|
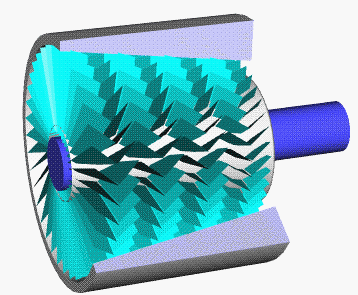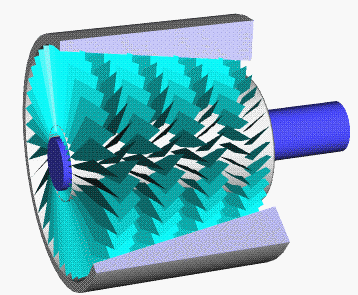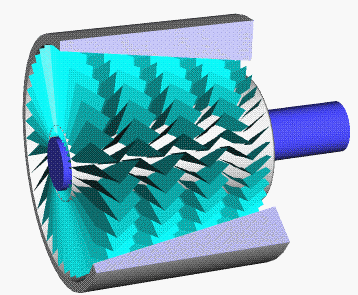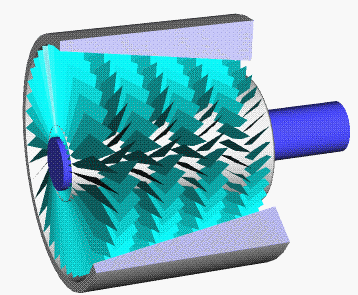
Swing-piston Engine
A swing-piston engine is a type of internal combustion engine in which the pistons move in a circular motion inside a ring-shaped "cylinder", moving closer and further from each other to provide compression and expansion. Generally two sets of pistons are used, geared to move in a fixed relationship as they rotate around the cylinder. In some versions the pistons oscillate around a fixed center, as opposed to rotating around the entire engine. The design has also been referred to as a oscillating piston engine, vibratory engine when the pistons oscillate instead of rotate, or toroidal engine based on the shape of the "cylinder". Many swing-piston engines have been proposed, but none have been successful. Two attempts in about 2010 are the prototype American-made MYT engine and prototype Russian ORE for use in the Yo-Mobile hybrid car. Both claimed high fuel efficiency and high power-to-weight ratio, but there have been no successful demonstrations of claimed efficiency or that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high- temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons ( piston engine), turbine blades ( gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle ( jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Compressor
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine. Axial flow compressors produce a continuous flow of compressed gas, and have the benefits of high efficiency and large mass flow rate, particularly in relation to their size and cross-section. They do, however, require sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrol Aircraft
A maritime patrol aircraft (MPA), also known as a patrol aircraft, maritime reconnaissance aircraft, or by the older American term patrol bomber, is a fixed-wing aircraft designed to operate for long durations over water in maritime patrol roles — in particular anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-ship warfare (AShW), and search and rescue (SAR). Among other maritime surveillance resources, such as satellites, ships, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and helicopters, the MPA is an important asset. To perform ASW operations, MPAs typically carry air-deployable sonar buoys as well as torpedoes and are usually capable of extended flight at low altitudes. History First World War The first aircraft that would now be identified as maritime patrol aircraft were flown by the Royal Naval Air Service and the French Aéronautique Maritime during the First World War, primarily on anti-submarine patrols. France, Italy and Austria-Hungary used large numbers of smaller patrol aircraft for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the First World War and Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italian Caproni Ca 30 and British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reducing industrial output. Tactical bombing is aimed at coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brayton Cycle
The Brayton cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of certain heat engines that have air or some other gas as their working fluid. The original Brayton engines used a piston compressor and piston expander, but modern gas turbine engines and airbreathing jet engines also follow the Brayton cycle. Although the cycle is usually run as an open system (and indeed must be run as such if internal combustion is used), it is conventionally assumed for the purposes of thermodynamic analysis that the exhaust gases are reused in the intake, enabling analysis as a closed system. The engine cycle is named after George Brayton (1830–1892), the American engineer who developed it originally for use in piston engines, although it was originally proposed and patented by Englishman John Barber in 1791. It is also sometimes known as the Joule cycle. The reversed Joule cycle uses an external heat source and incorporates the use of a regenerator. One type of Brayton cycle i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Fuel Consumption (shaft Engine)
Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC) is a measure of the fuel efficiency of any prime mover that burns fuel and produces rotational, or shaft power. It is typically used for comparing the efficiency of internal combustion engines with a shaft output. It is the rate of fuel consumption divided by the power produced. In traditional units, it measures fuel consumption in pounds per hour divided by the brake horsepower, lb/(hp⋅h); in SI units, this corresponds to the inverse of the units of specific energy, kg/J = s2/m2. It may also be thought of as power- specific fuel consumption, for this reason. BSFC allows the fuel efficiency of different engines to be directly compared. The term "brake" here as in " brake horsepower" refers to a historical method of measuring torque (see Prony brake). The BSFC calculation (in metric units) To calculate BSFC, use the formula : BSFC = \frac where: :'' r '' is the fuel consumption rate in grams per second (g/s) :'' P '' is the power pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Cycle
The Diesel cycle is a combustion process of a reciprocating internal combustion engine. In it, fuel is ignited by heat generated during the compression of air in the combustion chamber, into which fuel is then injected. This is in contrast to igniting the fuel-air mixture with a spark plug as in the Otto cycle (four-stroke/petrol) engine. Diesel engines are used in aircraft, automobiles, power generation, diesel–electric locomotives, and both surface ships and submarines. The Diesel cycle is assumed to have constant pressure during the initial part of the combustion phase (V_2 to V_3 in the diagram, below). This is an idealized mathematical model: real physical diesels do have an increase in pressure during this period, but it is less pronounced than in the Otto cycle. In contrast, the idealized Otto cycle of a gasoline engine approximates a constant volume process during that phase. Idealized Diesel cycle The image shows a p-V diagram for the ideal Diesel cycle; where p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Cycle
An Otto cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that describes the functioning of a typical spark ignition piston engine. It is the thermodynamic cycle most commonly found in automobile engines. The Otto cycle is a description of what happens to a gas as it is subjected to changes of pressure, temperature, volume, addition of heat, and removal of heat. The gas that is subjected to those changes is called the system. The system, in this case, is defined to be the fluid (gas) within the cylinder. By describing the changes that take place within the system, it will also describe in inverse, the system's effect on the environment. In the case of the Otto cycle, the effect will be to produce enough net work from the system so as to propel an automobile and its occupants in the environment. The Otto cycle is constructed from: :Top and bottom of the loop: a pair of quasi-parallel and isentropic processes (frictionless, adiabatic reversible). :Left and right sides of the loop: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induction that is mechanically powered (usually by a belt from the engine's crankshaft), as opposed to a turbocharger, which is powered by the kinetic energy of the exhaust gasses. However, up until the mid-20th century, a turbocharger was called a "turbosupercharger" and was considered a type of supercharger. The first supercharged engine was built in 1878, with usage in aircraft engines beginning in the 1910s and usage in car engines beginning in the 1920s. In piston engines used by aircraft, supercharging was often used to compensate for the lower air density at high altitudes. Supercharging is less commonly used in the 21st century, as manufacturers have shifted to turbochargers to reduce fuel consumption and/or increase power outputs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power-to-weight Ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power source. It is also used as a measurement of performance of a vehicle as a whole, with the engine's power output being divided by the weight (or mass) of the vehicle, to give a metric that is independent of the vehicle's size. Power-to-weight is often quoted by manufacturers at the peak value, but the actual value may vary in use and variations will affect performance. The inverse of power-to-weight, weight-to-power ratio (power loading) is a calculation commonly applied to aircraft, cars, and vehicles in general, to enable the comparison of one vehicle's performance to another. Power-to-weight ratio is equal to thrust per unit mass multiplied by the velocity of any vehicle. Power-to-weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysler IV-2220
The Chrysler XIV-2220 (XI-2220 from 1944) was an experimental 2,500 hp, 2,220 cubic inch (36.4 liter) liquid-cooled inverted- V-16 aircraft engine designed by Chrysler starting in 1940. Although several aircraft designs had considered using it, by the time it was ready for use in 1945 the war was already over. Only a few engines were built during the program, and it retained its 'X' designation the entire time as the XIV-2220, later XI-2220. The IV-2220 is historically important as it was Chrysler's first hemi, a design that would re-appear for many years later and is now a Chrysler trademark. Design and development Original design Chrysler had apparently been carrying out paper studies of a very large engine for a brief period starting in May 1940 and decided to present their work to the United States Army Air Corps. They proposed a large engine to provide 2,500 hp initially, with room for growth upwards. Instead of using advanced features such as sleeve valves for i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight Engine
The straight or inline engine is an internal combustion engine with all cylinders aligned in one row and having no offset. Usually found in four, six and eight cylinder configurations, they have been used in automobiles, locomotives and aircraft, although the term in-line has a broader meaning when applied to aircraft engines, see Inline engine (aviation). Design A straight engine is considerably easier to build than an otherwise equivalent horizontally opposed or V engine, because both the cylinder bank and crankshaft can be milled from a single metal casting, and it requires fewer cylinder heads and camshafts. In-line engines are also smaller in overall physical dimensions than designs such as the radial, and can be mounted in any direction. Straight configurations are simpler than their V-shaped counterparts. Although six-cylinder engines are inherently balanced, the four-cylinder models are inherently off balance and rough, unlike 90-degree V fours and horizontally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
.jpg)

