|
Synodic Month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Variations In Shona, Middle Eastern, and European traditions, the month starts when the young crescent moon first becomes visible, at evening, after conjunction with the Sun one or two days before that evening (e.g., in the Islamic calendar). In ancient Egypt, the lunar month began on the day when the waning moon could no longer be seen just before sunrise. Others run from full moon to full moon. Yet others use calculation, of varying degrees of sophistication, for example, the Hebrew calendar or the ecclesiastical lunar calendar. Calendars count integer days, so months may be 29 or 30 days in length, in some regular or irregular sequence. Lunar cycles are prominent, and calculated with great precision, in the ancient Hindu Panchangam calendar, widely used in the Indian subco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases ( synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based only directly on the solar year. The most commonly used calendar, the Gregorian calendar, is a solar calendar system that originally evolved out of a lunar calendar system. A purely lunar calendar is also distinguished from a lunisolar calendar, whose lunar months are brought into alignment with the solar year through some process of intercalation. The details of when months begin vary from calendar to calendar, with some using new, full, or crescent moons and others employing detailed calculations. Since each lunation is approximately days, (which gives a mean synodic month as 29.53059 days or 29 days 12 hours 44 minutes and 3 seconds) it is common for the months of a lunar calendar to alternate between 29 and 30 days. Since the period of 12 such lunations, a lunar year, is 354 days, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar Month
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record (often paper) of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills. Periods in a calendar (such as years and months) are usually, though not necessarily, synchronized with the cycle of the sun or the moon. The most common type of pre-modern calendar was the lunisolar calendar, a lunar calendar that occasionally adds one intercalary month to remain synchronized with the solar year over the long term. Etymology The term ''calendar'' is taken from , the term for the first day of the month in the Roman calendar, related to the verb 'to call out', referring to the "calling" of the new moon when it was first s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years differently so as to make the average calendar year 365.2425 days long, more closely approximating the 365.2422-day 'tropical' or 'solar' year that is determined by the Earth's revolution around the Sun. The rule for leap years is: There were two reasons to establish the Gregorian calendar. First, the Julian calendar assumed incorrectly that the average solar year is exactly 365.25 days long, an overestimate of a little under one day per century, and thus has a leap year every four years without exception. The Gregorian reform shortened the average (calendar) year by 0.0075 days to stop the drift of the calendar with respect to the equinoxes.See Wikisource English translation of the (Latin) 1582 papal bull '' Inter gravissimas''. Second, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Station
Often called lunar mansion, a lunar station or lunar house is a segment of the ecliptic through which the Moon passes in its orbit around the Earth. The concept was used by several ancient cultures as part of their calendrical system. Stations in different cultures In general, though not always, the zodiac is divided into 27 or 28 segments relative to the vernal equinox point or the fixed stars – one for each day of the lunar month. (A sidereal month lasts about days.) The Moon's position is charted with respect to those fixed segments. Since the Moon's position at any given stage will vary according to Earth's position in its own orbit, lunar stations are an effective system for keeping track of the passage of seasons. Various cultures have used sets of lunar stations astrologically; for example, the Jyotisha astrological '' nakshatras'' of Hindu culture, the Arabic manzils (''manazil al-qamar''), the Twenty-Eight Mansions of Chinese astronomy, and the 36&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Celestial Reference Frame
The International Celestial Reference System (ICRS) is the current standard celestial reference system adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Its origin is at the barycenter of the Solar System, with axes that are intended to "show no global rotation with respect to a set of distant extragalactic objects". This fixed reference system differs from previous reference systems, which had been based on Catalogues of Fundamental Stars that had published the positions of stars based on direct "observations of heir equatorial coordinates, right ascension and declination" and had adopted as "privileged axes ... the mean equator and the dynamical equinox" at a particular date and time. The International Celestial Reference Frame (ICRF) is a realization of the International Celestial Reference System using reference celestial sources observed at radio wavelengths. In the context of the ICRS, a reference ''frame'' (RF) is the physical realization of a reference ''system,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Stars
In astronomy, fixed stars ( la, stellae fixae) is a term to name the full set of glowing points, astronomical objects actually and mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background, unlike the few lights visible at naked eye, including comets, which appear to move slowly between those "fixed" stars along days, weeks or months on the foreground. Generally speaking, the fixed stars comprise all visible stars other than the Sun, plus the faint strip of the Milky Way. Due to their star-like appareance when sighted at naked eye, individual nebulae and other deep-sky objects also are counted among the fixed stars, despite the fact they are not true stars. The term is actually a misnomer due to the fact that those celestial objects are not really fixed with respect to one another; this is only a perceptual illusion, as stars and other extrasolar astronomical objects are so far away from Earth that human vision is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
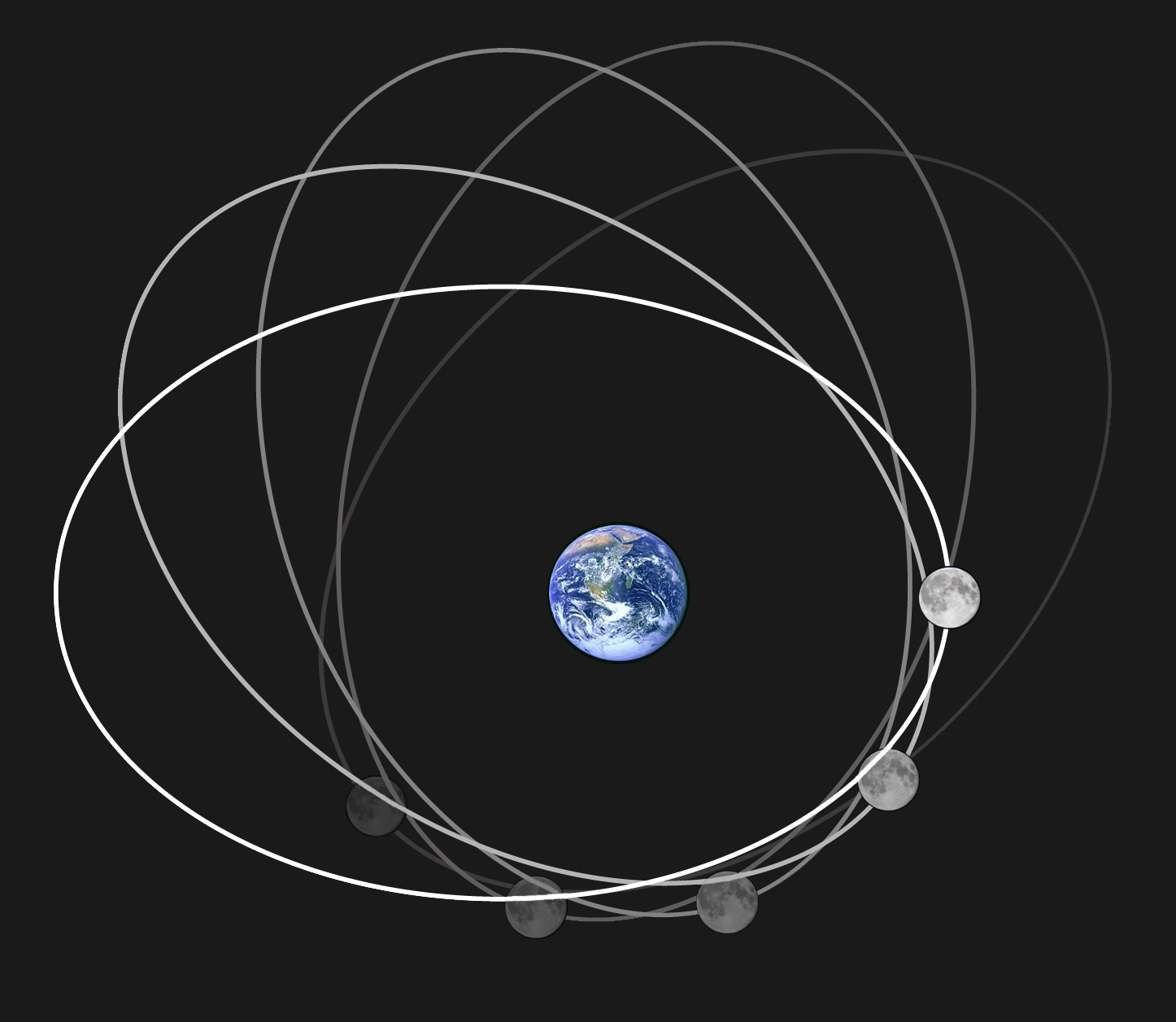
Orbit Of The Moon
The Moon orbits Earth in the prograde direction and completes one revolution relative to the Vernal Equinox and the stars in about 27.32 days (a tropical month and sidereal month) and one revolution relative to the Sun in about 29.53 days (a synodic month). Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about from Earth's centre (about 73% of its radius), forming a satellite system called the Earth–Moon system. On average, the distance to the Moon is about from Earth's centre, which corresponds to about 60 Earth radii or 1.282 light-seconds. With a mean orbital velocity of 1.022 km/s (0.635 miles/s, 2,286 miles/h), the Moon covers a distance approximately its diameter, or about half a degree on the celestial sphere, each hour. The Moon differs from most satellites of other planets in that its orbit is close to the ecliptic plane instead of to its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Theory
Lunar theory attempts to account for the motions of the Moon. There are many small variations (or perturbations) in the Moon's motion, and many attempts have been made to account for them. After centuries of being problematic, lunar motion can now be modeled to a very high degree of accuracy (see section Modern developments). Lunar theory includes: * the background of general theory; including mathematical techniques used to analyze the Moon's motion and to generate formulae and algorithms for predicting its movements; and also * quantitative formulae, algorithms, and geometrical diagrams that may be used to compute the Moon's position for a given time; often by the help of tables based on the algorithms. Lunar theory has a history of over 2000 years of investigation. Its more modern developments have been used over the last three centuries for fundamental scientific and technological purposes, and are still being used in that way. Applications Applications of lunar theory have i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Phase
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the terminology of the 4 major phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, last quarter and 4 minor phases: waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. The lunar phases gradually change over a synodic month (~29.53 days) as the Moon's orbital positions around Earth and Earth around the Sun shift. The visible side of the Moon is variously sunlit, depending on the position of the Moon in its orbit. Thus, this face's sunlit portion can vary from 0% (at new moon) to 100% (at full moon). Each of the 4 major lunar phases (see below) is ~7.4 days, with +/− 19 hours in variation (6.58–8.24 days) due to the elliptical shape of the Moon's orbit. Phases of the Moon There are four ''principal'' (primary/major) lunar phases: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)

_MET_DP-13486-011.jpg)