|
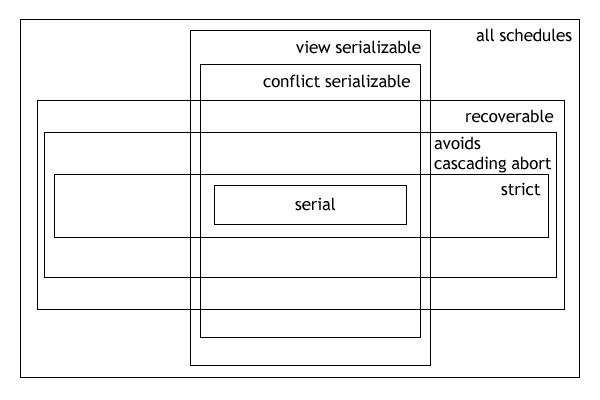
Serializability
In concurrency control of databases, Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987)''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems''(free PDF download), Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001)''Transactional Information Systems'' Elsevier, transaction processing (transaction management), and various transactional applications (e.g., transactional memoryMaurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss. ''Transactional memory: architectural support for lock-free data structures.'' Proceedings of the 20th annual international symposium on Computer architecture (ISCA '93). Volume 21, Issue 2, May 1993. and software transactional memory), both centralized and distributed, a transaction schedule is serializable if its outcome (e.g., the resulting database state) is equal to the outcome of its transactions executed serially, i.e. without overlapping in time. Transactions are normally executed concurrently (they overlap), since this is the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrency Control
In information technology and computer science, especially in the fields of computer programming, operating systems, multiprocessors, and databases, concurrency control ensures that correct results for concurrent operations are generated, while getting those results as quickly as possible. Computer systems, both software and hardware, consist of modules, or components. Each component is designed to operate correctly, i.e., to obey or to meet certain consistency rules. When components that operate concurrently interact by messaging or by sharing accessed data (in memory or storage), a certain component's consistency may be violated by another component. The general area of concurrency control provides rules, methods, design methodologies, and theories to maintain the consistency of components operating concurrently while interacting, and thus the consistency and correctness of the whole system. Introducing concurrency control into a system means applying operation constraints w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serializability
In concurrency control of databases, Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987)''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems''(free PDF download), Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001)''Transactional Information Systems'' Elsevier, transaction processing (transaction management), and various transactional applications (e.g., transactional memoryMaurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss. ''Transactional memory: architectural support for lock-free data structures.'' Proceedings of the 20th annual international symposium on Computer architecture (ISCA '93). Volume 21, Issue 2, May 1993. and software transactional memory), both centralized and distributed, a transaction schedule is serializable if its outcome (e.g., the resulting database state) is equal to the outcome of its transactions executed serially, i.e. without overlapping in time. Transactions are normally executed concurrently (they overlap), since this is the mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
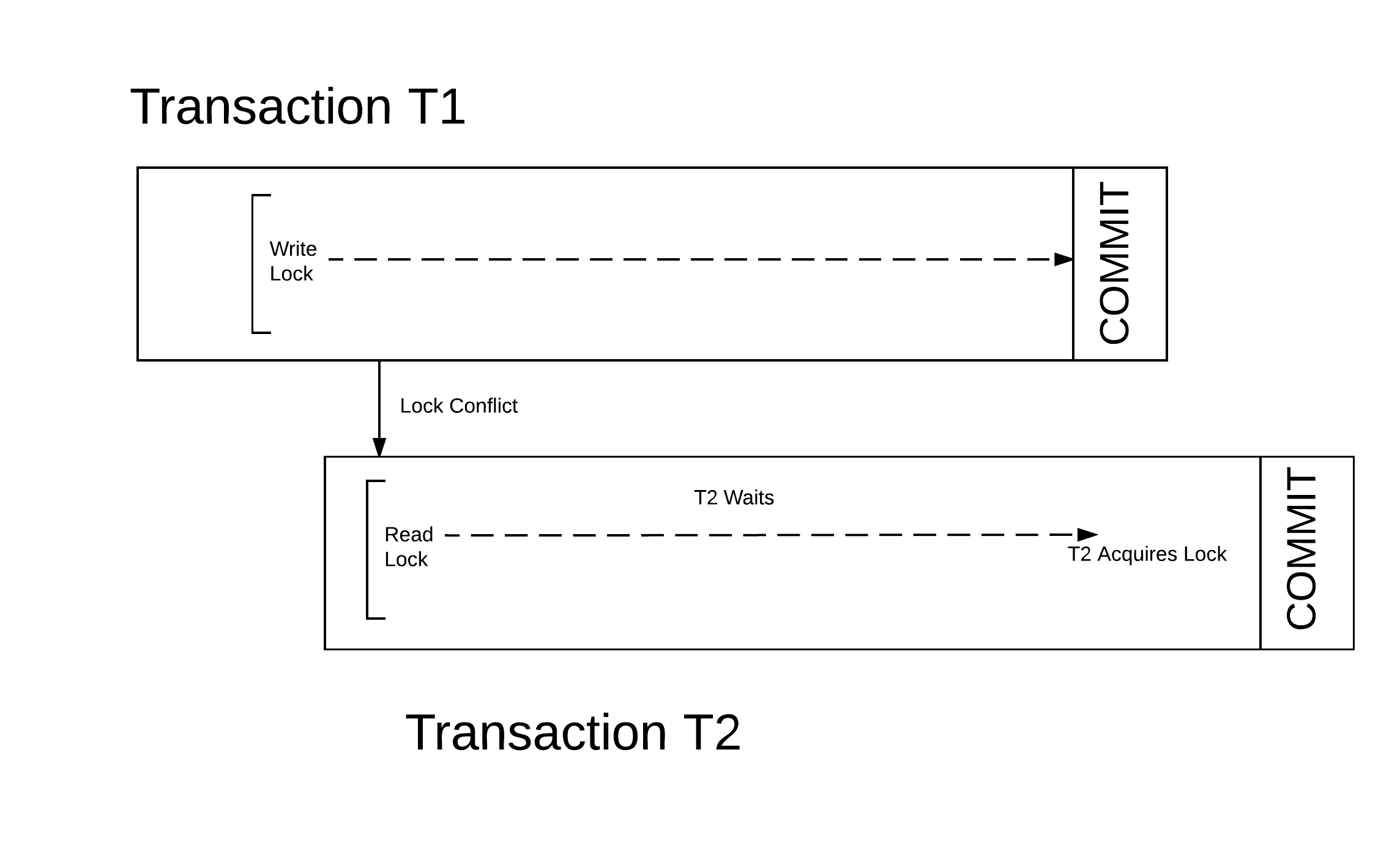
Two-phase Locking
In databases and transaction processing, two-phase locking (2PL) is a concurrency control method that guarantees serializability. Philip A. Bernstein, Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman (1987) ''Concurrency Control and Recovery in Database Systems'' Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Gerhard Weikum, Gottfried Vossen (2001) ''Transactional Information Systems'' Elsevier, It is also the name of the resulting set of database transaction schedules (histories). The protocol uses locks, applied by a transaction to data, which may block (interpreted as signals to stop) other transactions from accessing the same data during the transaction's life. By the 2PL protocol, locks are applied and removed in two phases: # Expanding phase: locks are acquired and no locks are released. # Shrinking phase: locks are released and no locks are acquired. Two types of locks are used by the basic protocol: ''Shared'' and ''Exclusive'' locks. Refinements of the basic protocol may use more lock types. Using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snapshot Isolation
In databases, and transaction processing (transaction management), snapshot isolation is a guarantee that all reads made in a transaction will see a consistent snapshot of the database (in practice it reads the last committed values that existed at the time it started), and the transaction itself will successfully commit only if no updates it has made conflict with any concurrent updates made since that snapshot. Snapshot isolation has been adopted by several major database management systems, such as InterBase, Firebird, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Anywhere, MongoDB and Microsoft SQL Server (2005 and later). The main reason for its adoption is that it allows better performance than serializability, yet still avoids most of the concurrency anomalies that serializability avoids (but not all). In practice snapshot isolation is implemented within multiversion concurrency control (MVCC), where generational values of each data item (versions) are maintained: MVCC is a common way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transactional Memory
In computer science and engineering, transactional memory attempts to simplify concurrent programming by allowing a group of load and store instructions to execute in an atomic way. It is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. Transactional memory systems provide high-level abstraction as an alternative to low-level thread synchronization. This abstraction allows for coordination between concurrent reads and writes of shared data in parallel systems. Motivation In concurrent programming, synchronization is required when parallel threads attempt to access a shared resource. Low-level thread synchronization constructs such as locks are pessimistic and prohibit threads that are outside a critical section from making any changes. The process of applying and releasing locks often functions as additional overhead in workloads with little conflict among threads. Transactional memory provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
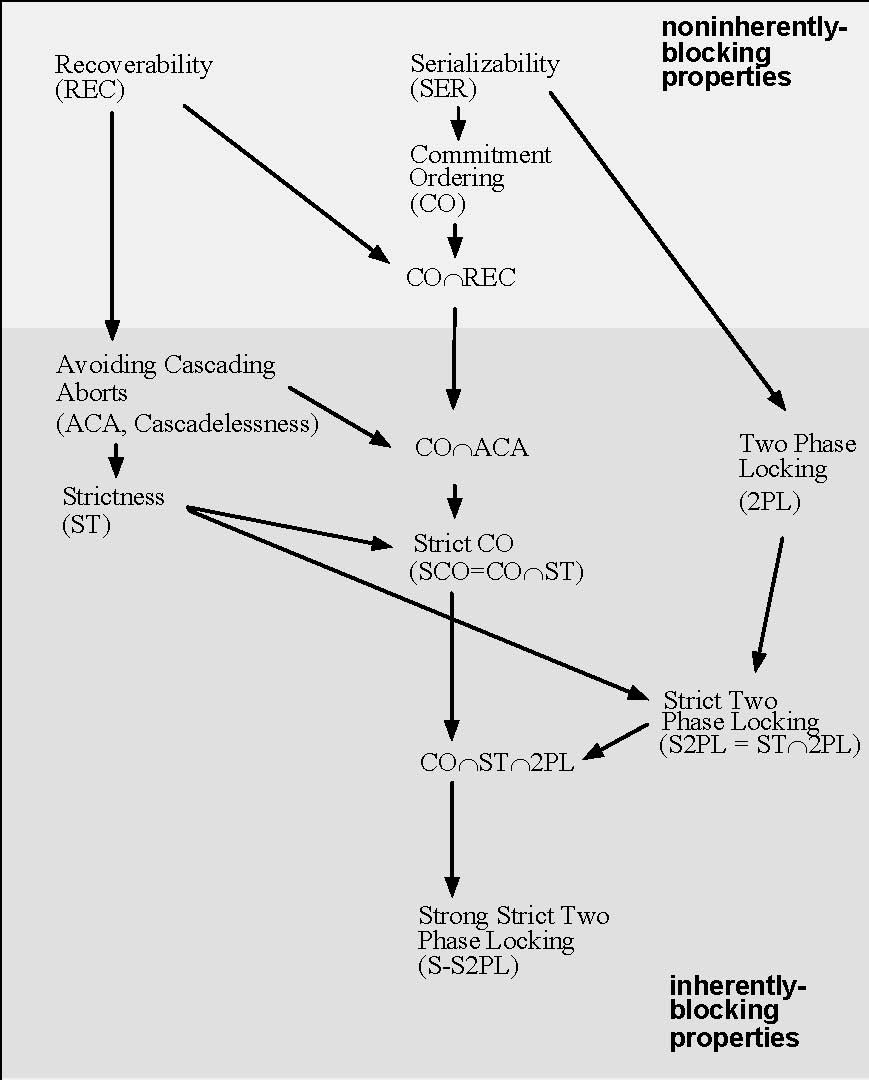
Avoiding Cascading Aborts
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe execution of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Not all transaction operation types should be included in a schedule, and typically only selected operation types (e.g., data access operations) are included, as needed to reason about and describe certain phenomena. Schedules and schedule properties are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. Formal description The following is an example of a schedule: ;D In this example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schedule (computer Science)
In the fields of databases and transaction processing (transaction management), a schedule (or history) of a system is an abstract model to describe execution of transactions running in the system. Often it is a ''list'' of operations (actions) ordered by time, performed by a set of transactions that are executed together in the system. If the order in time between certain operations is not determined by the system, then a ''partial order'' is used. Examples of such operations are requesting a read operation, reading, writing, aborting, committing, requesting a lock, locking, etc. Not all transaction operation types should be included in a schedule, and typically only selected operation types (e.g., data access operations) are included, as needed to reason about and describe certain phenomena. Schedules and schedule properties are fundamental concepts in database concurrency control theory. Formal description The following is an example of a schedule: ;D In this example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Transactional Memory
In computer science, software transactional memory (STM) is a concurrency control mechanism analogous to database transactions for controlling access to shared memory in concurrent computing. It is an alternative to lock-based synchronization. STM is a strategy implemented in software, rather than as a hardware component. A transaction in this context occurs when a piece of code executes a series of reads and writes to shared memory. These reads and writes logically occur at a single instant in time; intermediate states are not visible to other (successful) transactions. The idea of providing hardware support for transactions originated in a 1986 paper by Tom Knight. The idea was popularized by Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss.Maurice Herlihy and J. Eliot B. Moss. ''Transactional memory: architectural support for lock-free data structures.'' Proceedings of the 20th annual international symposium on Computer architecture (ISCA '93). Volume 21, Issue 2, May 1993. In 1995 Nir Shav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Transaction
A distributed transaction is a database transaction in which two or more network hosts are involved. Usually, hosts provide transactional resources, while the transaction manager is responsible for creating and managing a global transaction that encompasses all operations against such resources. Distributed transactions, as any other transactions, must have all four ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) properties, where atomicity guarantees all-or-nothing outcomes for the unit of work (operations bundle). Open Group, a vendor consortium, proposed the X/Open Distributed Transaction Processing (DTP) Model (X/Open XA), which became a de facto standard for behavior of transaction model components. Databases are common transactional resources and, often, transactions span a couple of such databases. In this case, a distributed transaction can be seen as a database transaction that must be synchronized (or provide ACID properties) among multiple participating databases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replication (computer Science)
Replication in computing involves sharing information so as to ensure consistency between redundant resources, such as software or hardware components, to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or accessibility. Terminology Replication in computing can refer to: * ''Data replication'', where the same data is stored on multiple storage devices * ''Computation replication'', where the same computing task is executed many times. Computational tasks may be: ** ''Replicated in space'', where tasks are executed on separate devices ** ''Replicated in time'', where tasks are executed repeatedly on a single device Replication in space or in time is often linked to scheduling algorithms. Access to a replicated entity is typically uniform with access to a single non-replicated entity. The replication itself should be transparent to an external user. In a failure scenario, a failover of replicas should be hidden as much as possible with respect to quality of service. Computer scientis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |