|
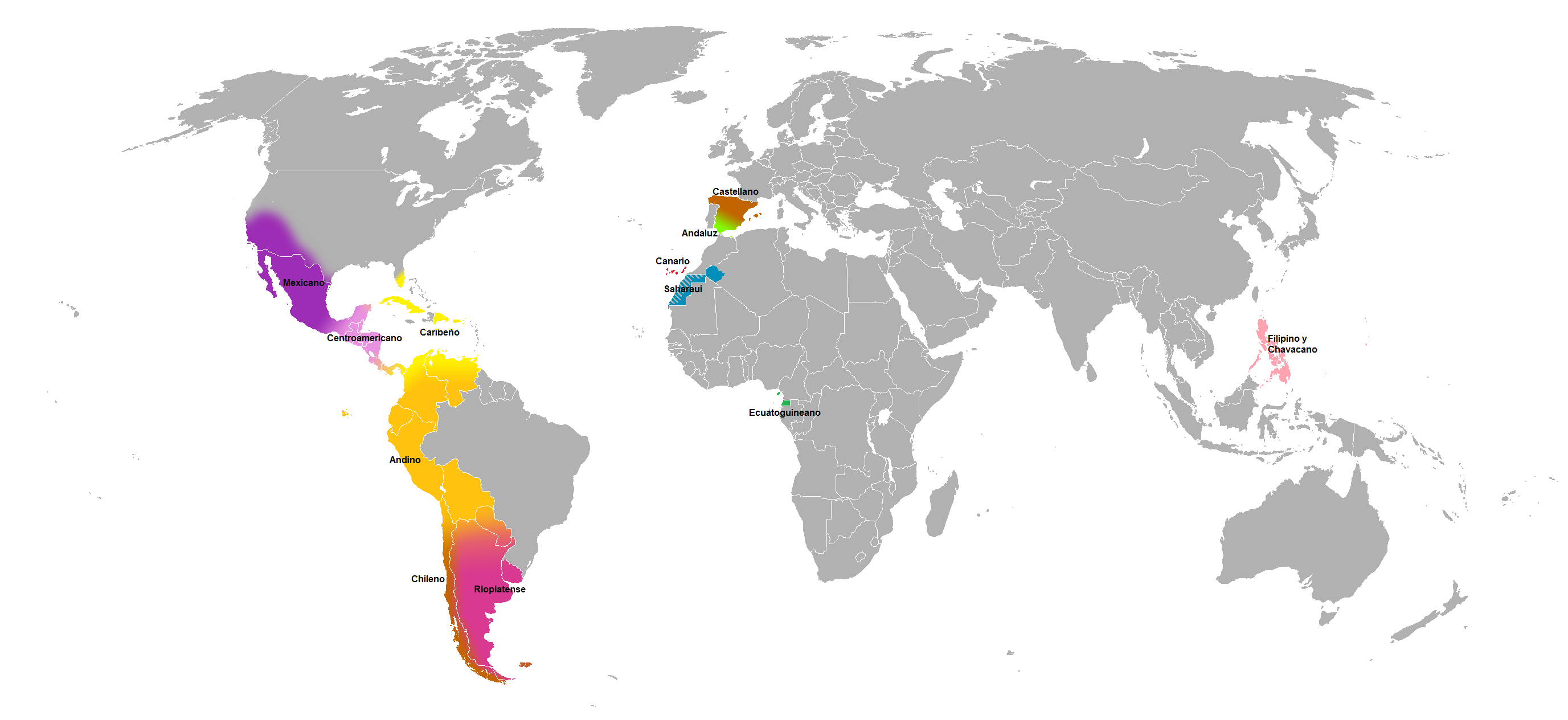
Spanish Language In South America
The Spanish language in South America varies within the different countries and regions of the continent. The term "South American Spanish" (Spanish language, Spanish: ''español sudamericano'' or ''español suramericano'') is sometimes used as a broad name for the dialects of Spanish spoken on the continent, but such a term is only ''geographical'' and has little or no ''linguistic'' relevance. Spanish is the most widely spoken language of the South American continent, followed closely by Portuguese. The diverse Spanish dialects of the continent have no unifying feature to set them apart from non-South American varieties. The Spanish of the Andean Spanish, Andean highlands is historically conservative, having some traits in common with the Spanish of central Mexican Spanish, Mexico, while varieties spoken in Rioplatense Spanish, Argentina and Venezuelan Spanish, Venezuela share some phonological innovations with the Spanish spoken on Caribbean Spanish, Caribbean islands. In some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries. It is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in Iberia after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. The oldest Latin texts with traces of Spanish come from mid-northern Iberia in the 9th century, and the first systematic written use of the language happened in Toledo, a prominent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish (), also known as Rioplatense Castilian, is a variety of Spanish spoken mainly in and around the Río de la Plata Basin of Argentina and Uruguay. It is also referred to as River Plate Spanish or Argentine Spanish. It is the most prominent dialect to employ ''voseo'' in both speech and writing. Many features of Rioplatense are also shared with the varieties spoken in south and eastern Bolivia, and Paraguay. This dialect is often spoken with an intonation resembling that of the Neapolitan language of Southern Italy, but there are exceptions. As Rioplatense is considered a dialect of Spanish and not a distinct language, there are no credible figures for a total number of speakers. The total population of these areas would amount to some 25–30 million, depending on the definition and expanse. Location Rioplatense is mainly based in the cities of Buenos Aires, Rosario, Santa Fe, La Plata, Mar del Plata and Bahía Blanca in Argentina, the most populated citie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Coast Spanish
Peruvians ( es, peruanos) are the citizens of Peru. There were Andean and coastal ancient civilizations like Caral, which inhabited what is now Peruvian territory for several millennia before the Spanish conquest in the 16th century; Peruvian population decreased from an estimated 5–9 million in the 1520s to around 600,000 in 1620 mainly because of infectious diseases carried by the Spanish. Spaniards and Africans arrived in large numbers in 1532 under colonial rule, mixing widely with each other and with Native Peruvians. During the Republic, there has been a gradual immigration of European people (especially from Spain and Italy, and in a less extent from Germany, France, Croatia, and the British Isles). Chinese and Japanese arrived in large numbers at the end of the 19th century. With 31.2 million inhabitants according to the 2017 Census, Peru is the fifth most populous country in South America. Its demographic growth rate declined from 2.6% to 1.6% between 1950 and 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Spanish
Peruvian Spanish is a family of dialects of the Spanish language that have been spoken in Peru since brought over by Spanish conquistadors in 1492. There are four varieties spoken in the country, by about 94.4% of the population. The four Peruvian dialects are Andean Spanish, Peruvian Coastal Spanish, Andean-Coastal Spanish, and Amazonic Spanish. History The Spanish language first arrived in Peru in 1532. During colonial and early republican times, the Spanish spoken colloquially in the coast and in the cities of the highland possessed strong local features, but as a result of dialect leveling in favor of the standard language, the language of urban Peruvians today is more or less uniform in pronunciation throughout most of the country. Vestiges of the older dialect of the coast can be found in the speech of black Peruvians, which retains Andalusian features such as the aspiration or deletion of final /s/ and the deletion of final /r/. The dialect of Arequipa, Loncco, in it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraguayan Spanish
Paraguayan Spanish ( es, español paraguayo) is the set of dialects of the Spanish language spoken in Paraguay. In addition, it influences the speech of the Argentine provinces of Misiones, Corrientes, Formosa, and, to a lesser extent, Chaco. Paraguayan Spanish possesses marked characteristics of Spanish previously spoken in northern Spain, because the majority of the first settlers were from Old Castile and the Basque Country. The Guarani language is co-official with Spanish in Paraguay,Simon Romero"An Indigenous Language With Unique Staying Power" ''The New York Times'', March 12, 2012 and most Paraguayans speak both languages. Guaraní is the home language of more than half the population of Paraguay, with higher proportions of its use in rural areas, and those who speak Spanish at home slightly in the majority in the cities. In addition to the strong influence of Guarani, Paraguayan Spanish is also influenced by River Plate Spanish due to the geographical, historical, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian Spanish
Spanish is the most-widely spoken language in Ecuador, though great variations are present depending on several factors, the most important one being the geographical region where it is spoken. The three main regional variants are: * Equatorial Pacific Spanish or Equatorial Coastal Spanish * Andean Spanish * Amazonic Spanish Additionally to the characteristics described below, Ecuadorian Spanish shares many characteristics that are widespread in Spanish in the Americas. Other sociolinguistic factors that influence in the way of speaking are the ethnic or social class of the speaker, and whether the speaker lives in an urban or rural area. Since the Coast and the Highlands are the most populous areas, these are the country's most widely used dialects, despite being quite different from each other. For instance, there are many idioms specific to each region or province, and others that are used and understood nationwide. Pacific Coast This Spanish variant is classified wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilote Spanish
Chilote is a dialect of Spanish language spoken on the southern Chilean islands of Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé or simply, ''Chiloé''). It has distinct differences from standard Chilean Spanish in accent, pronunciation, grammar and vocabulary, especially by influences from local dialect of Mapuche language (called ''huilliche'' or ''veliche'') and some conservative traits. After the battle of Curalaba (1598) and the Destruction of the Seven Cities Chiloé was further isolated from the rest of Chile and developed a culture with little influence from Spain or mainland Chile. During the 17th and 18th centuries most of the archipelago's population was bilingual and according to John Byron many Spaniards preferred to use Mapudungun because they considered it more beautiful. Around the same time, Governor Narciso de Santa María complained that Spanish settlers in the islands could not speak Spanish properly, but could speak Veliche, and that this second lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Spanish
Chilean Spanish ( es, español chileno) is any of several varieties of the Spanish language spoken in most of Chile. Chilean Spanish dialects have distinctive pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and slang usages that differ from those of Standard Spanish. Formal Spanish in Chile has recently incorporated an increasing number of colloquial elements. The Royal Spanish Academy recognizes 2,214 words and idioms exclusively or mainly produced in Chilean Spanish, in addition to many still unrecognized slang expressions. Alongside Honduran Spanish, Chilean Spanish has been identified by various linguists as one of the two most divergent varieties. Variation and accents In Chile, there are not many differences between the Spanish spoken in the northern, central and southern areas of the country, although there are notable differences in zones of the far south—such as Aysén, Magallanes (mainly along the border with Argentina), and Chiloé—and in Arica in the extreme north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivian Spanish
Bolivian Spanish (or Castilian) is the variety of Spanish spoken by the majority of the population in Bolivia, either as a mother tongue or as a second language. Within the Spanish of Bolivia there are different regional varieties. In the border areas, Bolivia shares dialectal features with the neighboring countries. Throughout Bolivia the preservation of phonemic contrast between and the lateral (i.e. the absence of yeísmo) is the norm.Lipski 1994:188 Aspiration of syllable-final is frequent in the lowlands, while in the highlands the sibilant tends to be preserved, realized either as a laminal or, frequently, an apical .Canfield 1981:29 In highland dialects, the "trill" phoneme (orthographic or word-initial ) is often assibilated, realized as a voiced apicoalveolar fricative, or alveolar approximant, which pronunciation is similar to the sound of () in English. In highland Bolivian Spanish there is "intense reduction" of unstressed vowels in contact with , often resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuyo Spanish
Cuyo Spanish or Cuyano Spanish (Castellano Cuyano) is the dialect of Spanish that evolved in the historical province of Cuyo and that is now spoken in the Argentine provinces of Mendoza and San Juan. To a lesser extent it is also spoken in the provinces of San Luis and La Rioja. Cuyo Spanish shares a series of common traits with Chilean Spanish due to settlement history and commercial ties. Later on, under the Argentine Republic Rioplatense Spanish, the dialect of Buenos Aires and Uruguay Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ... influenced Cuyo Spanish. References Spanish dialects of South America Languages of Argentina Spanish Argentine {{Argentina-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast. It is part of the Southern Cone region of South America. Uruguay covers an area of approximately and has a population of an estimated 3.4 million, of whom around 2 million live in the metropolitan area of its capital and largest city, Montevideo. The area that became Uruguay was first inhabited by groups of hunter–gatherers 13,000 years ago. The predominant tribe at the moment of the arrival of Europeans was the Charrúa people, when the Portuguese first established Colónia do Sacramento in 1680; Uruguay was colonized by Europeans late relative to neighboring countries. The Spanish founded Montevideo as a military stronghold in the early 18th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean Spanish
Andean Spanish is a dialect of Spanish spoken in the central Andes, from southern Colombia, with influence as far south as northern Chile and Northwestern Argentina, passing through Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. It is influenced principally by Castilian, Canarian and Andalusian Spanish, which is favoured in the cities, but in rural areas and some cities, there is influence of Quechua, Aymara, and other indigenous languages. Phonology * In Andean Spanish, the is never aspirated in the final position and so is pronounced , not , but it is sometimes pronounced apical, rather than laminal, a trait characteristic of Northern Spain. The apical sound is sometimes perceived as transitional between and , and it is associated with a large number of northern Spanish settlers in Andean region. In southern Bolivia and northern Chile, syllable-final /s/ is mostly aspirated. * As in all American dialects of Spanish, Andean Spanish has ( is not distinguished from ). Thus, ("house") and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)