|
Tank Steering Systems
Tank steering systems allow a tank, or other continuous track vehicle, to turn. Because the tracks cannot be angled relative to the hull (in any operational design), steering must be accomplished by speeding one track up, slowing the other down (or reversing it), or a combination of both. Half-track vehicles avoid this by combining steerable wheels and fixed-speed tracks. Early steering systems were adopted from tracked work vehicles, generally using a clutch to reduce power to one track, causing it to slow down. These designs have numerous problems, notably when climbing hills or running at high speed, as the reduction in power causes the overall speed to slow. Delivering power to both tracks while turning them at different speeds is a difficult design problem. A series of more advanced designs were introduced, especially through World War II, that maintained power to both tracks during steering, a concept known as regenerative steering. Some also allowed one track to move for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holt Tractor
The Holt tractors were a range of continuous track haulers built by the Holt Manufacturing Company of Stockton, California which were named after company founder Benjamin Holt. Between 1908 and 1913, twenty-seven of the first 100 Holt caterpillar track-type tractors were used on the Los Angeles Aqueduct project, which provided a good proving ground for these machines. Military use They were widely used by the British, French and American armies in the First World War for hauling heavy artillery including the BL 9.2-inch howitzer and the BL 8-inch howitzer. Around 2,000 Holt 75s along with 698 Holt 120s and 63 Holt 60s saw military use during the war. The French Schneider CA1 and Saint-Chamond and German A7V tanks were based on Holt tractors. Specification There were at least three models used for military purposes: the Holt 75, the Holt 120 and to a lesser extent the Holt 60. The Holt 75 was first produced in 1913. It used two tracks for steering. It had a maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against Anti-tank warfare, anti-tank weapons. The T-34 had a profound effect on the conflict on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front, and had a long-lasting impact on tank design. The tank was praised by German generals when encountered during Operation Barbarossa, although its armour and armament were surpassed later in the war. Its main strength was its cost and production time, meaning that German panzer forces would often fight against Soviet tank forces several times their own size. The T-34 was also a critical part of the mechanized divisions that formed the backbone of the Deep operation, deep battle strategy. The T-34 was the mainstay of the Soviet Red Army armoured warfare, armoured forces throughout the war. Its general specifications remained n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
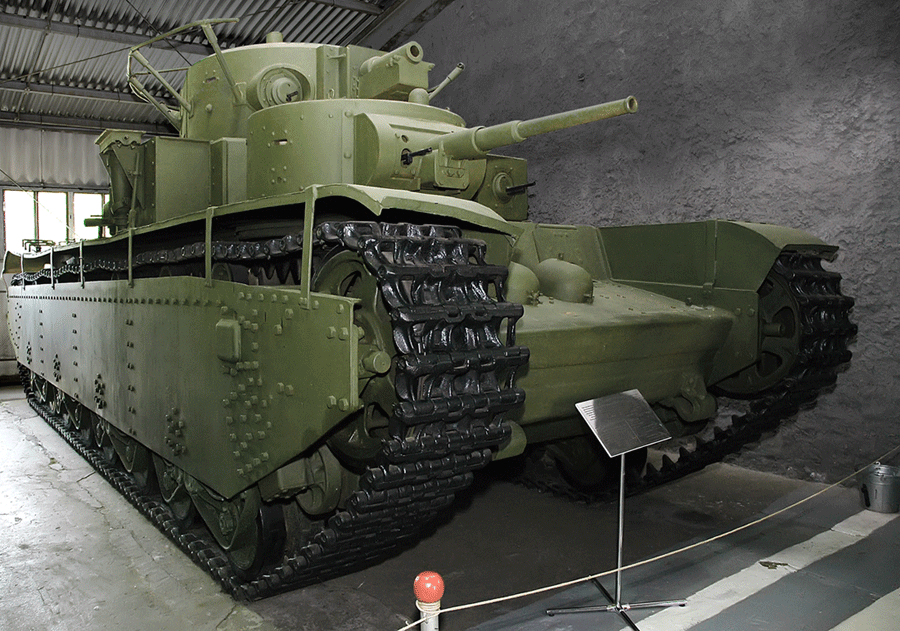
T-35
The T-35 was a Soviet multi- turreted heavy tank of the interwar period and early Second World War that saw limited service with the Red Army. Often called a land battleship, it was the only five-turreted heavy tank in the world to reach production, but proved to be slow and mechanically unreliable. Most of the T-35 tanks still operational at the time of Operation Barbarossa were lost due to mechanical failure rather than enemy action. It was designed to complement the contemporary T-28 medium tank; however, very few were built. Outwardly, it was large; but internally, the spaces were cramped with the fighting compartments separated from each other. Some of the turrets obscured the entrance hatches. Production history The T-35 was developed by the OKMO design bureau of the Bolshevik Factory, which began work on a heavy tank in 1930. Two teams developed separate designs. The team headed by German engineer Grotte worked on the 100-ton four-turreted TG-5 tank, armed with a 107& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
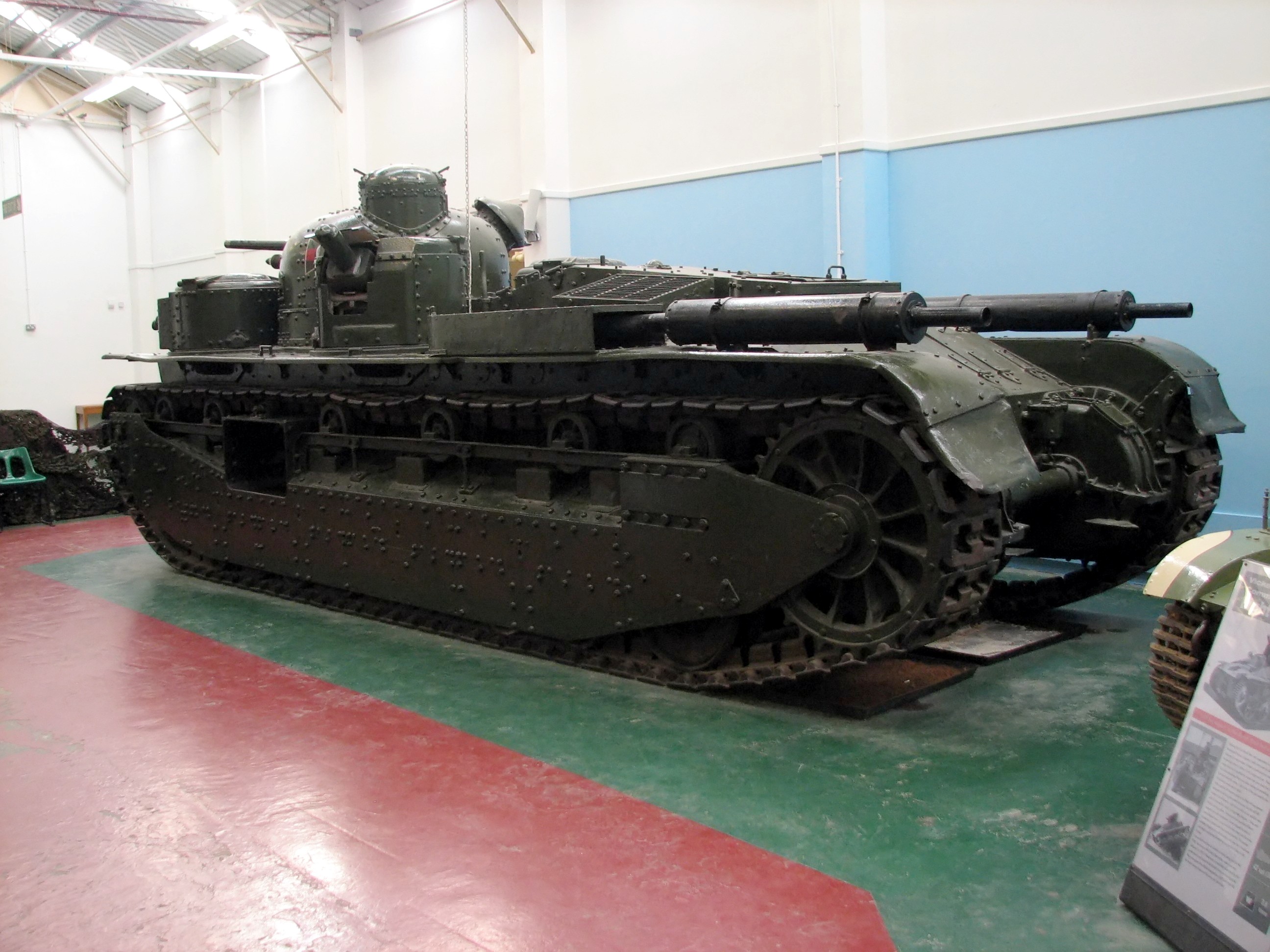
Vickers Independent
The Independent A1E1 is a multi-turreted tank that was designed by the British armaments manufacturer Vickers between the First and Second World Wars. Although it only ever reached the prototype stage and only a single example was built, it influenced many other tank designs. The A1E1 design can be seen as a possible influence on the Soviet T-100 and T-28 tanks, the German ''Neubaufahrzeug'' tanks, and the British Medium Mk III and Cruiser Mk I (triple turret) tank designs. The Soviet T-35 tank was heavily influenced by its design. Design The Independent was a multi-turret design, having a central gun turret armed with the 3 pounder (47 mm) gun, and four subsidiary turrets each armed with a 0.303 inch Vickers machine gun. The subsidiary turrets were mounted two at the front and two to the rear of the turret (about halfway along the hull). The gun of the left rear turret was able to elevate to engage aircraft. The tank was designed to have heavy firepower, self-defence capabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-34 Model 1940
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank from World War II. When introduced, its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was more powerful than many of its contemporaries, and its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The T-34 had a profound effect on the conflict on the Eastern Front, and had a long-lasting impact on tank design. The tank was praised by German generals when encountered during Operation Barbarossa, although its armour and armament were surpassed later in the war. Its main strength was its cost and production time, meaning that German panzer forces would often fight against Soviet tank forces several times their own size. The T-34 was also a critical part of the mechanized divisions that formed the backbone of the deep battle strategy. The T-34 was the mainstay of the Soviet Red Army armoured forces throughout the war. Its general specifications remained nearly unchanged until early 1944, when it received a firepower upgrade with the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
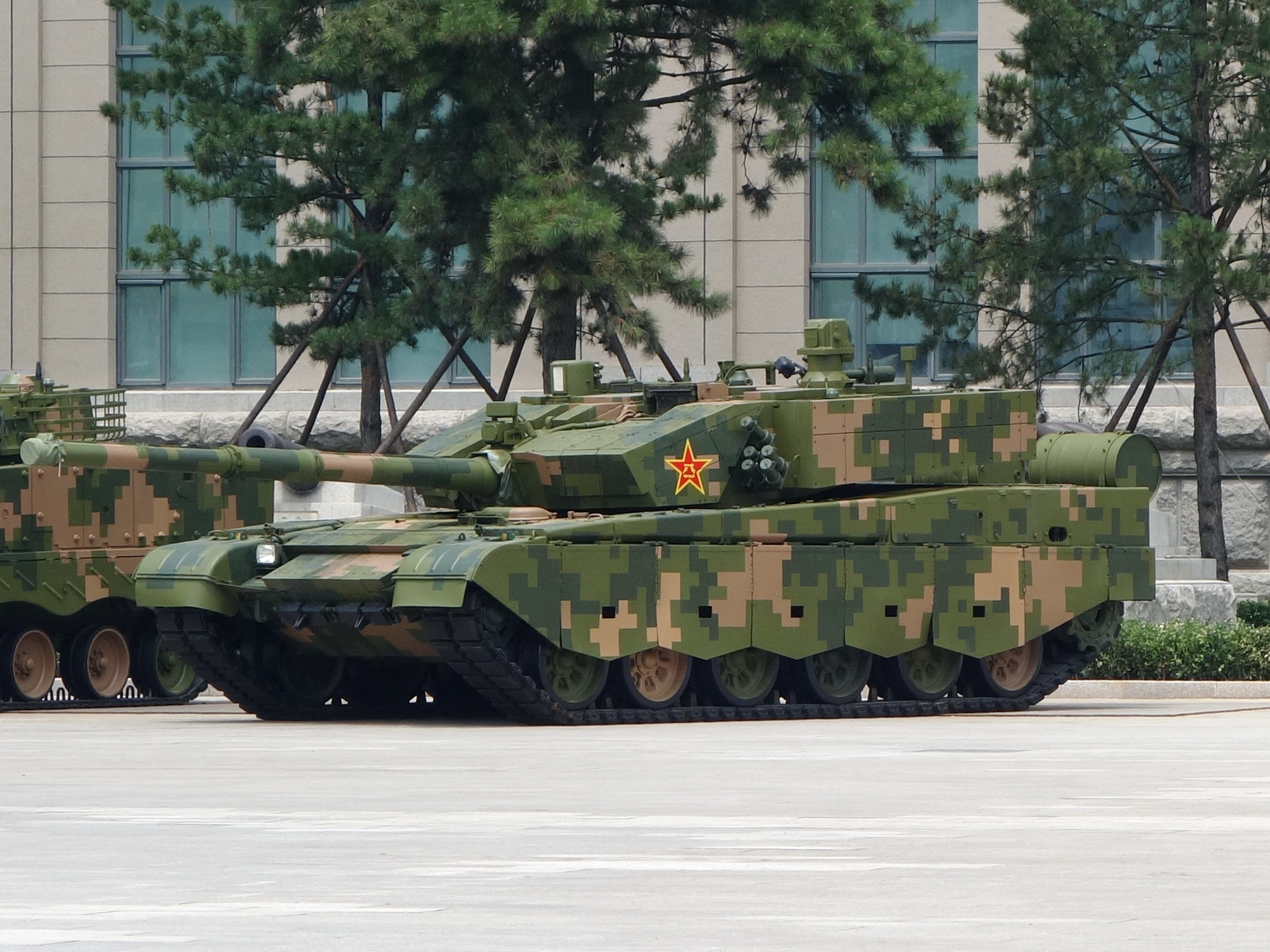
Type 99 Tank
The Type 99 () or ZTZ-99 is a Chinese third generation main battle tank (MBT).US Army TRADOC Intelligence Support Activity (2011:5-40) The vehicle was a replacement for the aging Type 88 introduced in the late 1980s. The Type 99 MBT was China's first mass-produced third-generation main battle tank. Combining modular composite armour and tandem-charge defeating ERA, 125 mm smoothbore gun with ATGM-capability, high mobility, digital systems and optics, the Type 99 represents a shift towards rapid modernization by the PLA. The Type 99 is based on the Soviet T-72 chassis. The tank entered People's Liberation Army (PLA) service in 2001. The People's Liberation Army Ground Force (PLAGF) is the sole operator of the Type 99. Three main versions of the Type 99 have been deployed: the Type 98 prototype, Type 99 and the Type 99A. The Type 99 forms the core of China’s modern maneuver combat capabilities, with over 1,300 tanks built for the past two decades. Development The develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
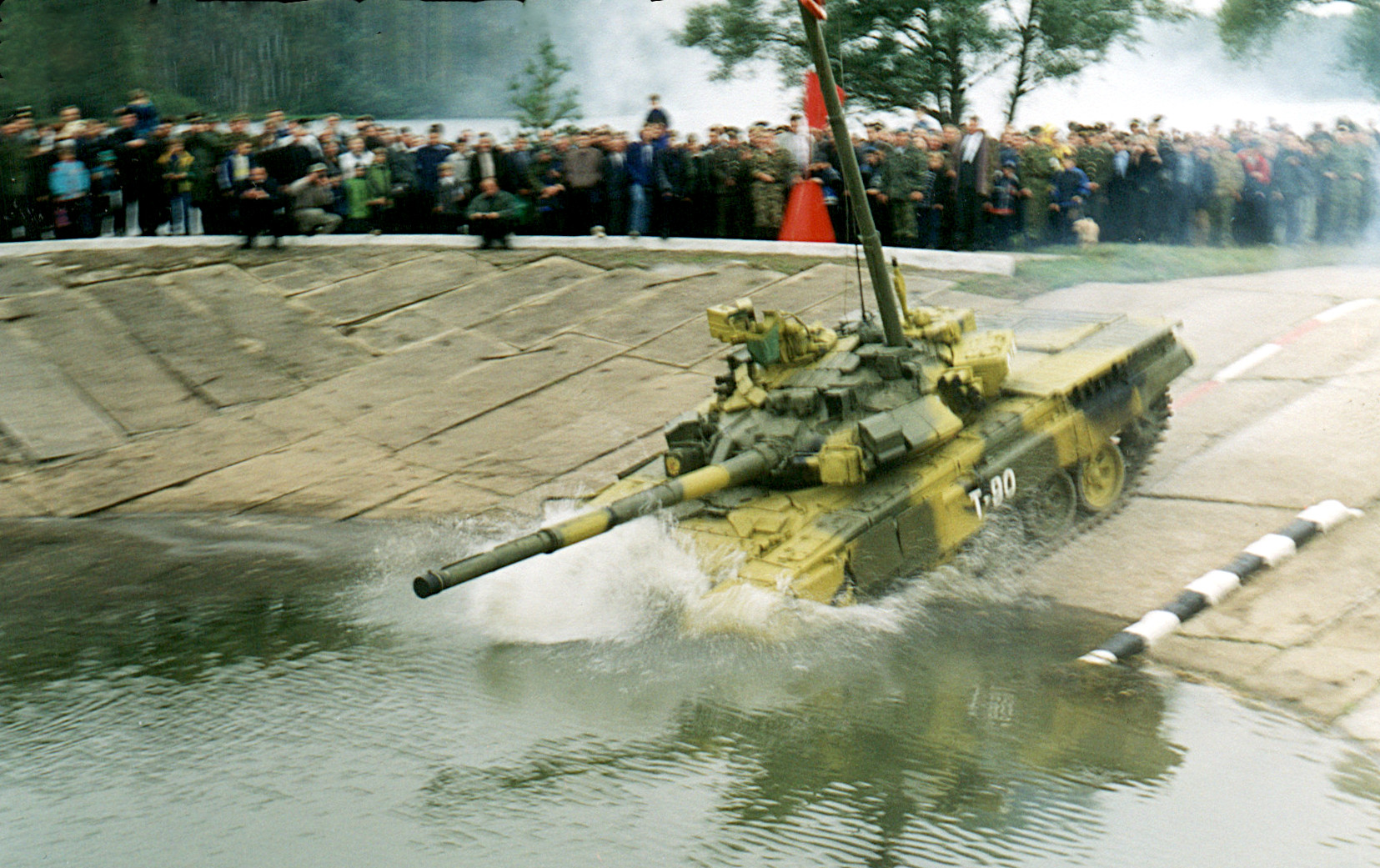
T-90
The T-90 is a third-generation Russian main battle tank developed from, and designed to replace the T-72. It uses a 125mm 2A46 smoothbore main gun, the 1A45T fire-control system, an upgraded engine, and gunner's thermal sight. Standard protective measures include a blend of steel and composite armour, smoke grenade dischargers, Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour (ERA) and the Shtora infrared anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) jamming system. The T-90 was designed and built by Uralvagonzavod, in Nizhny Tagil, Russia. It entered service with the Russian army in 1992. Development The T-90 has its origins in a Soviet-era program aimed at developing a replacement for the T-64, T-72 and T-80 series of main battle tanks (MBT). The T-72 platform was selected as the basis for the new generation of tank owing to its cost-effectiveness, simplicity and automotive qualities. The Kartsev-Venediktov Design Bureau from Nizhny Tagil was responsible for the design work and prepared tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
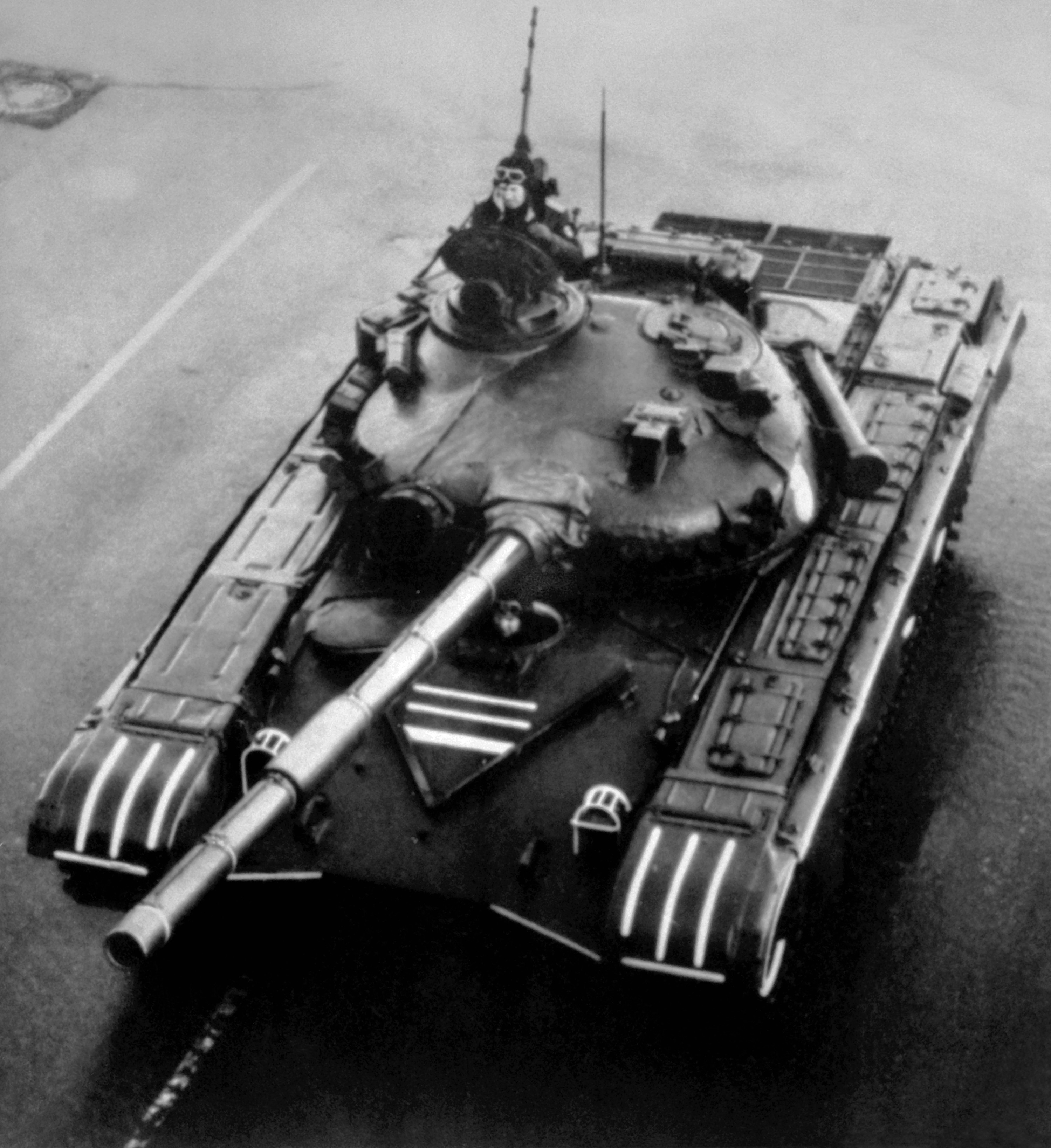
T-72
The T-72 is a family of Soviet Union, Soviet main battle tanks that entered production in 1973. The T-72 was a development based on the T-64 using thought and design of the previous Object 167M. About 25,000 T-72 tanks have been built, and refurbishment has enabled many to remain in service for decades. It has been widely exported and has seen service in 40 countries and in numerous conflicts. The Russian T-90 introduced in 1992 and the Chinese Type 99 tank, Type 99 are further developments of the T-72. Production and development of various modernized T-72 models continues today. Development Development from the T-64 The T-72 was a product of a rivalry between design teams. Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau, Morozov KB was led by Alexander Alexandrovich Morozov, Alexander Morozov in Kharkiv. Uralvagonzavod, Uralvagon KB was led by Leonid Kartsev in Nizhny Tagil. To improve on the T-62, two designs based on the tank were tested in 1964: Nizhny Tagil's Object 167 (T- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-64
The T-64 is a Soviet tank manufactured in Kharkiv, and designed by Alexander Morozov. The tank was introduced in the early 1960s. It was a more advanced counterpart to the T-62: the T-64 served in tank divisions, while the T-62 supported infantry in motor rifle divisions. It introduced advanced features including composite armour, a compact engine and transmission, and a smoothbore 125-mm gun equipped with an autoloader to allow the crew to be reduced to three so the tank could be smaller and lighter. In spite of being armed and armoured like a heavy tank, the T-64 weighed only . These features made the T-64 expensive to build, significantly more so than previous generations of Soviet tanks. This was especially true of the power plant, which was time-consuming to build and cost twice as much as more conventional designs. Several proposals were made to improve the T-64 with new engines, but chief designer Alexander Alexandrovich Morozov's political power in Moscow kept t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IS Tank Family
The IS tanks () were a series of heavy tanks developed as a successor to the KV-series by the Soviet Union during World War II. The IS acronym is the anglicized initialism of Joseph Stalin (, '). The heavy tanks were designed as a response to the capture of a German Tiger I in 1943. They were mainly designed as breakthrough tanks, firing a heavy high-explosive shell that was useful against entrenchments and bunkers. The IS-2 went into service in April 1944 and was used as a spearhead by the Red Army in the final stage of the Battle of Berlin. The IS-3 served on the Chinese-Soviet border, the Hungarian Revolution, the Prague Spring and on both sides of the Six-Day War. The series eventually culminated in the T-10 heavy tank. Design and production KV-85/IS-85/IS-1 The KV-85 was a KV-1S with the new turret from the Object 237 (IS-85) still in development, mounting the 85mm D-5T gun. The tank was a result of the USSR's tank design bureau being torn in two, one half f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panzer 38(t)
The 38(t), originally known as the ČKD, Českomoravská Kolben-Daněk (ČKD) LT vz. 38, was a tank designed during the 1930s, which saw extensive service during World War II. Developed in Czechoslovakia by ČKD, the type was adopted by Nazi Germany following the German occupation of Czechoslovakia. With the German Army and other Axis forces, the type saw service in the invasions of Poland, France and the USSR. Production ended in 1942, when its main armament was deemed inadequate. In all, over 1,400 Pz. 38(t)s were manufactured. The chassis of the Pz. 38(t) continued to be produced for the Marder III (1942–1944) with some of its components used in the later Hetzer (''Jagdpanzer'' 38, 1944–1945) tank destroyer and its derivative vehicles. The (t) stands for , the German word for Czech; the Czechoslovak military designation was LT vz. 38 (, Light Tank model 38). Manufacturer's designations included TNH series, TNHPS, LTP and LTH. The special vehicle () designation for the ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |