|
Sames Of Commagene
Sames I (also spelled Samos I), was the Orontid king of Sophene and Commagene, ruling around 260 BC. Name The name of "Samos" is possibly derived from the Avestan name ''Sāma'', the father of the Avestan hero Garshasp, which would indicate some sort of custom of Iranian religious or epic lore amongst the Orontids. Biography The Kingdom of Sophene was ruled by the Orontid dynasty of Iranian origin, which was descended from Orontes I, a Bactrian nobleman who was the son-in-law of the Achaemenid King of Kings Artaxerxes II (). According to the Greek writer Strabo (died 24 AD) in his '' Geographica'', Sophene first emerged as a distinct kingdom under Zariadres (), who was installed as its ruler by the Seleucid king Antiochus III the Great (). He further adds that following the defeat of Antiochus III against the Romans, Zariadres declared independence. However this report is strongly contradicted by epigraphic and numismatic evidence. Sophene most likely emerged as a disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
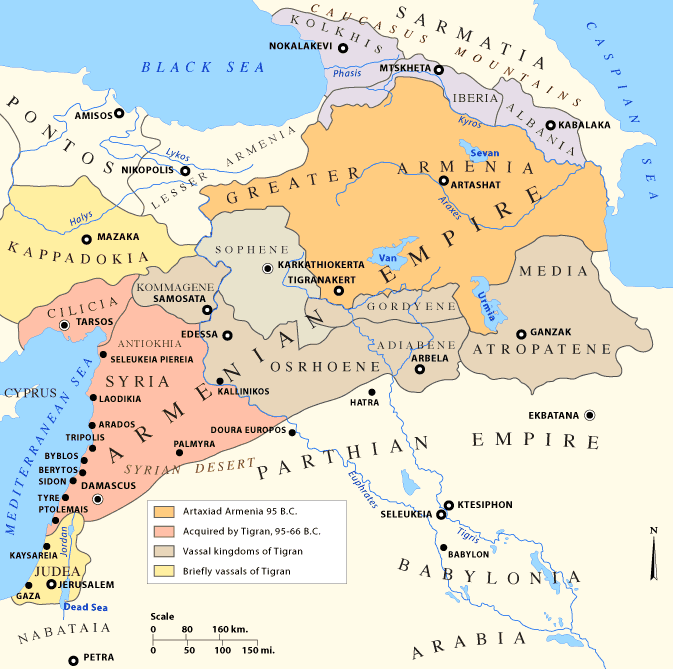
Kingdom Of Sophene
The Kingdom of Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopʻkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnḗ), was a Hellenistic-era political entity situated between ancient Armenia and Syria. Ruled by the Orontid dynasty, the kingdom was culturally mixed with Greek, Armenian, Iranian, Syrian, Anatolian and Roman influences. Founded around the 3rd century BCE, the kingdom maintained independence until when the Artaxiad king Tigranes the Great conquered the territories as part of his empire. Sophene laid near medieval Kharput, which is present day Elazığ. Name The name Sophene is thought to derive from the ethnonym ''Ṣuppani'', a people who lived in the region in the first half of the 1st millennium BCE and appear in Hittite and Assyrian sources. According to historian Nicholas Adontz, the Ancient Greek ''Sōphēnḗ'' was coined after the Armenian ''Tsopʻkʻ'', which stems directly from ''Ṣuppani''. History The Kingdom of Sophene was ruled by the Orontid dynasty of Iranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zariadres
Zariadres was an Orontid ruler of Sophene. Name ''Zariadres'' () is the Greek transliteration of an Iranian name, attested as ZRYTR (ZRYHR) in the Aramaic engravings in Sevan and Siwnik, and as ''Zareh'' in Armenian sources. The name is derived from Old Iranian ''Zari āθra'' ("with golden fire"). Biography Strabo cites Sophene being taken over by a "general" of king Antiochus III by 200 BC, called Zariadres.Strabo, ''Geography'' 11.14.5 Following the defeat of Antiochus III by the Romans at the Battle of Magnesia in 190 BC, Zariadres and Artaxias revolted and with Roman consent began to reign as kings under the terms of the Treaty of Apamea in 188 BC—Zariadres over Sophene and Artaxias over Armenia. It is possible that Zariadres (Dsariadres) was the father of Abdissares, although the scant historical records have Abdissares ruling before Zariadres. The name written as Dsariadris might be a Greek corruption of the name Bagdassar. A hypothesis is that king Bagdassar w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Persian continued to function as a prestige language. It descended from Old Persian, the language of the Achaemenid Empire and is the linguistic ancestor of Modern Persian, an official language of Iran, Afghanistan ( Dari) and Tajikistan ( Tajik). Name "Middle Iranian" is the name given to the middle stage of development of the numerous Iranian languages and dialects. The middle stage of the Iranian languages begins around 450 BCE and ends around 650 CE. One of those Middle Iranian languages is Middle Persian, i.e. the middle stage of the language of the Persians, an Iranian people of Persia proper, which lies in the south-western highlands on the border with Babylonia. The Persians called their language ''Parsik'', meaning "Persian" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building complex infrastructure, such as road systems and an organized postal system; the use of official languages across its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Armenia (antiquity)
The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք '; la, Armenia Maior), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three royal dynasties: Orontid (331 BC–200 BC), Artaxiad (189 BC–12 AD) and Arsacid (52–428). The root of the kingdom lies in one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia called Armenia (Satrapy of Armenia), which was formed from the territory of the Kingdom of Ararat (860 BC–590 BC) after it was conquered by the Median Empire in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty after the conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire. Under the Seleucid Empire (312–63 BC), the Armenian throne was divided in two—Armenia Maio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I (r. c. 171–132 BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce. The Parthians largely adopted the art, architecture, religious beliefs, and royal insignia of their culturally heterogene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian origin), which possibly may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. The kingdom was proclaimed by Mithridates I in 281BC and lasted until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 63BC. The Kingdom of Pontus reached its largest extent under Mithridates VI the Great, who conquered Colchis, Cappadocia, Bithynia, the Greek colonies of the Tauric Chersonesos, and for a brief time the Roman province of Asia. After a long struggle with Rome in the Mithridatic Wars, Pontus was defeated. The western part of it was incorporated into the Roman Republic as the province Bithynia et Pontus; the eastern half survived as a client kingdom until 62 AD. As the greater part of the kingdom lay within the region of Cappadocia, which in early ages extended from the borders of Cilicia to the Euxine (Black Sea), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Cappadocia
Cappadocia ( el, Καππαδοκία) was a Hellenistic-era Iranian kingdom centered in the historical region of Cappadocia in Asia Minor (present-day Turkey). It developed from the former Achaemenid satrapy of Cappadocia, and it was founded by its last satrap, Ariarathes (later Ariarathes I). Throughout its history, it was ruled by three families in succession; the House of Ariarathes (331–96 BC), the House of Ariobarzanes (96–36 BC), and lastly that of Archelaus (36 BC–17 AD). In 17 AD, following the death of Archelaus, during the reign of Roman emperor Tiberius (14–37 AD), the kingdom was incorporated as a Roman province. Origins and history Under the Achaemenids, the "Iranization" of Asia Minor had been significant, and a large Iranian presence had been established in western Asia Minor, Pontus and Cappadocia. Ariarathes had been satrap of Cappadocia for 19 years and a loyal supporter of the Achaemenid kings. By blood, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syro-Hittite States
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti and Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian belonging to the Anatolian group of Indo-European languages, and Aramaic belonging to the Northwest Semitic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arzanene
Arzanene ( el, Ἀρζανηνή) or Aghdznik () was a historical region in the southwest of the ancient kingdom of Armenia. It was ruled by one of the four ''bdeashkhs'' (''bidakhsh'', ''vitaxa'') of Armenia, the highest ranking nobles below the king who ruled over the kingdom's border regions. Its probable capital was the fortress-city of Arzen. The region briefly became home to the capital of Armenia during the reign of Tigranes the Great, who built his namesake city Tigranocerta there. Arzanene was placed under the direct suzerainty of the Roman Empire after the Peace of Nisibis in 298. It was briefly brought back under Armenian control c. 371 but was soon lost again following the partition of Armenia in 387. Name It is generally agreed the Greco-Roman name of Arzanene is derived from the city of Arzan (''Arzn'' or ''Aghzn'' in Armenian), which was probably the capital of the province. The name is identified with the ''Alzi'' or ''Alše'' mentioned in Neo-Assyrian and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Armenia
Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք, translit=Mets Hayk) is the name given to the Armenian state that emerged on the Armenian Highlands during the reign of King Artaxias I at the turn of the 2nd century BC. The term was used to refer principally to the fifteen provinces that made up Armenian kingdoms throughout the classical, late antique, and medieval periods by contemporary Armenian and non-Armenian authors alike. Extent Though its borders were never exactly defined, Greater Armenia usually referred to the stretch of land beginning from the Euphrates River to the west, the region of Artsakh and parts of what are now Azerbaijan and Iranian Azerbaijan to the east, parts of the modern state of Georgia to the north, with its southern boundary rounding the northern tip of Mesopotamia. The Romans referred to it in Latin as ''Armenia Maior'' while the Greek-speaking peoples called it ''Armenia Megale'' (), to differentiate it from Lesser Armenia (''Pok'r Hayk′'', in Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
%2C_Nisa_mint.jpg)