|
Tangasauridae
Tangasauridae is an extinct family of diapsids known from fossil specimens from Madagascar, Kenya and Tanzania that are Late Permian to Early Triassic in age. Fossils have been found of numerous specimens of common members of this family such as '' Hovasaurus'' in different stages of ontogenic development. Recent material from the Middle Sakamena Formation of the Morondava Basin of Madagascar that dates back to the early Triassic period suggests that the Tangasauridae were relatively unaffected by the Permian-Triassic extinction event. Description and phylogeny Tangasaurids are known to have been a highly derived group of diapsids. One subfamily, Kenyasaurinae, is composed of taxa that were fully terrestrial. They had long toes and highly developed sternums that made them well suited to life on land. On the other hand, the other subfamily, Tangasaurinae, is composed of taxa that were adapted to an aquatic life. They had webbed feet and a laterally compressed tails that al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapsida
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeoscelidians, appeared about three hundred million years ago during the late Carboniferous period. All diapsids other than the most primitive ones in the clade Araeoscelidia are often placed into the clade Neodiapsida. The diapsids are extremely diverse, and include birds and all modern reptile groups, including turtles, which were historically thought to lie outside the group. All modern reptiles and birds are placed within the neodiapsid subclade Sauria. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 17,084 species of diapsid animals are extant: 9,159 birds, and 7,925 sn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younginiformes
Younginiformes is a group of diapsid reptiles known from the Permian-Triassic of Africa and Madagascar. It has been used as a replacement for " Eosuchia". Younginiformes (including '' Acerosodontosaurus'', '' Hovasaurus'', '' Kenyasaurus'', '' Tangasaurus'', '' Thadeosaurus'' and ''Youngina'') were historically suggested to be lepidosauromorphs, but are currently thought to be basal non- saurian neodiapsids. The group is sometimes divided into two families, Tangasauridae and Younginidae. The monophyly of the group is disputed. A 2009 study found them to be an unresolved polytomy at the base of Neodiapsida, while a 2011 study recovered the group as paraphyletic. A 2022 study recovered the Younginiformes as a monophyletic group of basal neodiapsid reptiles, also including '' Claudiosaurus'' and '' Saurosternon'' as part of the group. Some younginiforms like ''Hovasaurus'' and ''Acerosodontosaurus'' are thought to have had an amphibious lifestyle, while others like ''Kenyasaurus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
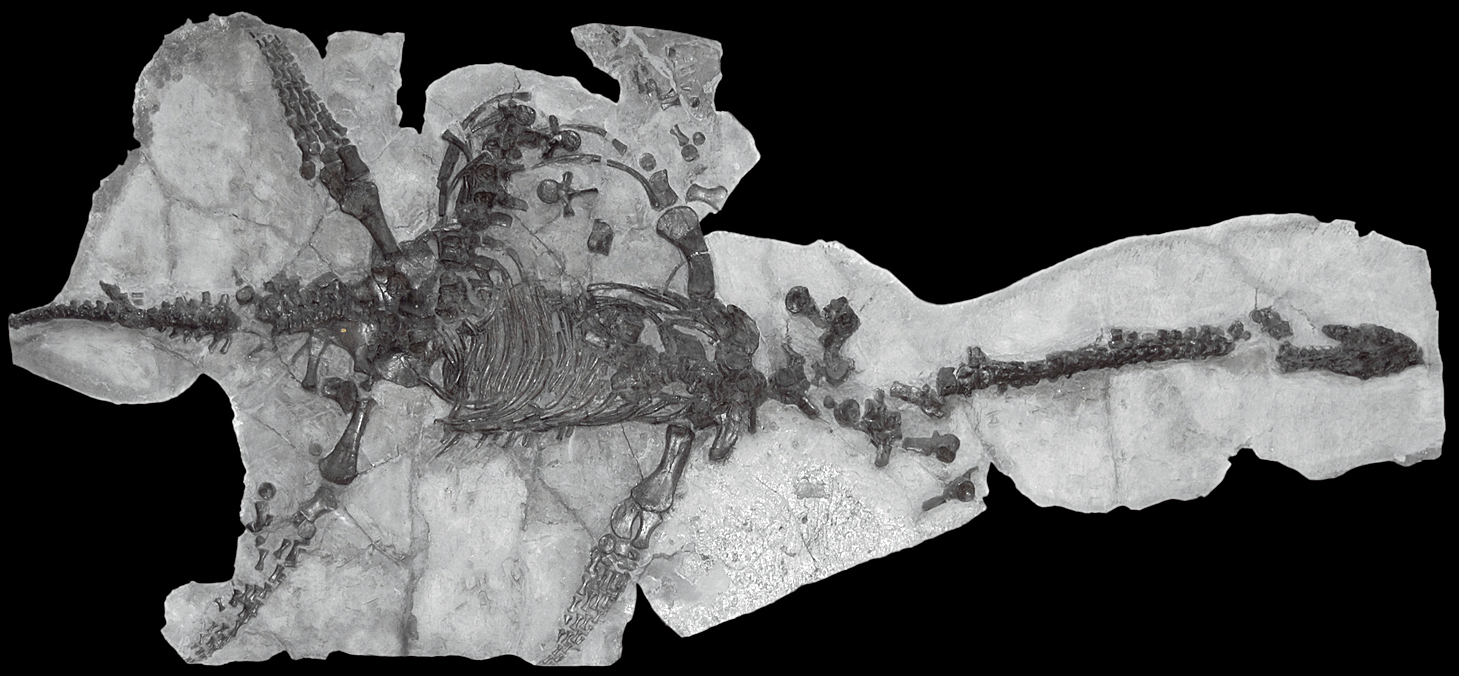
Hovasaurus
''Hovasaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal diapsid reptile. It lived in what is now Madagascar during the Late Permian and Early Triassic, being a survivor of the Permian–Triassic extinction event and the paleontologically youngest member of the Tangasauridae. Fossils have been found in the Permian Lower and Triassic Middle Sakamena Formations of the Sakamena Group, where it is amongst the commonest fossils. Its morphology suggests an aquatic ecology. Description ''Hovasaurus'' resembled a slender lizard, two thirds of total length was taken up by its long tail. It had snout-vent length up to long, with long tail. It was well adapted to an aquatic life, with the tail being laterally flattened like that of a sea snake. Some stones have been found in the abdomen of fossil ''Hovasaurus'', indicating the creatures swallowed these for ballast, preventing them from floating to the surface when hunting fish. Paleoenvironment The Lower Sakamena Formation was deposited in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Paleontology And Evolution
''Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution'' is an advanced textbook on vertebrate paleontology by Robert L. Carroll, published in 1988 by WH Freeman. It provides a very detailed technical account of various groups of living and fossil vertebrates. The book, which is written in the style of Alfred Sherwood Romer's ''Vertebrate Paleontology'', presented more recent overall coverage of the subject. At the rear of the book is a 53-page Classification list which lists every genus known at the time of publication, along with locality and stratigraphic range. ''Vertebrate Paleontology and Evolution'' appeared in print in 1988, just before the cladistic taxonomy became popular in vertebrate paleontology. The books thus uses the classical systematic scheme, including a number of paraphyletic taxa that are not recognised under phylogenetic nomenclature Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plesiosauria
The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia. Plesiosaurs first appeared in the latest Triassic Period, possibly in the Rhaetian stage, about 203 million years ago. They became especially common during the Jurassic Period, thriving until their disappearance due to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event at the end of the Cretaceous Period, about 66 million years ago. They had a worldwide oceanic distribution, and some species at least partly inhabited freshwater environments. Plesiosaurs were among the first fossil reptiles discovered. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, scientists realised how distinctive their build was and they were named as a separate order in 1835. The first plesiosaurian genus, the eponymous '' Plesiosaurus'', was named in 1821. Since then, more than a hundred valid species have been described. In the early twenty-first century, the number of discoveries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothosauria
Nothosaurs (superfamily Nothosauroidea) were Triassic marine sauropterygian reptiles. They averaged about in length, with a long body and tail. The feet were paddle-like, and are known to have been webbed in life, to help power the animal when swimming. The neck was quite long, and the head was elongated and flattened, and relatively small in relation to the body. The margins of the long jaws were equipped with numerous sharp outward-pointing teeth, indicating a diet of fish and squid. Taxonomy The Nothosauroidea has been suggested to consist of two suborders, the Pachypleurosauria, which are small primitive forms, and the Nothosauria (including two families Nothosauridae and Simosauridae), which may have evolved from pachypleurosaurs. The relation of pachypleurosaurs to Nothosauroidea is uncertain, as several analyses recover the clade as basal to Eusauropterygia, e.i. the clade formed by Nothosauria and Pistosauroidea, instead as the sister taxon of Nothosauria. Many re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodontia
Placodonts ("Tablet (pharmacy), tablet tooth, teeth") are an Extinction, extinct order (biology), order of marine reptiles that lived during the Triassic period, becoming extinct at the end of the period. They were part of Sauropterygia, the group that includes Plesiosauria, plesiosaurs. Placodonts were generally between in length, with some of the largest measuring long. The first specimen was discovered in 1830. They have been found throughout central Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and China. Palaeobiology The earliest forms, like ''Placodus'', which lived in the early to middle Triassic, resembled barrel-bodied lizards superficially similar to the marine iguana of today, but larger. In contrast to the marine iguana, which feeds on algae, the placodonts ate Mollusca, molluscs and so their teeth were flat and tough to crush shells. In the earliest periods, their size was probably enough to keep away the top sea predators of the time: the sharks. However, as time passe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropterygia
Sauropterygia ("lizard flippers") is an extinct taxon of diverse, aquatic diapsid reptiles that developed from terrestrial ancestors soon after the end-Permian extinction and flourished during the Triassic before all except for the Plesiosauria became extinct at the end of that period. The plesiosaurs would continue to diversify until the end of the Mesozoic, when they became extinct as part of the end-Cretaceous mass extinction. Sauropterygians are united by a radical adaptation of their pectoral girdle, adapted to support powerful flipper strokes. Some later sauropterygians, such as the pliosaurs, developed a similar mechanism in their pelvis. Other than being diapsids, their affinities to other reptiles have long been contentious. Sometimes suggested to be closely related to turtles, other proposals have considered them most closely related to Lepidosauromorpha or Archosauromorpha, and/or the marine reptile groups Thalattosauria and Ichthyosauromorpha. Origins an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superorder
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word ''sternum'' originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (''stérnon'') 'chest'. Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |