|
Sextic Equation
In algebra, a sextic (or hexic) polynomial is a polynomial of degree six. A sextic equation is a polynomial equation of degree six—that is, an equation whose left hand side is a sextic polynomial and whose right hand side is zero. More precisely, it has the form: :ax^6+bx^5+cx^4+dx^3+ex^2+fx+g=0,\, where and the ''coefficients'' may be integers, rational numbers, real numbers, complex numbers or, more generally, members of any field. A sextic function is a function defined by a sextic polynomial. Because they have an even degree, sextic functions appear similar to quartic functions when graphed, except they may possess an additional local maximum and local minimum each. The derivative of a sextic function is a quintic function. Since a sextic function is defined by a polynomial with even degree, it has the same infinite limit when the argument goes to positive or negative infinity. If the leading coefficient is positive, then the function increases to positive infinity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextic Graph
In algebra, a sextic (or hexic) polynomial is a polynomial of degree six. A sextic equation is a polynomial equation of degree six—that is, an equation whose left hand side is a sextic polynomial and whose right hand side is zero. More precisely, it has the form: :ax^6+bx^5+cx^4+dx^3+ex^2+fx+g=0,\, where and the ''coefficients'' may be integers, rational numbers, real numbers, complex numbers or, more generally, members of any field. A sextic function is a function defined by a sextic polynomial. Because they have an even degree, sextic functions appear similar to quartic functions when graphed, except they may possess an additional local maximum and local minimum each. The derivative of a sextic function is a quintic function. Since a sextic function is defined by a polynomial with even degree, it has the same infinite limit when the argument goes to positive or negative infinity. If the leading coefficient is positive, then the function increases to positive infinity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of a polynomial, a series, or an expression; it is usually a number, but may be any expression (including variables such as , and ). When the coefficients are themselves variables, they may also be called parameters. For example, the polynomial 2x^2-x+3 has coefficients 2, −1, and 3, and the powers of the variable x in the polynomial ax^2+bx+c have coefficient parameters a, b, and c. The constant coefficient is the coefficient not attached to variables in an expression. For example, the constant coefficients of the expressions above are the number 3 and the parameter ''c'', respectively. The coefficient attached to the highest degree of the variable in a polynomial is referred to as the leading coefficient. For example, in the expressions above, the leading coefficients are 2 and ''a'', respectively. Terminology and definition In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Stem
In linguistics, a word stem is a part of a word responsible for its lexical meaning. The term is used with slightly different meanings depending on the morphology of the language in question. In Athabaskan linguistics, for example, a verb stem is a root that cannot appear on its own and that carries the tone of the word. Athabaskan verbs typically have two stems in this analysis, each preceded by prefixes. In most cases, a word stem is not modified during its declension, while in some languages it can be modified (apophony) according to certain morphological rules or peculiarities, such as sandhi. For example in Polish: ("city"), but ("in the city"). In English: "sing", "sang", "sung". Uncovering and analyzing cognation between word stems and roots within and across languages has allowed comparative philology and comparative linguistics to determine the history of languages and language families. Usage In one usage, a word stem is a form to which affixes can be attache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Function
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d where the coefficients , , , and are complex numbers, and the variable takes real values, and a\neq 0. In other words, it is both a polynomial function of degree three, and a real function. In particular, the domain and the codomain are the set of the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. A cubic function has either one or three real roots (which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single inflection point. It may have two critical points, a local minimum and a local maximum. Otherwise, a cubic function is monotonic. The graph of a cubic function is symmetric with respect to its inflection point; that is, it is invariant under a rotation of a half turn around this point. Up to an affine transformation, there are only thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeoli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
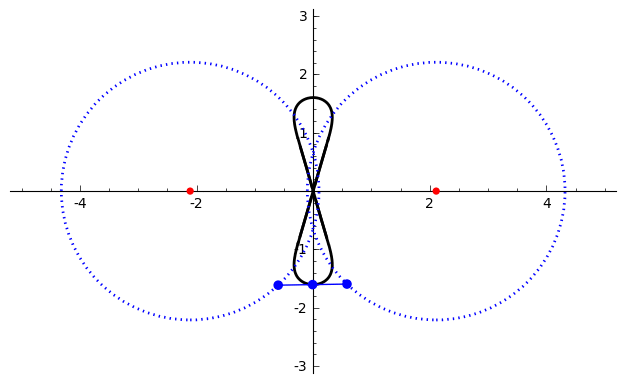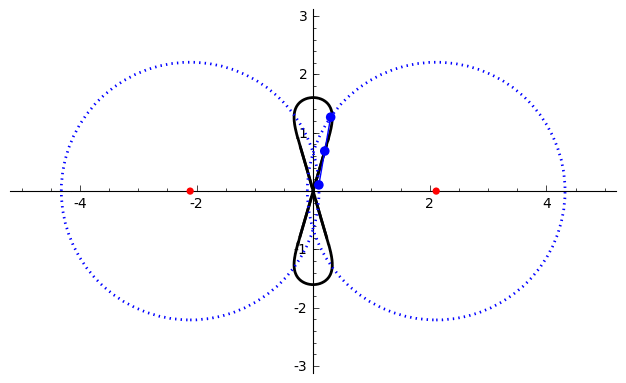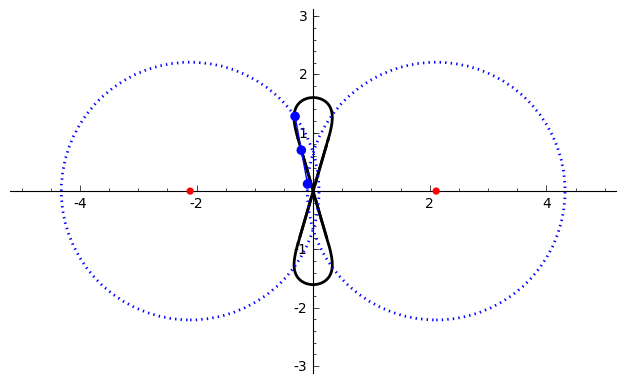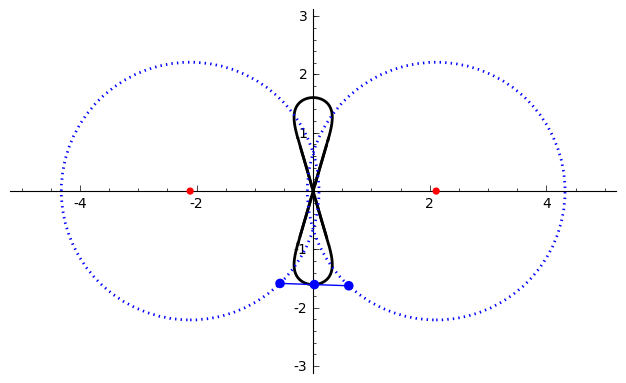
Watt's Curve
In mathematics, Watt's curve is a tricircular plane algebraic curve of degree six. It is generated by two circles of radius ''b'' with centers distance 2''a'' apart (taken to be at (±''a'', 0)). A line segment of length 2''c'' attaches to a point on each of the circles, and the midpoint of the line segment traces out the Watt curve as the circles rotate partially back and forth or completely around. It arose in connection with James Watt's pioneering work on the steam engine. The equation of the curve can be given in polar coordinates as :r^2=b^2-\left \sin\theta\pm\sqrt\right2. Derivation Polar coordinates The polar equation for the curve can be derived as follows: Working in the complex plane, let the centers of the circles be at ''a'' and ''−a'', and the connecting segment have endpoints at ''−a''+''be''''i'' λ and ''a''+''be''''i'' ρ. Let the angle of inclination of the segment be ψ with its midpoint at ''re''''i'' θ. Then the endpoints are also given by ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintic Equation
In algebra, a quintic function is a function of the form :g(x)=ax^5+bx^4+cx^3+dx^2+ex+f,\, where , , , , and are members of a field, typically the rational numbers, the real numbers or the complex numbers, and is nonzero. In other words, a quintic function is defined by a polynomial of degree five. Because they have an odd degree, normal quintic functions appear similar to normal cubic functions when graphed, except they may possess one additional local maximum and one additional local minimum. The derivative of a quintic function is a quartic function. Setting and assuming produces a quintic equation of the form: :ax^5+bx^4+cx^3+dx^2+ex+f=0.\, Solving quintic equations in terms of radicals (''n''th roots) was a major problem in algebra from the 16th century, when cubic and quartic equations were solved, until the first half of the 19th century, when the impossibility of such a general solution was proved with the Abel–Ruffini theorem. Finding roots of a quintic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Klein
Christian Felix Klein (; 25 April 1849 – 22 June 1925) was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work with group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and on the associations between geometry and group theory. His 1872 Erlangen program, classifying geometries by their basic symmetry groups, was an influential synthesis of much of the mathematics of the time. Life Felix Klein was born on 25 April 1849 in Düsseldorf, to Prussian parents. His father, Caspar Klein (1809–1889), was a Prussian government official's secretary stationed in the Rhine Province. His mother was Sophie Elise Klein (1819–1890, née Kayser). He attended the Gymnasium in Düsseldorf, then studied mathematics and physics at the University of Bonn, 1865–1866, intending to become a physicist. At that time, Julius Plücker had Bonn's professorship of mathematics and experimental physics, but by the time Klein became his assistant, in 1866, Plücker's interest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kampé De Fériet Function
In mathematics, the Kampé de Fériet function is a two-variable generalization of the generalized hypergeometric series, introduced by Joseph Kampé de Fériet Marie-Joseph Kampé de Fériet (Paris, 14 May 1893 – Villeneuve d'Ascq, 6 April 1982) was professor at Université Lille Nord de France from 1919 to 1969. Besides his works on mathematics and fluid mechanics, he directed the ''Institut de mé .... The Kampé de Fériet function is given by : ^F_\left( \begin a_1,\cdots,a_p\colon b_1,b_1';\cdots;b_q,b_q'; \\ c_1,\cdots,c_r\colon d_1,d_1';\cdots;d_s,d_s'; \end x,y\right)= \sum_^\infty\sum_^\infty\frac\frac\cdot\frac. Applications The general sextic equation can be solved in terms of Kampé de Fériet functions. References * * * External links * Hypergeometric functions {{analysis-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilizer (group Theory)
In mathematics, a group action on a space is a group homomorphism of a given group into the group of transformations of the space. Similarly, a group action on a mathematical structure is a group homomorphism of a group into the automorphism group of the structure. It is said that the group ''acts'' on the space or structure. If a group acts on a structure, it will usually also act on objects built from that structure. For example, the group of Euclidean isometries acts on Euclidean space and also on the figures drawn in it. For example, it acts on the set of all triangles. Similarly, the group of symmetries of a polyhedron acts on the vertices, the edges, and the faces of the polyhedron. A group action on a vector space is called a representation of the group. In the case of a finite-dimensional vector space, it allows one to identify many groups with subgroups of , the group of the invertible matrices of dimension over a field . The symmetric group acts on any set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |