|
Separable Verb
A separable verb is a verb that is composed of a lexical core and a separable particle. In some sentence positions, the core verb and the particle appear in one word, whilst in others the core verb and the particle are separated. The particle cannot be accurately referred to as a prefix because it can be separated from the core verb. German, Dutch, Afrikaans and Hungarian are notable for having many separable verbs. Separable verbs challenge theories of sentence structure because when they are separated, it is not evident how the compositionality of meaning should be understood. The separation of such verbs is called tmesis. Examples The German verb ''ankommen'' is a separable verb, and is used here as the first illustration: The first two examples, sentences a and b, contain the "simple" tenses. In matrix declarative clauses that lack auxiliary verbs, the verb and its particle (both in bold) are separated, the verb appearing in V2 position and the particle appearing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done. For some examples: * I ''washed'' the car yesterday. * The dog ''ate'' my homework. * John ''studies'' English and French. * Lucy ''enjoys'' listening to music. *Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence)'' * Mike T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject–object–verb Word Order
In linguistic typology, a subject–object–verb (SOV) language is one in which the subject, object, and verb of a sentence always or usually appear in that order. If English were SOV, "Sam beer drank" would be an ordinary sentence, as opposed to the actual Standard English "Sam drank beer" which is subject–verb–object (SVO). The term is often loosely used for ergative languages like Adyghe and Basque that really have agents instead of subjects. Incidence Among natural languages with a word order preference, SOV is the most common type (followed by subject–verb–object; the two types account for more than 75% of natural languages with a preferred order). Languages that have SOV structure include all Indo-Iranian languages ( Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Marathi, Nepali, Pāli, Pashto, Persian, Punjabi, Sindhi, Sinhalese, Urdu, Zazaki, Kurdish), Ainu, Akkadian, Amharic, Armenian, Assyrian, Aymara, Basque, Burmese, Burushaski, Cherokee, Dakota, Dogo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb Types
A verb () is a word (part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done. For some examples: * I ''washed'' the car yesterday. * The dog ''ate'' my homework. * John ''studies'' English and French. * Lucy ''enjoys'' listening to music. *Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence)'' *Mike Trout ''is'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separable Verbs Trees 2'
Separability may refer to: Mathematics * Separable algebra, a generalization to associative algebras of the notion of a separable field extension * Separable differential equation, in which separation of variables is achieved by various means * Separable extension, in field theory, an algebraic field extension * Separable filter, a product of two or more simple filters in image processing * Separable ordinary differential equation, a class of equations that can be separated into a pair of integrals * Separable partial differential equation, a class of equations that can be broken down into differential equations in fewer independent variables * Separable permutation, a permutation that can be obtained by direct sums and skew sums of the trivial permutation * Separable polynomial, a polynomial whose number of distinct roots is equal to its degree * Separable sigma algebra, a separable space in measure theory * Separable space, a topological space that contains a countable, den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separable Verbs Tees 1
Separability may refer to: Mathematics * Separable algebra, a generalization to associative algebras of the notion of a separable field extension * Separable differential equation, in which separation of variables is achieved by various means * Separable extension, in field theory, an algebraic field extension * Separable filter, a product of two or more simple filters in image processing * Separable ordinary differential equation, a class of equations that can be separated into a pair of integrals * Separable partial differential equation, a class of equations that can be broken down into differential equations in fewer independent variables * Separable permutation, a permutation that can be obtained by direct sums and skew sums of the trivial permutation * Separable polynomial, a polynomial whose number of distinct roots is equal to its degree * Separable sigma algebra, a separable space in measure theory * Separable space, a topological space that contains a countable, den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependency Grammar
Dependency grammar (DG) is a class of modern grammatical theories that are all based on the dependency relation (as opposed to the ''constituency relation'' of phrase structure) and that can be traced back primarily to the work of Lucien Tesnière. Dependency is the notion that linguistic units, e.g. words, are connected to each other by directed links. The (finite) verb is taken to be the structural center of clause structure. All other syntactic units (words) are either directly or indirectly connected to the verb in terms of the directed links, which are called ''dependencies''. Dependency grammar differs from phrase structure grammar in that while it can identify phrases it tends to overlook phrasal nodes. A dependency structure is determined by the relation between a word (a head) and its dependents. Dependency structures are flatter than phrase structures in part because they lack a finite verb phrase constituent, and they are thus well suited for the analysis of languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catena (linguistics)
In linguistics, a catena (English pronunciation: , plural catenas or catenae; from Latin for "chain") is a unit of syntax and morphology, closely associated with dependency grammars. It is a more flexible and inclusive unit than the constituent and may therefore be better suited than the constituent to serve as the fundamental unit of syntactic and morphosyntactic analysis. The catena has served as the basis for the analysis of a number of phenomena of syntax, such as idiosyncratic meaning, ellipsis mechanisms (e.g. gapping, stripping, VP-ellipsis, pseudogapping, sluicing, answer ellipsis, comparative deletion), predicate-argument structures, and discontinuities (topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, extraposition, etc.). The catena concept has also been taken as the basis for a theory of morphosyntax, i.e. for the extension of dependencies into words; dependencies are acknowledged between the morphs that constitute words. While the catena concept has been applied main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Separable Verbs Tree 0
Separability may refer to: Mathematics * Separable algebra, a generalization to associative algebras of the notion of a separable field extension * Separable differential equation, in which separation of variables is achieved by various means * Separable extension, in field theory, an algebraic field extension * Separable filter, a product of two or more simple filters in image processing * Separable ordinary differential equation, a class of equations that can be separated into a pair of integrals * Separable partial differential equation, a class of equations that can be broken down into differential equations in fewer independent variables * Separable permutation, a permutation that can be obtained by direct sums and skew sums of the trivial permutation * Separable polynomial, a polynomial whose number of distinct roots is equal to its degree * Separable sigma algebra, a separable space in measure theory * Separable space, a topological space that contains a countable, den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
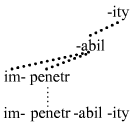
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed. Prefixes, like other affixes, can be either inflectional, creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and same lexical category (but playing a different role in the sentence), or derivational, creating a new word with a new semantic meaning and sometimes also a different lexical category. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually bound morphemes. In English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose. The word ''prefix'' is itself made up of the stem ''fix'' (meaning "attach", in this case), and the prefix ''pre-'' (meaning "before"), both o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Compositionality
In semantics, mathematical logic and related disciplines, the principle of compositionality is the principle that the meaning of a complex expression is determined by the meanings of its constituent expressions and the rules used to combine them. This principle is also called Frege's principle, because Gottlob Frege is widely credited for the first modern formulation of it. The principle was never explicitly stated by Frege, and it was arguably already assumed by George Boole decades before Frege's work. The principle of compositionality is highly debated in linguistics, and among its most challenging problems there are the issues of contextuality, the non-compositionality of idiomatic expressions, and the non-compositionality of quotations. History Discussion of compositionality started to appear at the beginning of the 19th century, during which it was debated whether what was most fundamental in language was compositionality or contextuality, and compositionality was usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrasal Verb
In the traditional grammar of Modern English, a phrasal verb typically constitutes a single semantic unit composed of a verb followed by a particle (examples: ''turn down'', ''run into'' or ''sit up''), sometimes combined with a preposition (examples: ''get together with'', ''run out of'' or ''feed off of''). Alternative terms include verb-adverb combination, verb-particle construction, two-part word/verb or three-part word/verb (depending on the number of particles) and multi-word verb. Phrasal verbs ordinarily cannot be understood based upon the meanings of the individual parts alone but must be considered as a whole: the meaning is non-compositional and thus unpredictable. Phrasal verbs are differentiated from other classifications of multi-word verbs and free combinations by criteria based on idiomaticity, replacement by a single-word verb, wh-question formation and particle movement. Types The category "phrasal verb" is mainly used in English as a second language te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
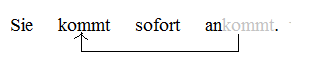
.jpg)