|
San Giovanni A Porta Latina
San Giovanni a Porta Latina (Italian: "Saint John Before the Latin Gate") is a Basilica church in Rome, Italy, near the Porta Latina (on the Via Latina) of the Aurelian Wall. History According to Tertullian, as quoted by Saint Jerome, in the year 92, St John the Evangelist survived martyrdom at Rome under the Emperor Domitian by being immersed in a vat of boiling oil, from which he emerged unharmed. He was later exiled to the island of Patmos. This event was traditionally said to have occurred at the Latin Gate (located on the southern portion of the Roman wall). The nearby chapel of ''San Giovanni in Oleo'' is said to be on the very spot. The event was referred to in the Roman Martyrology, which was begun in the seventh century, though the event was celebrated before then. A feast in the Roman calendar also celebrated the event until 1960, when Pope John XXIII removed most of the secondary feasts for a saint. The black-letter day of S. John Evang. ante portam Latinam is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domitian
Domitian ( ; ; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was Roman emperor from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Flavian dynasty. Described as "a ruthless but efficient autocrat", his authoritarian style of ruling put him at sharp odds with the Roman Senate, Senate, whose powers he drastically curtailed. Domitian had a minor and largely ceremonial role during the reigns of his father and brother. After the death of his brother, Domitian was declared emperor by the Praetorian Guard. His 15-year reign was the longest since Tiberius. As emperor, Domitian strengthened the economy by revaluing the Roman currency, Roman coinage, expanded the border defenses of the empire, and initiated a massive building program to restore the damaged city of Rome. Significant wars were fought in Britain, where his general Gnaeus Julius Agricola, Agricola made significant gains in his attempt to conquer Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Adrian I
Pope Adrian I (; 700 – 25 December 795) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 1 February 772 until his death on 25 December 795. Descended from a family of the military aristocracy of Rome known as ''domini de via Lata'', he was the son of Theodore, who died when Hadrian was still very young; he was welcomed by his paternal uncle Theodotus (or Theodatus) ''consul, dux et primicerius Sanctae Romanae Ecclesiae''. Adrian and his predecessors had to contend with periodic attempts by the Lombards to expand their holdings in Italy at the expense of the papacy. Not receiving any support from Constantinople, the popes looked for help to the Franks. Adrian's tenure saw the culmination of on-going territorial disputes between Charlemagne and his brother Carloman I. The Lombard king Desiderius supported the claims of Carloman's sons to their late father's land, and requested Pope Adrian crown Carloman's sons "Kings of the Franks". When the Pope failed to do so, Desider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lectern
A lectern is a standing reading desk with a slanted top, on which documents or books are placed as support for reading aloud, as in a scripture reading, lecture, or sermon. A lectern is usually attached to a stand or affixed to some other form of support. To facilitate eye contact and improve posture when facing an audience, lecterns may have adjustable height and slant. People reading from a lectern, called lectors, generally do so while standing. The word has its origins in the medieval Latin term ''lectrum'', related to ''legere'' which means 'to read'. In pre-modern usage, the word ''lectern'' was used to refer specifically to the "reading desk or stand ... from which the Scripture lessons (''lectiones'') ... are chanted or read." One 1905 dictionary states that "the term is properly applied only to the class mentioned [church book stands] as independent of the pulpit." By the 1920s, however, the term was being used in a broader sense; for example, in reference to a memorial se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
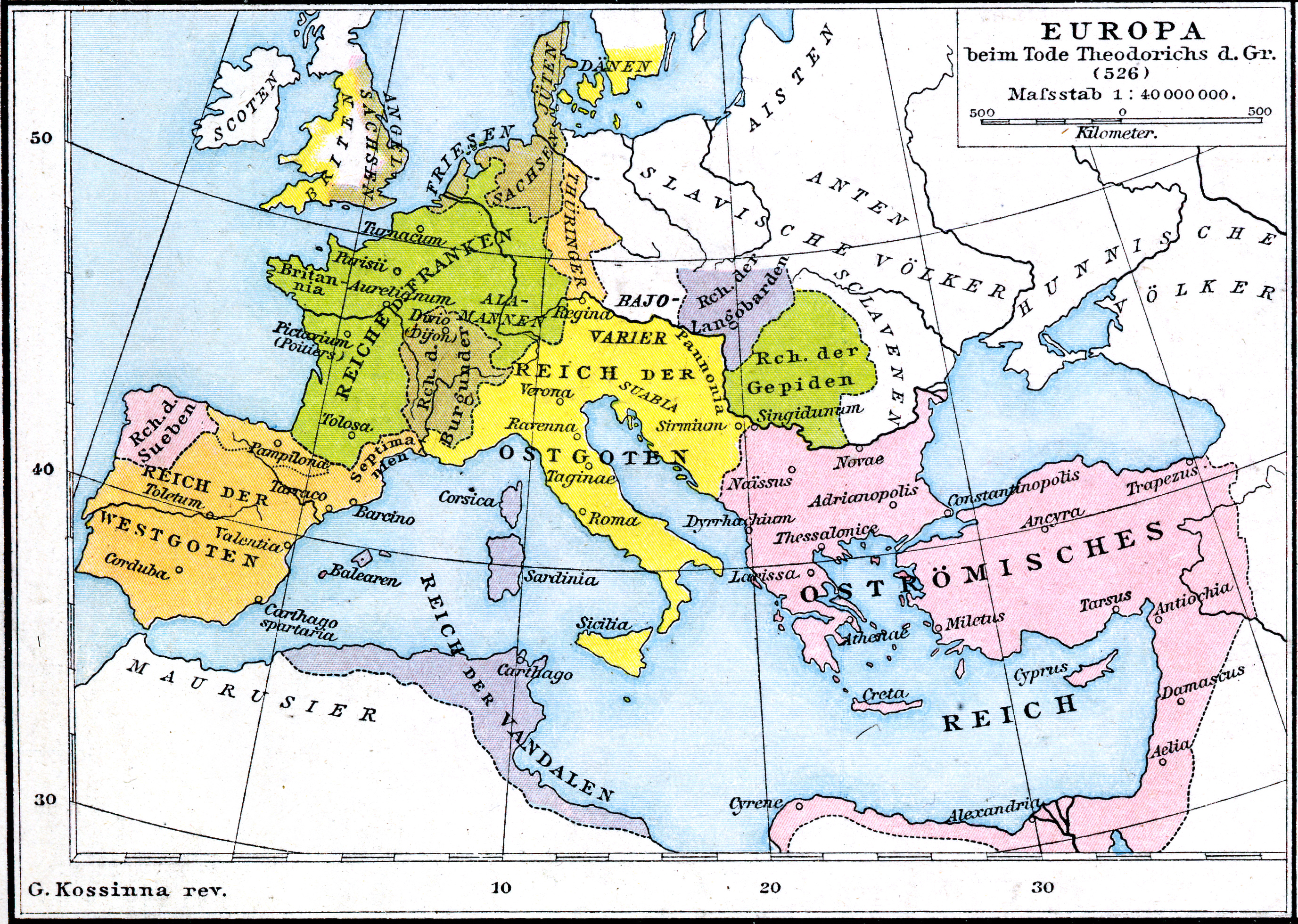
Theodoric The Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician (ancient Rome)#Late Roman and Byzantine period, patrician of the Byzantine Empire#Loss of the Western Roman Empire, Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (''rex''), some scholars characterize him as a Roman Emperor#Later assertions to the title, Western Roman emperor in all but name, since he ruled a large part of the former Western Roman Empire described as a ''Res Publica'', had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497 which he used, was referred to by the imperial title ''princeps'' by the Italian aristocracy and exercised imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoth
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Gelasius I
Pope Gelasius I was the bishop of Rome from 1 March 492 to his death on 21 November 496. Gelasius was a prolific author whose style placed him on the cusp between Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages.The title of his biography by Walter Ullmann expresses this:''Gelasius I. (492–496): Das Papsttum an der Wende der Spätantike zum Mittelalter'' (Stuttgart) 1981. Some scholars have argued that his predecessor Felix III may have employed him to draft papal documents, although this is not certain. During his pontificate he called for strict Catholic orthodoxy, more assertively demanded obedience to papal authority, and, consequently, increased the tension between the Western and Eastern Churches. Surprisingly, he also had cordial relations with the Ostrogothic Kingdom, Ostrogoths, who were Arianism, Arians (i.e. Nontrinitarianism, Non-trinitarian Christians), and therefore perceived as Heresy in Christianity, heretics from the perspective of Nicene Christianity, Nicene Christians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Ordinariate Of Our Lady Of Walsingham
The Personal Ordinariate of Our Lady of Walsingham in England and Wales is a personal ordinariate in the Latin Church of the Catholic Church immediately exempt, being directly subject to the Holy See. It is within the territory of the Catholic Bishops' Conference of England and Wales, of which its ordinary is a member, and also encompasses Scotland. It was established on 15 January 2011 for groups of former Anglicans in England and Wales in accordance with the apostolic constitution ''Anglicanorum coetibus'' of Pope Benedict XVI, which was supplemented with the ''Complementary Norms'' of Pope Francis in 2013. The personal ordinariate is set up in such a way that "corporate reunion" of former Anglicans with the Catholic Church is possible while also preserving elements of a "distinctive Anglican patrimony". The Liturgy used is the Divine Worship: The Missal (2015, 2020), an adaption of the Roman Rite with Anglican elements. Each ordinariate has its own Liturgical Calendar. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the title given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christianity, Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The Book of Common Prayer (1549), first prayer book, published in 1549 in the reign of King Edward VI of England, was a product of the English Reformation following the break with Catholic Church, Rome. The 1549 work was the first prayer book to include the complete forms of service for daily and Sunday worship in English. It contains Morning Prayer (Anglican), Morning Prayer, Evening Prayer (Anglican), Evening Prayer, the Litany, Holy Communion, and occasional services in full: the orders for Baptism, Confirmation, Marriage, "Anointing of the Sick, prayers to be said with the sick", and a funeral service. It also sets out in full the "propers" (the parts of the service that vary weekly or daily throughout the Church's Year): the introits, collects, and epistle and gospel rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Roman Calendar Of 1960
This article lists the feast days of the General Roman Calendar as approved on 25 July 1960 by Pope John XXIII's '' motu proprio'' '' Rubricarum instructum'' and promulgated by the Sacred Congregation of Rites the following day, 26 July 1960, by the decree ''Novum rubricarum''. This 1960 calendar was incorporated into the 1962 edition of the Roman Missal, continued use of which Pope Benedict XVI authorized in his 7 July 2007 motu proprio ''Summorum Pontificum'', and which Pope Francis updated in his 16 July 2021 motu proprio '' Traditionis custodes'', for use as a Traditional Latin Mass. ''Novum rubricarum'' replaced the former classifications of Doubles, Semidoubles, and Simples with I, II, and III class feasts and commemorations. It removed a few feasts, in particular duplications such as the Feast of the Cross (3 May and 14 September), the Chair of Peter (18 January and 22 February), Saint Peter (1 August and 29 June), Saint John the Evangelist (6 May and 27 December), Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope John XXIII
Pope John XXIII (born Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli; 25 November 18813 June 1963) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death on 3 June 1963. He is the most recent pope to take the pontifical name "John". Roncalli was among 13 children born to Marianna Mazzola and Giovanni Battista Roncalli in a family of sharecroppers who lived in Sotto il Monte, a village in the province of Bergamo, Lombardy. He was ordained to the priesthood on 10 August 1904 and served in a number of posts, as nuncio in France and a delegate to Bulgaria, Greece and Turkey. In a consistory on 12 January 1953 Pope Pius XII made Roncalli a cardinal as the Cardinal-priest of Santa Prisca in addition to naming him as the Patriarch of Venice. Roncalli was unexpectedly elected pope on 28 October 1958 at age 76 after Pope Pius XII's death. Pope John XXIII surprised those who expected him to be a caretaker pope by calling the historic S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |