|
Siege Of Motya
The siege of Motya took place either in 398 or 397 BC in western Sicily. Dionysius, after securing peace with Carthage in 405 BC, had steadily increased his military power and had tightened his grip on Syracuse. He had fortified Syracuse against sieges and had created a large army of mercenaries and a large fleet, in addition to employing the catapult and quinqueremes for the first time in history. In 398 BC, he attacked and sacked the Phoenician city of Motya despite the Carthaginian relief effort led by Himilco. Carthage also lost most of her territorial gains secured in 405 BC after Dionysius declared war on Carthage in 398 BC. Background Carthage had stayed away from Sicilian affairs for 70 years after the defeat at Himera in 480 BC. However, Carthage, responding to the appeal for aid of Segesta against Selinus, had sent an expedition to Sicily, resulting in the sacking of Selinus and Himera in 409 BC under the leadership of Hannibal Mago. Responding to Greek raids on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Sicilian War
The Sicilian Wars, or Greco-Punic Wars, were a series of conflicts fought between ancient Carthage and the List of ancient Greek cities, Greek city-states led by Syracuse, Sicily over control of Sicily and the western Mediterranean between 580 and 265 BC. Carthage's economic success and its dependence on seaborne trade led to the creation of a powerful navy to discourage both pirates and rival nations. They had inherited their naval strength and experience from their forebears, the Phoenicians, but had increased it because, unlike the Phoenicians, the Punics did not want to rely on a foreign nation's aid. This, coupled with its success and growing hegemony, brought Carthage into increasing conflict with the Greeks, the other major power contending for control of the central Mediterranean. The Greeks, like the Phoenicians, were expert sailors who had established thriving colonies throughout the Mediterranean. These two rivals fought their wars on the island of Sicily, which lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Caltanissetta and is the only in Italy with a population and area that exceed those of the provincial capital. Gela was founded in 698 BC by Greek colonists from Rhodes and Crete; it was an influential ''polis'' in Sicily in the 7th and 6th centuries BC and became one of the most powerful cities until the 5th c. BC. Aeschylus, the famous playwright, lived here and died in 456 BC. In 1943, during the Invasion of Sicily, the Allied forces made their first landing on the island at Gela.La Monte, John L. & Lewis, Winston B. ''The Sicilian Campaign, 10 July17 August 1943'' (1993) United States Government Printing Office pp.56-96 History Ancient era Archaeology has shown that the acropolis of Gela was occupied during the Copper Age i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eryx (Sicily)
Eryx ( grc-gre, Ἔρυξ, ''Éryx''; xpu, 𐤀𐤓𐤊, ) was an ancient city and a mountain in the west of Sicily, about 10 km from Drepana (modern Trapani), and 3 km from the sea-coast. It was located at the site of modern Erice. Mount Eryx The mountain, now called Monte Erice, is a wholly isolated peak, rising in the midst of a low undulating tract, which causes its elevation to appear much more considerable than it really is, so that it was regarded in ancient as well as modern times as the most lofty summit in the whole island next to Aetna, though its real elevation does not exceed 2184 English feet. Hence we find Eryx alluded to by Virgil and other Latin poets as a mountain of the first order of magnitude, and associated with Athos, Aetna, etc. On its summit stood a celebrated temple of Venus or Aphrodite, founded, according to the current legend, by Aeneas, whence the goddess derived the surname of Venus Erycina, by which she is often mentioned by Latin write ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
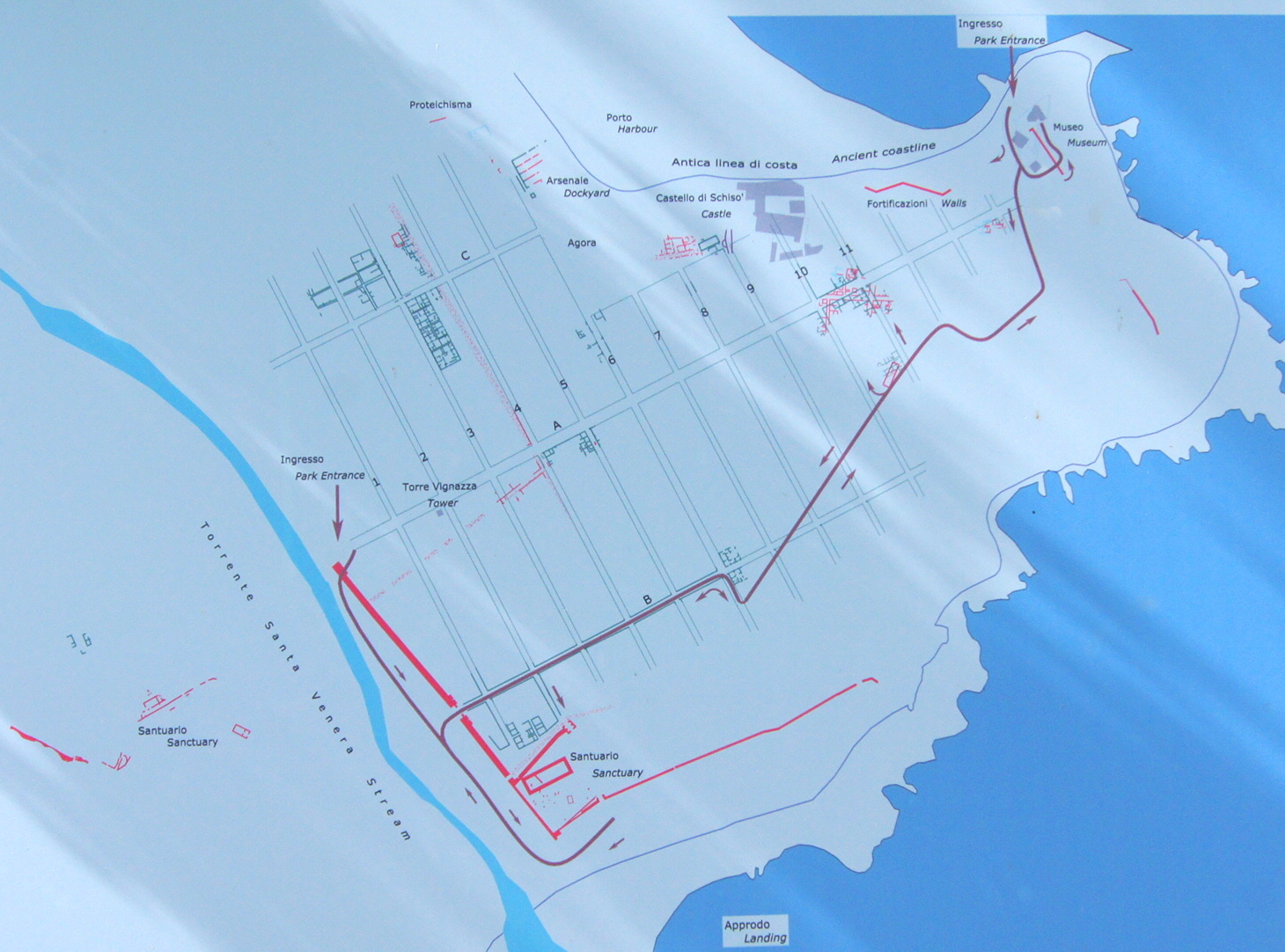
Naxos (Sicily)
Naxos or Naxus ( grc-gre, Νάξος) was an ancient Greek city, presently situated in modern Giardini Naxos near Taormina on the east coast of Sicily. Much of the site has never been built on and parts have been excavated in recent years. Its remains are open to the public and an on-site museum contains many finds. Location The city occupied a low rocky headland, now called Cape Schisò, formed by an ancient lava flow, immediately to the north of the Acesines (modern Alcantara) stream. Name There can be little doubt that the name was derived from the origin of the first colonists from Naxos in Greece. This has become even more definite since 1977 when the marble ''cippus'' (or sacred stone) inscribed with a dedication to the goddess Enyo was found in the large sanctuary west of the Santa Venera river. The characters are written in the unique 7th c. BC script of Greek Naxos. History Foundation Ancient writers agree that Naxos was the most ancient of all the Greek col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catana
Catania (, , Sicilian and ) is the second largest municipality in Sicily, after Palermo. Despite its reputation as the second city of the island, Catania is the largest Sicilian conurbation, among the largest in Italy, as evidenced also by the presence of important road and rail transport infrastructures as well as by the main airport in Sicily, fifth in Italy. It is located on Sicily's east coast, at the base of the active volcano, Mount Etna, and it faces the Ionian Sea. It is the capital of the 58-municipality region known as the Metropolitan City of Catania, which is the seventh-largest metropolitan city in Italy. The population of the city proper is 311,584, while the population of the Metropolitan City of Catania is 1,107,702. Catania was founded in the 8th century BC by Chalcidian Greeks. The city has weathered multiple geologic catastrophes: it was almost completely destroyed by a catastrophic earthquake in 1169. A major eruption and lava flow from nearby Mount Etna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhegion
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label=Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated population of nearly 200,000 and is the twenty-first most populous city in Italy, after Modena, and the 100th most populated city in Europe. Reggio Calabria is located in the exact center of the Mediterranean and is known for its climate, ethnic and cultural diversity. It is the third economic centre of mainland Southern Italy. About 560,000 people live in the metropolitan area, recognised in 2015 by Italy as a metropolitan city. Reggio is located on the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula and is separated from the island of Sicily by the Strait of Messina. It is situated on the slopes of the Aspromonte, a long, craggy mountain range that runs up through the centre of the region. As a major functional pole in the region, it has strong historical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devastating defeat for the Athenian forces, severely impacting Athens. The expedition was hampered from the outset by uncertainty in its purpose and command structure—political maneuvering in Athens swelled a lightweight force of twenty ships into a massive armada, and the expedition's primary proponent, Alcibiades, was recalled from command to stand trial before the fleet even reached Sicily. Still, the Athenians achieved early successes. Syracuse, the most powerful state in Sicily, responded exceptionally slowly to the Athenian threat and, as a result, was almost completely invested before the arrival of back up in the form of Spartan general, Gylippus, who galvanized its inhabitants into action. From that point forward, however, as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetna (city)
Aetna (Ancient Greek: , ''Aítnē''), was an ancient city of Sicily, situated at the foot of the mountain of the same name, on its southern declivity. It was originally a Sicelian city, and was called Inessa or Inessum. History After the death of Hieron I and the expulsion of the colonists whom he had established at Catana (modern Catania), the latter withdrew to Inessa, a place of great natural strength, which they occupied, and transferred to it the name of Aetna, previously given by Hieron to his new colony at Catana. In consequence of this they continued to regard Hieron as their oekist or founder. The new name, however, appears not to have been universally adopted, and we find Thucydides at a later period still employing the old appellation of Inessa. It seems to have fallen into the power of the Syracusans, and was occupied by them with a strong garrison; and in 426 BC, during the Sicilian Expedition, we find the Athenians under Laches in vain attempting to wrest it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Gela (405 BC)
The Battle of Gela took place in the summer of 405 BC in Sicily. The Carthaginian army under Himilco (a member of the Magonid family and kinsman of Hannibal Mago), which had spent the winter and spring in the captured city of Akragas, marched to confront the Greeks at Gela. The Syracuse government had deposed Daphnaeus, the unsuccessful general of the Greek army at Akragas, with Dionysius, another officer who had been a follower of Hermocrates. Dionysius schemed and gained full dictatorial powers. When the Carthaginians advanced on Gela and put the town under siege, Dionysius marched from Syracuse to confront the threat. He planned to use a complex three-pronged attack plan against the Carthaginians, which failed due to lack of proper coordination. Dionysius chose to evacuate Gela, as the defeat caused discontent in Syracuse and he did not wish to lose his power. Himilco sacked the abandoned city after the Greeks had fled to Camarina. Background Carthage had stayed away from Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in the city proper and about 650,000 in the Metropolitan City. It is located near the northeast corner of Sicily, at the Strait of Messina and it is an important access terminal to Calabria region, Villa San Giovanni, Reggio Calabria on the mainland. According to Eurostat the FUA of the metropolitan area of Messina has, in 2014, 277,584 inhabitants. The city's main resources are its seaports (commercial and military shipyards), cruise tourism, commerce, and agriculture (wine production and cultivating lemons, oranges, mandarin oranges, and olives). The city has been a Roman Catholic Archdiocese and Archimandrite seat since 1548 and is home to a locally important international fair. The city has the University of Messina, founded in 1548 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicel
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, but they rapidly fused into the culture of Magna Graecia. History Archaeological excavation has shown some Mycenean influence on Bronze Age Sicily. The earliest literary mention of Sicels is in the ''Odyssey''. Homer also mentions Sicania, but makes no distinctions: "they were (from) a faraway place and a faraway people and apparently they were one and the same" for Homer, Robin Lane Fox notes. It is possible that the Sicels and the Sicani of the Iron Age had consisted of an Illyrian population who (as with the Messapians) had imposed themselves on a native, Pre-Indo-European ("Mediterranean") population. Thucydides and other classical writers were aware of the traditions according to which the Sicels had once lived in Central Italy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |