|
Special Somatic Afferent Fiber
Special somatic afferent fibers (SSA) are the afferent nerve fibers that carry information from the special senses of vision, hearing and balance. The cranial nerves containing SSA fibers are the optic nerve (II) and the vestibulocochlear nerve The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the bra ... (VIII). The term "SSA" also encompasses both special somatic and special visceral afferent fibers.Drake et al. (2010), Gray's Anatomy for Students, 2nd Ed., Churchill Livingstone. References External links Overview at mmi.mcgill.ca Neuroanatomy {{Neuroanatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afferent Nerve Fiber
Afferent nerve fibers are the axons (nerve fibers) carried by a sensory nerve that relay sensory information from sensory receptors to regions of the brain. Afferent projections ''arrive'' at a particular brain region. Efferent nerve fibers are carried by efferent nerves and ''exit'' a region to act on muscles and glands. In the peripheral nervous system afferent and efferent nerve fibers are part of the somatic nervous system and arise from outside of the spinal cord. Sensory nerves carry the afferent fibers to enter into the spinal cord, and motor nerves carry the efferent fibers out of the spinal cord to act on skeletal muscles. In the central nervous system non-motor efferents are carried in efferent nerves to act on glands. Structure Afferent neurons are pseudounipolar neurons that have a single process leaving the cell body dividing into two branches: the long one towards the sensory organ, and the short one toward the central nervous system (e.g. spinal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Senses
In medicine and anatomy, the special senses are the senses that have specialized organs devoted to them: * vision (the eye) * hearing and balance (the ear, which includes the auditory system and vestibular system) * smell (the nose) * taste (the tongue) The distinction between special and general senses is used to classify nerve fibers running to and from the central nervous system – information from special senses is carried in special somatic afferents and special visceral afferents. In contrast, the other sense, touch, is a somatic sense which does not have a specialized organ but comes from all over the body, most noticeably the skin but also the internal organs ( viscera). Touch includes mechanoreception (pressure, vibration and proprioception), pain ( nociception) and heat ( thermoception), and such information is carried in general somatic afferents and general visceral afferents. Vision Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual System
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and more. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
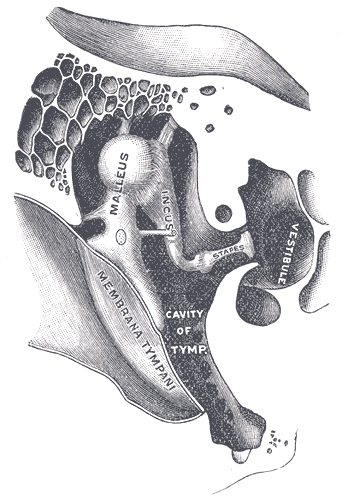
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equilibrioception
The sense of balance or equilibrioception is the perception of balance and spatial orientation. It helps prevent humans and nonhuman animals from falling over when standing or moving. Equilibrioception is the result of a number of sensory systems working together; the eyes (visual system), the inner ears (vestibular system), and the body's sense of where it is in space (proprioception) ideally need to be intact. The vestibular system, the region of the inner ear where three semicircular canals converge, works with the visual system to keep objects in focus when the head is moving. This is called the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The balance system works with the visual and skeletal systems (the muscles and joints and their sensors) to maintain orientation or balance. Visual signals sent to the brain about the body's position in relation to its surroundings are processed by the brain and compared to information from the vestibular and skeletal systems. Vestibular system In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge from the cerebrum, and the remaining ten pairs arise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optic Nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus. Structure The optic nerve has been classified as the second of twelve paired cranial nerves, but it is technically part of the central nervous system, rather than the peripheral nervous system because it is derived from an out-pouching of the diencephalon ( optic stalks) during embryonic development. As a consequence, the fibers of the optic nerve are covered with myelin produced by oligodendrocytes, rather than Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea. Structure The vestibulocochlear nerve consists mostly of bipolar neurons and splits into two large divisions: the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve. Cranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem). This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle. The vestibulocochlear ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Visceral Afferent Fibers
A Special visceral afferent fibers (SVA) is a afferent fiber that develop in association with the gastrointestinal tract. They carry the special senses of smell ( olfaction) and taste (gustation). The cranial nerves containing SVA fibers are the olfactory nerve (I), the facial nerve (VII), the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), and the vagus nerve (X). The facial nerve receives taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste ...; the glossopharyngeal from the posterior 1/3, and the vagus nerve from the epiglottis. The sensory processes, using their primary cell bodies from the inferior ganglion, send projections to the medulla, from which they travel in the tractus solitarius, later terminating at the rostral nucleus solitarius.Bhatnagar C. Subhash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |