|
T Wave Alternans
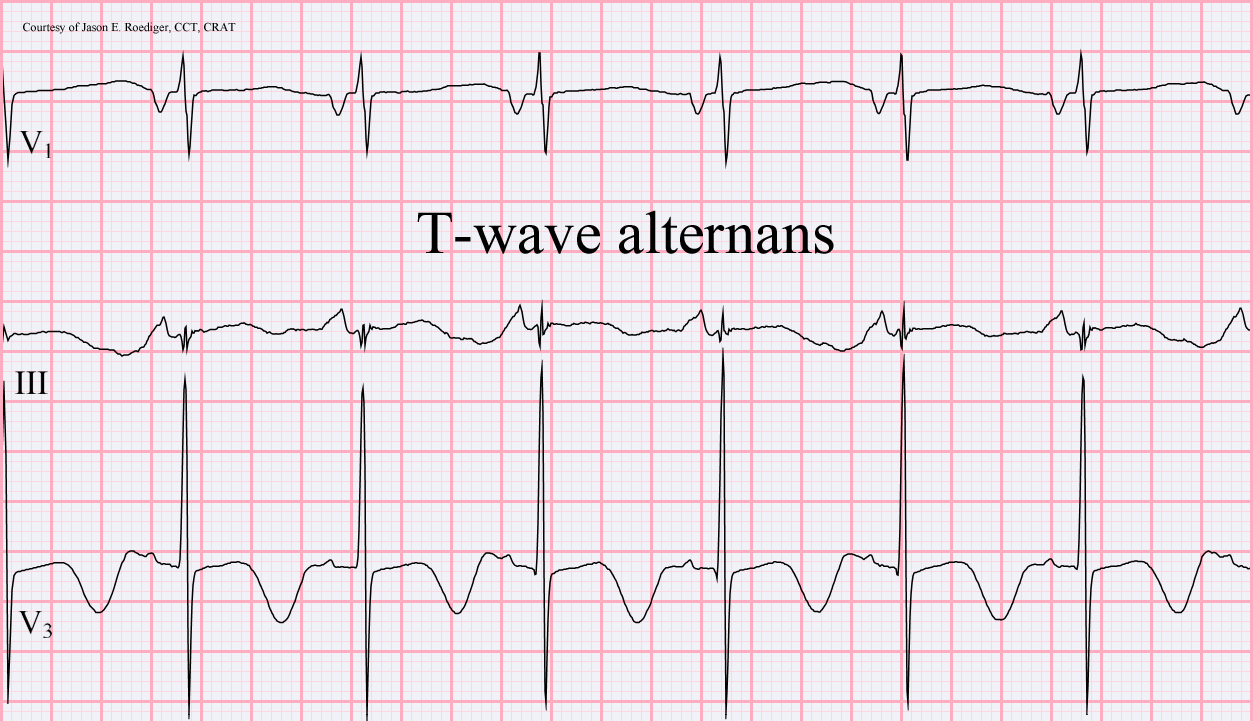
In cardiology, T wave alternans (TWA) is a periodic beat-to-beat variation in the amplitude or shape of the T wave in an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). TWA was first described in 1908. At that time, only large variations ("macroscopic" TWA) could be detected. Those large TWAs were associated with increased susceptibility to lethal ventricular tachycardias. Most modern references to TWA refer to microvolt T wave alternans (MTWA), a non-invasive heart test that can identify patients who are at increased risk of sudden cardiac death. It is most often used in patients who have had myocardial infarctions (heart attacks) or other heart damage to see if they are at high risk of developing a potentially lethal cardiac arrhythmia. Those who are found to be at high risk would therefore benefit from the placement of a defibrillator device which can stop an arrhythmia and save the patient's life. The TWA test uses an ECG measurement of the heart's electrical conduction using electrodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-wave Alternans
{{disambig ...
The term T-wave may refer to: * T wave, a portion of the recording of a heartbeat in an electrocardiogram * Terahertz radiation, electromagnetic radiation in the microwave band * T wave (seismic), a form of seismic wave A seismic wave is a mechanical wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth or another planetary body. It can result from an earthquake (or generally, a quake), volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide and a large ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defibrillator
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). Defibrillation delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''counter-shock'') to the heart. Although not fully understood, this process depolarizes a large amount of the heart muscle, ending the arrhythmia. Subsequently, the body's natural pacemaker in the sinoatrial node of the heart is able to re-establish normal sinus rhythm. A heart which is in asystole (flatline) cannot be restarted by defibrillation; it would be treated only by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and medication, and then by cardioversion or defibrillation if it converts into a shockable rhythm. A device that administers defibrillation is called a defibrillator. In contrast to defibrillation, synchronized electrical cardioversion is an electrical shock delivered in synchrony to the cardiac cycle. Although the person may still b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania state border. Cleveland is the most populous city on Lake Erie, the second-most populous city in Ohio, and the 53rd-most populous city in the U.S. with a population of 372,624 in 2020. The city anchors the Cleveland metropolitan area, the 33rd-largest in the U.S. at 2.18 million residents, as well as the larger Cleveland– Akron– Canton combined statistical area with 3.63 million residents. Cleveland was founded in 1796 near the mouth of the Cuyahoga River as part of the Connecticut Western Reserve in modern-day Northeast Ohio by General Moses Cleaveland, after whom the city was named. The city's location on the river and the lake shore allowed it to grow into a major commercial and industrial metropolis by the late 19th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn Research Center
NASA John H. Glenn Research Center at Lewis Field is a NASA center within the cities of Brook Park, Ohio, Brook Park and Cleveland between Cleveland Hopkins International Airport and the Rocky River Reservation of Cleveland Metroparks, with a subsidiary facility in Sandusky, Ohio. Its director is James A. Kenyon. Glenn Research Center is one of ten major NASA facilities, whose primary mission is to develop science and technology for use in aeronautics and space. , it employed about 1,650 civil servants and 1,850 support contractors on or near its site. In 2010, the formerly on-site NASA Visitors Center moved to the Great Lakes Science Center in the North Coast Harbor area of downtown Cleveland. History The installation was established in 1942 as part of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) and was later incorporated into the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as a laboratory for aircraft engine research. It was first named the Aircraft Engine Rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude and semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves or triangle waves, ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value ( DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximum ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector (geometric)
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Euclidean vectors can be added and scaled to form a vector space. A '' vector quantity'' is a vector-valued physical quantity, including units of measurement and possibly a support, formulated as a '' directed line segment''. A vector is frequently depicted graphically as an arrow connecting an ''initial point'' ''A'' with a ''terminal point'' ''B'', and denoted by \stackrel \longrightarrow. A vector is what is needed to "carry" the point ''A'' to the point ''B''; the Latin word means 'carrier'. It was first used by 18th century astronomers investigating planetary revolution around the Sun. The magnitude of the vector is the distance between the two points, and the direction refers to the direction of displacement from ''A'' to ''B''. Many algebraic operations on real numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repolarization
In neuroscience, repolarization refers to the change in membrane potential that returns it to a negative value just after the depolarization phase of an action potential which has changed the membrane potential to a positive value. The repolarization phase usually returns the membrane potential back to the resting membrane potential. The efflux of potassium (K+) ions results in the falling phase of an action potential. The ions pass through the selectivity filter of the K+ channel pore. Repolarization typically results from the movement of positively charged K+ ions out of the cell. The repolarization phase of an action potential initially results in hyperpolarization, attainment of a membrane potential, termed the afterhyperpolarization, that is more negative than the resting potential. Repolarization usually takes several milliseconds. Repolarization is a stage of an action potential in which the cell experiences a decrease of voltage due to the efflux of potassium (K+) io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Arrhythmia
Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. Essentially, this is anything but normal sinus rhythm. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death. Arrhythmias are often categorized into four groups: extra beats, supraventricular tachycardias, ventricular arrhythmias and bradyarrhythmias. Extra beats incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiology
Cardiology () is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a sub-specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery. Specializations All cardiologists in the branch of medicine study the disorders of the heart, but the study of adult and child heart disorders each require different training pathways. Therefore, an adult cardiologist (often simply called "cardiologist") is inadequately trained to take care of children, and pediatric cardiologists are not trained to treat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudden Cardiac Death
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest ''SCA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly circulate around the body and the blood flow to the brain and other organs is decreased. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to lose consciousness and brain cells can start to die due to lack of oxygen. Coma and persistent vegetative state may result from cardiac arrest. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of central pulses and abnormal or absent breathing. Cardiac arrest and resultant hemodynamic collapse often occur due to arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms). Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia are most commonly recorded. However, as many incidents of cardiac arrest occur out-of-hospital or when a person is not having their cardiac activity monitored, it is difficult to identify the specific mechanism in each case. Structural heart disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |