltic Finnic languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish language, Finnish and Estonian language, Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states. ''ö'' after front-harmonic vowels. The lack of ''õ'' in these languages as an innovation rather than a retention has been proposed, and recently resurrected. Germanic loanwords found throughout Northern Finnic but absent in Southern are also abundant, and even several Baltic examples of this are known. Northern Finnic in turn divides into two main groups. The most Eastern Finnic group consists of the East Finnish dialects as well as Ingrian, Karelian and Veps; the proto-language of these was likely spoken in the vicinity of Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
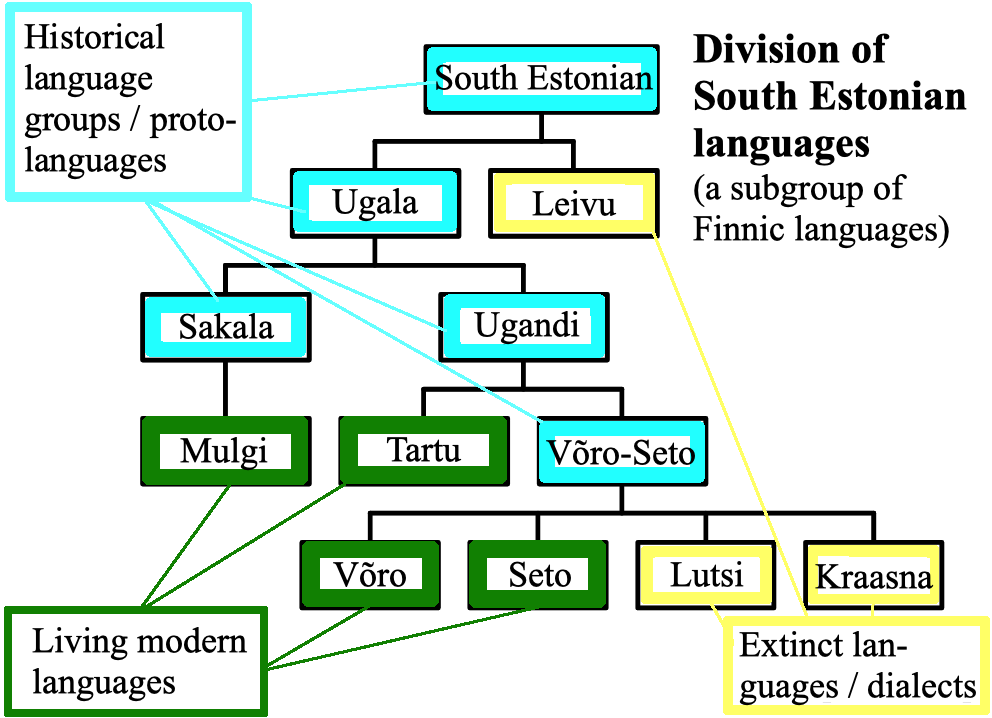
South Estonian
South Estonian, or Võro-Seto, is a Finnic language spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompassing the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto dialects. Diachronically speaking, Estonian and South Estonian are in separate branches of the Finnic languages, with Estonian being more closely related to Finnish than it is to South Estonian. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonian. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were implemented further throughout the country. The government officials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,300 other islands and islets on the east coast of the Baltic Sea. Its capital Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest List of cities and towns in Estonia, urban areas. The Estonian language is the official language and the first language of the Estonians, majority of its population of nearly 1.4 million. Estonia is one of the least populous members of the European Union and NATO. Present-day Estonia has been inhabited since at least 9,000 BC. The Ancient Estonia#Early Middle Ages, medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last pagan civilisations in Europe to adopt Christianity following the Northern Crusades in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartu County
Tartu County ( or ''Tartumaa'') is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is located in eastern Estonia bordering Põlva County, Valga County, Viljandi County and Jõgeva County. The area of Tartu County is , which covers 6.9% of the territory of Estonia. In 2022 Tartu County had a population of 157,758 – constituting 11.9% of the total population in Estonia. The city of Tartu is the centre of the county located at a distance of from Tallinn. Tartu County is divided into 8 local governments – 1 urban and 7 rural municipalities. Geography Tartu County lies in South Estonia, between Lake Võrtsjärv and Lake Peipus. Estonia's only navigable river, River Emajõgi (100 km long), flows through the county, connecting Lake Peipus and Lake Võrtsjärv. Wavy plains are typical landscapes of Tartu County. One third of the county is covered with forests, a third is cultivated. A quarter is made up of wetlands at the headwaters and lower course of the Emajõgi. In the northern pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Map
A linguistic map is a thematic map showing the geographic distribution of the speakers of a language, or isoglosses of a dialect continuum of the same language, or language family. A collection of such maps is a linguistic atlas. The earliest such atlas was the ''Sprachatlas des Deutschen Reiches'' of Georg Wenker and Ferdinand Wrede, published beginning in 1888, followed by the ''Atlas Linguistique de la France'', of Jules Gilliéron between 1902 and 1910, the ''Linguistischer Atlas des dacorumänischen Sprachgebietes'' published in 1909 by Gustav Weigand and the ''AIS - Sprach- und Sachatlas Italiens und der Südschweiz'' of Karl Jaberg and Jakob Jud, published 1928–1940. The first linguistic atlas of the US was published by Hans Kurath. The ''Linguistic Atlas of England'' was the result of the Survey of English Dialects, led by Harold Orton and Eugen Dieth. The first computerised linguistic atlas was the Atlas Linguarum Europae, first published in 1975. See also *''A Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võro Language
Võro ( ; , ) is a South Estonian language. It has its own literary standard and efforts have been undertaken to seek official recognition as an indigenous regional language of Estonia. Võro has roughly 75,000 speakers (Võros), mostly in southeastern Estonia, in the eight parishes of the historical Võru County: Karula, Harglõ, Urvastõ, Rõugõ, Kanepi, Põlva, Räpinä and Vahtsõliina. These parishes are currently centred (due to redistricting) in Võru and Põlva counties, with parts extending into Valga and Tartu counties. Speakers can also be found in the cities of Tallinn and Tartu and the rest of Estonia. History Võro is a descendant of the old South Estonian regional language and is the least influenced by Standard Estonian (which is based on Northern Estonian dialects). Võro was once spoken further south and east of historical Võromaa in South Estonian-speaking enclaves Lutsi (Ludza), Leivu and Kraasna in what is now Latvia and Russia. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian Language
Estonian ( ) is a Finnic language and the official language of Estonia. It is written in the Latin script and is the first language of the majority of the country's population; it is also an official language of the European Union. Estonian is spoken natively by about 1.1 million people: 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 elsewhere. Classification By Convention (norm), conventions of historical linguistics, Estonian is classified as a part of the Finnic languages, Finnic (a.k.a. Baltic Finnic) branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic (a.k.a. Uralian, or Finno-Ugric languages, Finno-Ugric) language family. Other Finnic languages include Finnish language, Finnish and several endangered languages spoken around the Baltic Sea and in northwestern Russia. Estonian is typically subclassified as a Southern Finnic language, and it is the second-most-spoken language among all the Finnic languages. Alongside Finnish, Hungarian language, Hungarian and Maltese language, Maltese, Estonian is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 97,759 (as of 2024). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of Riga, Latvia. Tartu lies on the Emajõgi river, which connects the two largest lakes in Estonia, Lake Võrtsjärv and Lake Peipus. From the 13th century until the end of the 19th century, Tartu was known in most of the world by variants of its historical name Dorpat. Tartu, the largest urban centre of southern Estonia, is often considered the "intellectual capital city" of the country, especially as it is home to the nation's oldest and most renowned university, the University of Tartu (founded in 1632). Tartu also houses the Supreme Court of Estonia, the Ministry of Education and Research (Estonia), Ministry of Education and Research, the Estonian National Museum, and the oldest Estonian-language theatre, Vanemuine. It is also the birthplace of the Estonian Song Festivals. Tartu was designated as the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulgi Dialect
Mulgi (, South Estonian (including Mulgi): ''mulgi kiilʼ'') is a dialect of South Estonian spoken in Estonia. The 2021 Estonian census counted 13,960 speakers. Usage Mulgi is spoken only by the older generation, as children are taught in standard Estonian, and parents do not pass Mulgi down to their children. The (Mulgi Kultuuri Instituut) operated from 1934 to 1940, and also since 1989. It produces, publishes and distributes productions in Mulgi (tales, nursery rhymes, and songs). A Mulgi newspaper is printed irregularly. Two notable Mulgi writers are August Kitzberg (1855-1927) and Nikolai Baturin Nikolai Baturin (5 August 1936 – 16 May 2019) was an Estonian award-winning novelist and playwright. Biography and career Baturin was born in the village of Arumetsa in Suislepa Parish (now the village of Maltsa, Viljandi Parish), Viljandi C ... (1936-2019). References External links Mulgimaa Languages of Estonia South Estonian language {{Uralic-lang- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Estonian Census
The 2011 Population and Housing Census (PHC 2011) ( (''REL 2011'')). was a census that was carried out during 31 December 2011 – 31 March 2012 in Estonia by Statistics Estonia. The total actual population recorded was 1,294,455 persons. See also *Demographics of Estonia References External linksResults at Statistics Estonia Censuses in Estonia Demographics of Estonia Ethnic groups in Estonia 2011 in Estonia 2011 censuses, Estonia {{Estonia-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000s
File:2000s decade montage3.png, From top left, clockwise: The Twin Towers of the original World Trade Center (1973–2001), World Trade Center on fire and the Statue of Liberty on the left during the September 11 attacks, terrorist attacks on September 11, 2001; the euro enters into European currency in 2002; a statue of Saddam Hussein being toppled during the Iraq War in 2003, and in 2006, Hussein would be Execution of Saddam Hussein, executed for crimes against humanity; U.S. troops heading toward an army helicopter in War in Afghanistan (2001–2021), Afghanistan during the war on terror; social media platforms on the internet Web 2.0, become widely popular; a Chinese soldier gazes at the 2008 Summer Olympics commencing in Beijing; the 2008 financial crisis, the largest financial crisis since the Great Depression; 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, a tsunami from the Indian Ocean earthquake kills over 230,000 in 2004, and becomes the strongest earthquake since the 1964 Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |