|
Saccharomyces Kudriavzevii
''Saccharomyces kudriavzevii'', is a species of yeast in the ''Saccharomyces sensu stricto'' complex. Its type strain is NCYC 2889T. It is used in production of alcoholic beverages, including pinot noir wine, and hybrids of it are used in beer brewing. It is isolated widely from the bark of oak trees (Quercus family). Etymology “''Kudriavzevii”'' was named in honor of VI Kudriavzev, a Russian scientist who worked with yeast taxonomy and ecology, and also played a large role in introducing the wild strain of ''S. paradoxus'' into science. Other names include: · ''S. kudriavzevii'' is the common scientific name · Pinot Noir yeast History ''Saccharomyces kudriavzevii'' was initially isolated from decayed leaf (Kaneko & Banno, 1991) but is often isolated from bark of oak trees. Description The species belongs to the ''Saccharomyces'' genus and can be isolated from a variety of substrates and is unique in that it cannot live on galactose and is cryotolerant. Biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces
''Saccharomyces'' is a genus of fungi that includes many species of yeasts. ''Saccharomyces'' is from Greek σάκχαρον (sugar) and μύκης (fungus) and means ''sugar fungus''. Many members of this genus are considered very important in food production. It is known as the brewer's yeast or baker's yeast. They are unicellular and saprotrophic fungi. One example is ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', which is used in making bread, wine, and beer, and for human and animal health. Other members of this genus include the wild yeast '' Saccharomyces paradoxus'' that is the closest relative to ''S. cerevisiae'', '' Saccharomyces bayanus'', used in making wine, and ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' var. ''boulardii'', used in medicine. Morphology Colonies of ''Saccharomyces'' grow rapidly and mature in three days. They are flat, smooth, moist, glistening or dull, and cream in color. The inability to use nitrate and ability to ferment various carbohydrates are typical characteristics of ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryotolerant
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cariocanus
''Saccharomyces cariocanus'', a type of yeast in the ''Saccharomyces sensu stricto'' complex. Its type strain is NCYC 2890T. Analyses did not confirm the previously observed conspecificity with ''Saccharomyces paradoxus ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' is a wild yeast and the closest known species to the baker's yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is used in population genomics and phylogenetic studies to compare its wild characteristics to laboratory yeasts. Eco ...''. ''S. cariocanus'' exhibits postzygotic isolation from representative strains from all known geographical populations of ''S. paradoxus'': European, Far-East Asian, North American and Hawaiian. References Further reading * External linksUniProt entry cariocanus Yeasts used in brewing Fungi described in 2000 {{Ascomycota-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Mikatae
''Saccharomyces mikatae'', a type of yeast in the ''Saccharomyces sensu stricto'' complex. Its type strain is NCYC 2888T. The cells are round to short-oval in shape, they arrange singly, in pairs and short-chain. Their budding Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ... is multipolar. See also *'' Saccharomyces kudriavzevii'' *'' Saccharomyces cariocanus'' *'' Saccharomyces paradoxus'' References Further reading * External links UniProt entry [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
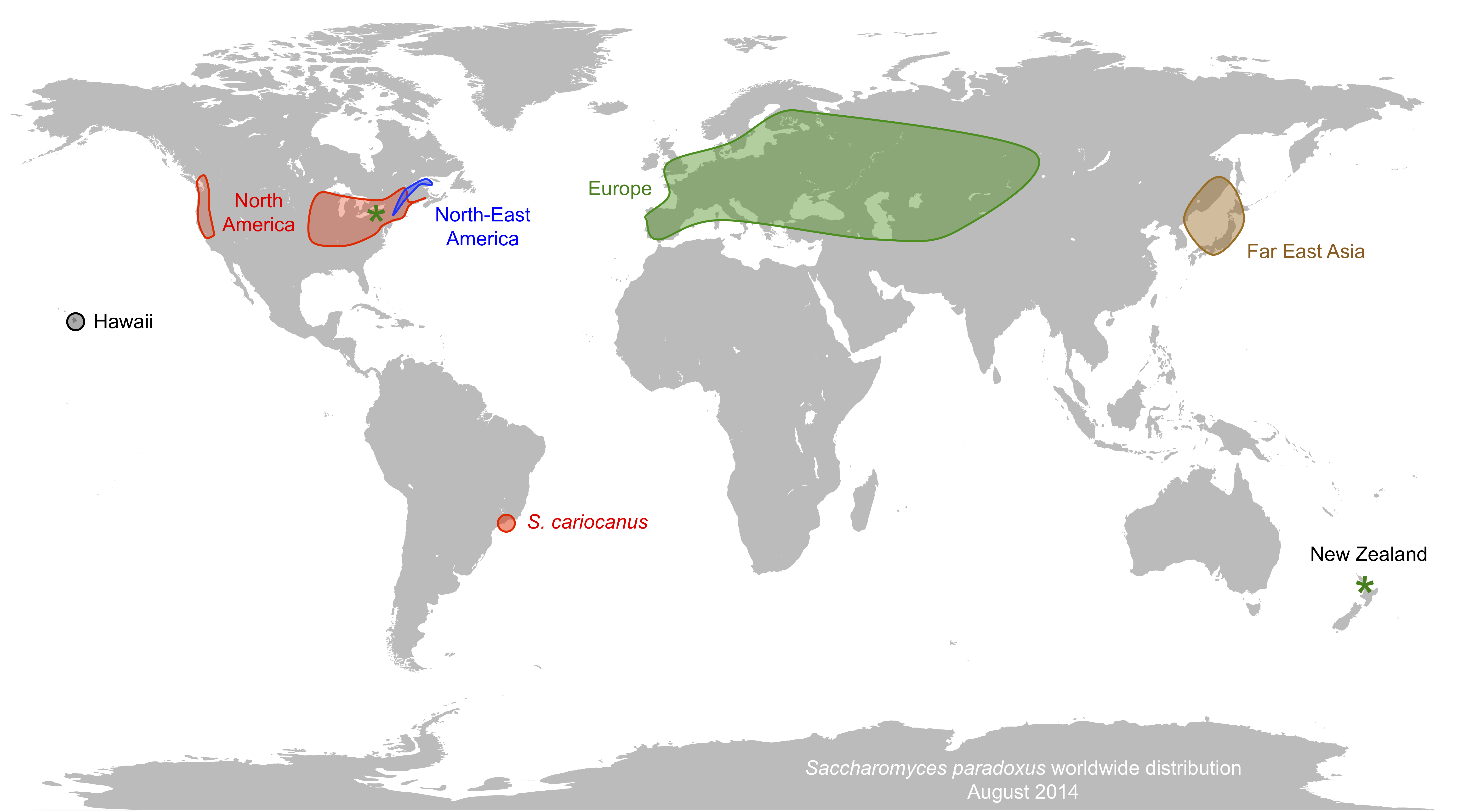
Saccharomyces Paradoxus
''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' is a wild yeast and the closest known species to the baker's yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''. It is used in population genomics and phylogenetic studies to compare its wild characteristics to laboratory yeasts. Ecology ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' is mostly isolated from deciduous trees (oak, maple, birch), and in some rare occasions on insects and fruits. It is often found in sympatry with other ''Saccharomyces'' species. Like ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', it has a worldwide distribution and it is mesophilic, which limits its natural distribution to low latitudes. However, ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' typically grows at lower temperatures than ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', resulting in a slight shift in its distribution toward cooler regions, like British islands and Eastern Canada. Biogeography Unlike most other ''Saccharomyces'' species, there is no evidence that ''Saccharomyces paradoxus'' has been domesticated by humans. Accordingly, its bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeasts Used In Brewing
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species. Yeasts are unicellular organisms that evolved from multicellular ancestors, with some species having the ability to develop multicellular characteristics by forming strings of connected budding cells known as pseudohyphae or false hyphae. Yeast sizes vary greatly, depending on species and environment, typically measuring 3–4 µm in diameter, although some yeasts can grow to 40 µm in size. Most yeasts reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by the asymmetric division process known as budding. With their single-celled growth habit, yeasts can be contrasted with molds, which grow hyphae. Fungal species that can take both forms (depending on temperature or other conditions) are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |