|
Superstes
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs. Classification and anatomy The group was first defined by Zittel (1888) on the recognition of the distinctive vertebral anatomy of the best known stereospondyls of the time, such as ''Mastodonsaurus'' and ''Metoposaurus''. The term 'stereospondylous' as a descriptor of vertebral anatomy was coined the following year by Fraas, referring to a vertebral position consisting largely or entirely of the intercentrum in addition to the neural arch. While the name 'Stereospondyli' is derived from the stereospondylous vertebral condition, there is a diversity of vertebral morphologies among stereospondyls, including the diplospondylous (' tupilakosaurid') co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderops
''Siderops'' is an extinct genus of chigutisaurid temnospondyl from Early Jurassic of Australia, containing the species ''S. kehli''. It is solely known from the holotype specimen, which consists of a nearly complete skull with mandible and postcrania were found within the Westgrove Ironstone Member of the Evergreen Formation of the Surat Basin in Queensland. dating to the late Toarcian at approximately 176.6 ma. ''Siderops'' was large, with a skull The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ... width wide and a total length of . References Jurassic temnospondyls Prehistoric amphibians of Australia Chigutisaurids Fossil taxa described in 1983 Early Jurassic amphibians {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metoposaurus
''Metoposaurus'' meaning "front lizard" is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl amphibian, known from the Late Triassic of Germany, Italy, Poland, and Portugal. https://www.app.pan.pl/archive/published/app47/app47-535.pdf This mostly aquatic animal possessed small, weak limbs, sharp teeth, and a large, flat head. This highly flattened creature mainly fed on fish, which it captured with its wide jaws lined with needle-like teeth. ''Metoposaurus'' was up to 3 m (10 feet) long and weighed about 450 kg (1,000 pounds). Many ''Metoposaurus'' mass graves have been found, probably from creatures that grouped together in drying pools during drought. Discovery and species Discovery The earliest mention of Metoposauridae dates back to 1842 when Von Meyer described the dorsal view of the skull roof of a labyrinthodont from the Keuper Schilfsandstein of Feuerbacher Haide near Stuttgart. Later, Meyer attempted a reconstruction of the same specimen and named it ''Metopias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhytidosteidae
Rhytidosteidae is a family of Temnospondyli that lived in the Permian and Triassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ... from Dias-da-Silva and Marsicano (2011): References *Yates, AM (2000), A new tiny rhytidosteid (Temnospondyli: Stereospondyi) from the Early Triassic of Australia and the possibility of hidden temnospondyl diversity. J. Vert Paleontol. 20:484-489. External linksRhytidosteidae at Palaeos. Stereospondyls Permian temnospondyls Triassic temnospondyls Amphibian families Lopingian first appearances Early Triassic extinctions {{Temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachana Nigra
''Arachana'' is an extinct genus of rhinesuchid-like temnospondyl known from the Early Triassic Buena Vista Formation of northeastern Uruguay. ''Arachana'' was first named by Graciela Piñeiro, Alejandro Ramos and Claudia Marsicano in 2012 and the type species is ''A. nigra''. It shares characteristics with both rhinesuchids and lydekkerinids, making it a transitional form between basal and more advanced stereospondyls. Description ''Arachana'' is known from the holotype FC-DPV 1369, a three-dimensionally preserved nearly complete skull that has not been distorted. It was collected in the Colonia Orozco locality from the Buena Vista Formation of the Norte Basin. The formation spans the boundary between the Permian and the Triassic, and it is uncertain whether FC-DPV 1369 was found in rocks above or below the boundary. ''Arachana'' shares several characters with rhinesuchids. For example, it has a large head with orbits or eye sockets placed slightly behind the mid-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
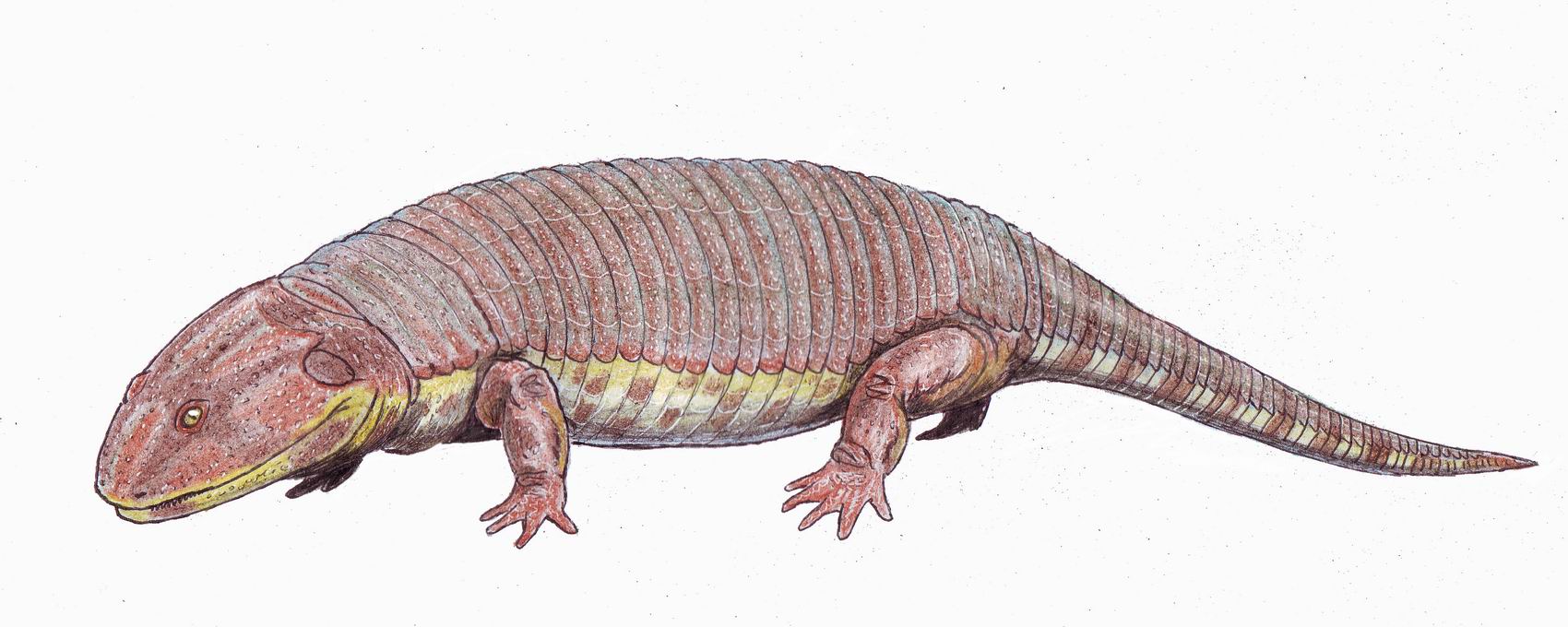
Peltobatrachus Pustulatus
''Peltobatrachus'' (from Greek ''pelte'', meaning shield and batrakhos, meaning frog) is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the late Permian period of Tanzania. The sole species, ''Peltobatrachus pustulatus'', is also the sole member of the family Peltobatrachidae. Description ''Peltobatrachus'' was a large, slow moving animal, up to in length. It was a fully terrestrial amphibian, only returning to the water to lay its eggs. To protect itself against predators such as the large gorgonopsid therapsids, it had developed an armadillo-like armored plating covering its body and tail. The armor consisted of broad plates on the shoulders and hips and narrower plates on the rest of the body. Although no teeth of the creature have been found, it probably fed on insects, worms, and snail A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospondylomorpha
Stereospondylomorpha is a clade of temnospondyls. It includes the superfamily Archegosauroidea and the more diverse group Stereospondyli. Stereospondylomorpha was first proposed by Yates and Warren (2000), who found Archegosauroidea and Stereospondyli to be sister taxa in their phylogenetic analysis. A similar clade is Archegosauriformes, named by Schoch and Milner (2000), which includes Stereospondyli and some Permian temnospondyls that are similar in appearance to stereospondyls, including the archegosauroids. However, according to Schoch and Milner's phylogeny, Archegosauroidea is a paraphyletic group of taxa that are successively basal to Stereospondyli, rather than a monophyletic sister taxon. ''Chinlestegophis'', a putative Triassic stereospondyl considered to be related to metoposauroids such as ''Rileymillerus'', has been noted to share many features with caecilian Caecilians (; ) are a group of limbless, vermiform or serpentine amphibians. They mostly live hidden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; and to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini. It also completely enclaves the country Lesotho. It is the southernmost country on the mainland of the Old World, and the second-most populous country located entirely south of the equator, after Tanzania. South Africa is a biodiversity hotspot, with unique biomes, plant and animal life. With over 60 million people, the country is the world's 24th-most populous nation and covers an area of . South Africa has three capital cities, with the executive, judicial and legislative branches of government based in Pretoria, Bloemfontein, and Cape Town respectively. The largest city is Johannesburg. About 80% of the population are Black South Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broomistega Putterilli
''Broomistega'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian in the family Rhinesuchidae. It is known from one species, ''Broomistega putterilli'', which was renamed in 2000 from ''Lydekkerina putterilli'' Broom 1930. Fossils are known from the Early Triassic ''Lystrosaurus'' Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin of present-day South Africa, a region that had been an enclave of Gondwana. Specimens of ''B. putterilli'' were once thought to represent young individuals of another larger rhinesuchid such as ''Uranocentrodon'', but the species is now regarded as a paedomorphic taxon, possessing the features of juvenile rhinesuchids into adulthood. In 2013, a well-preserved skeleton of ''Broomistega'' was discovered alongside the skeleton of the cynodont ''Thrinaxodon'' (a mammal relative) in a cast of a burrow. The individual probably entered the burrow while the cynodont was in a state of aestivation (dormancy), and afterwards a flash flood filled the burrow wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Permian
Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, a concept in econometrics Music * Late (album), ''Late'' (album), a 2000 album by The 77s * Late!, a pseudonym used by Dave Grohl on his ''Pocketwatch (album), Pocketwatch'' album * Late (rapper), an underground rapper from Wolverhampton * Late (song), "Late" (song), a song by Blue Angel * "Late", a song by Kanye West from ''Late Registration'' Other * Late (Tonga), an uninhabited volcanic island southwest of Vavau in the kingdom of Tonga * Late (The Handmaid's Tale), "Late" (''The Handmaid's Tale''), a television episode * LaTe, Laivateollisuus, Oy Laivateollisuus Ab, a defunct shipbuilding company * Late may refer to a person who is Dead See also * * * ''Lates'', a genus of fish in the lates perch family * Later (other) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |