|
Shortcuts To Adiabaticity
Shortcuts to adiabaticity (STA) are fast control protocols to drive the dynamics of system without relying on the adiabatic theorem. The concept of STA was introduced in a 2010 paper by Xi Chen et al. Their design can be achieved using a variety of techniques. A universal approach is provided by counterdiabatic driving, also known as transitionless quantum driving. Motivated by one of authors systematic study of dissipative Landau-Zener transition, the key idea was demonstrated earlier by a group of scientists from China, Greece and USA in 2000, as steering an eigenstate to destination. Counterdiabatic driving has been demonstrated in the laboratory using a time-dependent quantum oscillator. The use of counterdiabatic driving requires to diagonalize the system Hamiltonian, limiting its use in many-particle systems. In the control of trapped quantum fluids, the use of symmetries such as scale invariance and the associated conserved quantities has allowed to circumven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adiabatic Theorem
The adiabatic theorem is a concept in quantum mechanics. Its original form, due to Max Born and Vladimir Fock (1928), was stated as follows: :''A physical system remains in its instantaneous eigenstate if a given perturbation is acting on it slowly enough and if there is a gap between the eigenvalue and the rest of the Hamiltonian's spectrum.'' In simpler terms, a quantum mechanical system subjected to gradually changing external conditions adapts its functional form, but when subjected to rapidly varying conditions there is insufficient time for the functional form to adapt, so the spatial probability density remains unchanged. Diabatic vs. adiabatic processes At some initial time t_0 a quantum-mechanical system has an energy given by the Hamiltonian \hat(t_0); the system is in an eigenstate of \hat(t_0) labelled \psi(x,t_0). Changing conditions modify the Hamiltonian in a continuous manner, resulting in a final Hamiltonian \hat(t_1) at some later time t_1. The system will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi Chen
Xi Chen (Chinese: 陈汐) is a computer scientist. He is an associate professor of computer science at Columbia University. Chen won the 2021 Gödel Prize and Fulkerson Prize for his co-authored paper "Complexity of Counting CSP with Complex Weights" with Jin-Yi Cai. Biography Chen received his B.S. and Ph.D. from Tsinghua University. He was a postdoctoral fellow at Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton University, University of Southern California, and joined the Columbia faculty in 2011. Chen's research focuses on computational complexity theory. He also received a Presburger Award from the European Association for Theoretical Computer Science in 2015 and a Sloan Research Fellowship The Sloan Research Fellowships are awarded annually by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation since 1955 to "provide support and recognition to early-career scientists and scholars". This program is one of the oldest of its kind in the United States. ... in 2012. References Living ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Oscillator
量子調和振動子 は、 古典調和振動子 の 量子力学 類似物です。任意の滑らかな ポテンシャル は通常、安定した 平衡点 の近くで 調和ポテンシャル として近似できるため、最も量子力学における重要なモデル系。さらに、これは正確な 解析解法が知られている数少ない量子力学系の1つである。 author=Griffiths, David J. , title=量子力学入門 , エディション=2nd , 出版社=プレンティス・ホール , 年=2004 , isbn=978-0-13-805326-0 , author-link=David Griffiths (物理学者) , URL アクセス = 登録 , url=https://archive.org/details/introductiontoel00grif_0 One-dimensional harmonic oscillator Hamiltonian and energy eigenstates 粒子の ハミルトニアン は次のとおりです。 \hat H = \frac + \frac k ^2 = \frac + \frac m \omega^2 ^2 \, , ここで、 は粒子の質量、 は力定数、\omega = \sqrt は ��動子の [角周波数 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scale Invariance
In physics, mathematics and statistics, scale invariance is a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energy, or other variables, are multiplied by a common factor, and thus represent a universality. The technical term for this transformation is a dilatation (also known as dilation), and the dilatations can also form part of a larger conformal symmetry. *In mathematics, scale invariance usually refers to an invariance of individual functions or curves. A closely related concept is self-similarity, where a function or curve is invariant under a discrete subset of the dilations. It is also possible for the probability distributions of random processes to display this kind of scale invariance or self-similarity. *In classical field theory, scale invariance most commonly applies to the invariance of a whole theory under dilatations. Such theories typically describe classical physical processes with no characteristic length scale. *In quantum field t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Thermodynamics
Quantum thermodynamics is the study of the relations between two independent physical theories: thermodynamics and quantum mechanics. The two independent theories address the physical phenomena of light and matter. In 1905, Albert Einstein argued that the requirement of consistency between thermodynamics and electromagnetism leads to the conclusion that light is quantized obtaining the relation E= h \nu . This paper is the dawn of quantum theory. In a few decades quantum theory became established with an independent set of rules. Currently quantum thermodynamics addresses the emergence of thermodynamic laws from quantum mechanics. It differs from quantum statistical mechanics in the emphasis on dynamical processes out of equilibrium. In addition, there is a quest for the theory to be relevant for a single individual quantum system. Dynamical view There is an intimate connection of quantum thermodynamics with the theory of open quantum systems. Quantum mechanics inserts dynamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Engine
In physics, a quantum (plural quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a physical property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This means that the magnitude of the physical property can take on only discrete values consisting of integer multiples of one quantum. For example, a photon is a single quantum of light (or of any other form of electromagnetic radiation). Similarly, the energy of an electron bound within an atom is quantized and can exist only in certain discrete values. (Atoms and matter in general are stable because electrons can exist only at discrete energy levels within an atom.) Quantization is one of the foundations of the much broader physics of quantum mechanics. Quantization of energy and its influence on how energy and matter interact (quantum electrodynamics) is part of the fundamental framework for understanding and describing nature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Gas
An ideal Fermi gas is a state of matter which is an ensemble of many non-interacting fermions. Fermions are particles that obey Fermi–Dirac statistics, like electrons, protons, and neutrons, and, in general, particles with half-integer spin. These statistics determine the energy distribution of fermions in a Fermi gas in thermal equilibrium, and is characterized by their number density, temperature, and the set of available energy states. The model is named after the Italian physicist Enrico Fermi. This physical model can be accurately applied to many systems with many fermions. Some key examples are the behaviour of charge carriers in a metal, nucleons in an atomic nucleus, neutrons in a neutron star, and electrons in a white dwarf. Description An ideal Fermi gas or free Fermi gas is a physical model assuming a collection of non-interacting fermions in a constant potential well. Fermions are elementary or composite particles with half-integer spin, thus follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Phase Transition
In physics, a quantum phase transition (QPT) is a phase transition between different quantum phases ( phases of matter at zero temperature). Contrary to classical phase transitions, quantum phase transitions can only be accessed by varying a physical parameter—such as magnetic field or pressure—at absolute zero temperature. The transition describes an abrupt change in the ground state of a many-body system due to its quantum fluctuations. Such a quantum phase transition can be a second-order phase transition. Quantum phase transitions can also be represented by the topological fermion condensation quantum phase transition, see e.g. strongly correlated quantum spin liquid. In case of three dimensional Fermi liquid, this transition transforms the Fermi surface into a Fermi volume. Such a transition can be a first-order phase transition, for it transforms two dimensional structure ( Fermi surface) into three dimensional. As a result, the topological charge of Fermi liqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topological Defects
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a ''topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of a topological space, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. Basic examples of topological properties are: the dimension, which allows distinguishing between a line and a surface; compactness, which allows distinguishing between a line and a circle; connectedne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Therapy
Evolutionary therapy is a subfield of evolutionary medicine that utilizes concepts from evolutionary biology in management of diseases caused by evolving entities such as cancer and microbial infections. These evolving disease agents adapt to selective pressure introduced by treatment, allowing them to develop resistance to therapy, making it ineffective. Evolutionary therapy relies on the notion that Darwinian Evolution, Darwinian evolution is the main reason behind lethality of late stage cancer and Antimicrobial resistance, multi-drug resistant bacterial infections such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Thus, evolutionary therapy suggests that treatment of such highly dynamic evolving diseases should be changing over time to account for changes in disease populations. Adaptive treatment strategies typically cycle between different drugs or drug doses to take advantage of predictable patterns of disease evolution. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
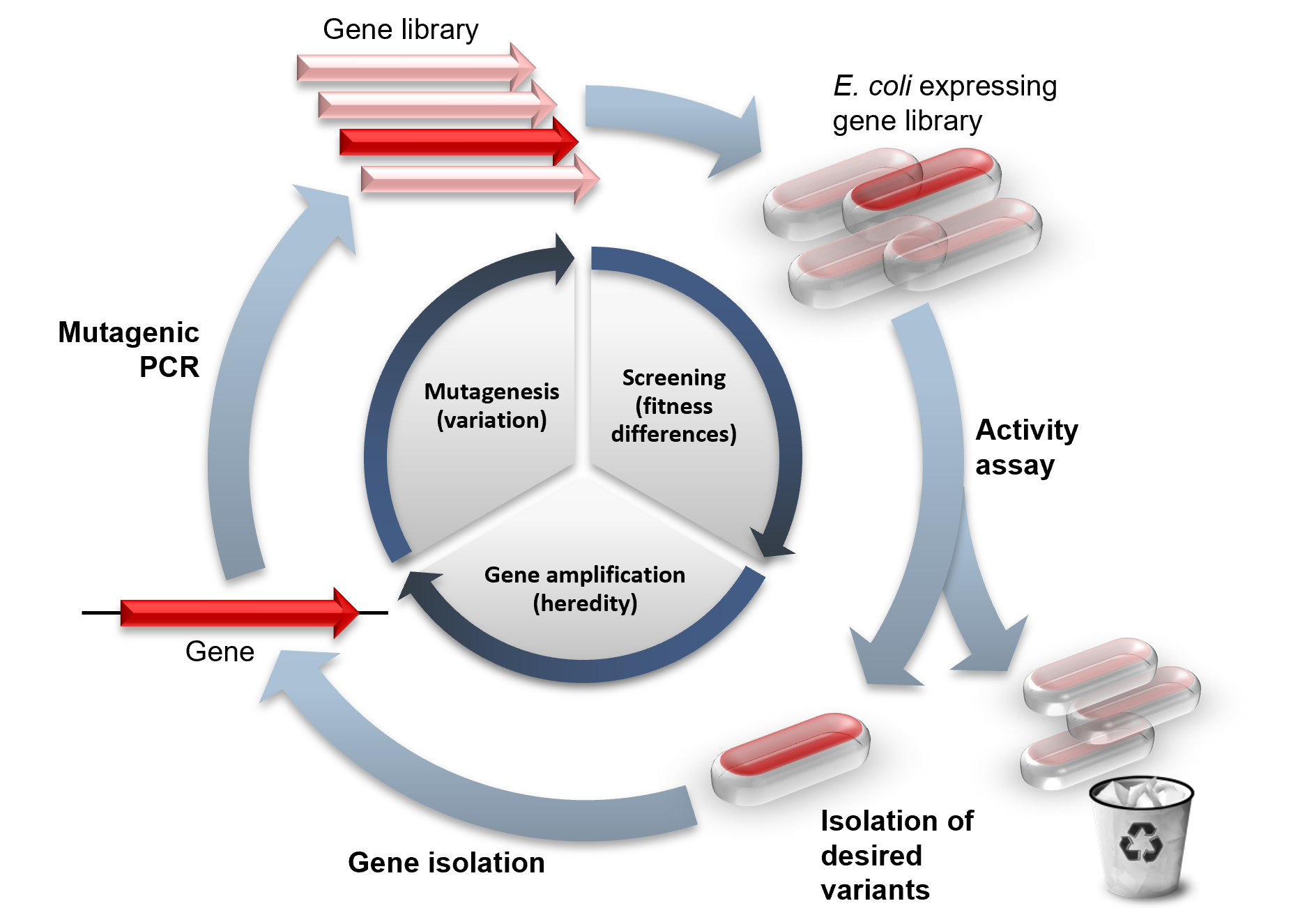
Directed Evolution
Directed evolution (DE) is a method used in protein engineering that mimics the process of natural selection to steer proteins or nucleic acids toward a user-defined goal. It consists of subjecting a gene to iterative rounds of mutagenesis (creating a library of variants), selection (expressing those variants and isolating members with the desired function) and amplification (generating a template for the next round). It can be performed '' in vivo'' (in living organisms), or '' in vitro'' (in cells or free in solution). Directed evolution is used both for protein engineering as an alternative to rationally designing modified proteins, as well as for experimental evolution studies of fundamental evolutionary principles in a controlled, laboratory environment. History Directed evolution has its origins in the 1960s with the evolution of RNA molecules in the "Spiegelman's Monster" experiment. The concept was extended to protein evolution via evolution of bacteria under s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |