|
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic Electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered, even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and Atomic spectral line, atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete cancellation of the magnetic field in the interior of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-temperature Superconductors
High-temperature superconductivity (high-c or HTS) is superconductivity in materials with a critical temperature (the temperature below which the material behaves as a superconductor) above , the boiling point of liquid nitrogen. They are "high-temperature" only relative to previously known superconductors, which function only closer to absolute zero. The first high-temperature superconductor was discovered in 1986 by IBM researchers Georg Bednorz and K. Alex Müller. Although the critical temperature is around , this material was modified by Ching-Wu Chu to make the first high-temperature superconductor with critical temperature . Bednorz and Müller were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1987 "for their important break-through in the discovery of superconductivity in ceramic materials". Most high-c materials are type-II superconductors. The major advantage of high-temperature superconductors is that they can be cooled using liquid nitrogen, in contrast to previously k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
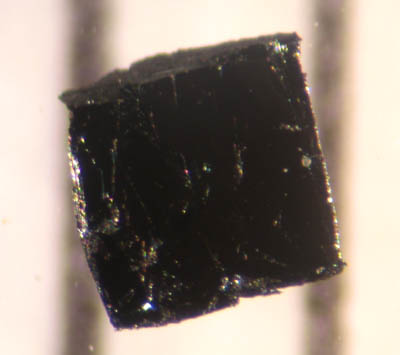
Cuprate Superconductor
Cuprate superconductors are a family of High-temperature superconductivity, high-temperature superconducting materials made of layers of copper oxides () alternating with layers of other metal oxides, which act as charge reservoirs. At ambient pressure, cuprate superconductors are the highest temperature superconductors known. Cuprates have a structure close to that of a two-dimensional material. Their superconducting properties are determined by electrons moving within weakly coupled copper-oxide () layers. Neighbouring layers contain ions such as lanthanum, barium, strontium, or other atoms that act to stabilize the structures and dope electrons or holes onto the copper-oxide layers. The undoped "parent" or "mother" compounds are Mott insulator, Mott insulators with long-range antiferromagnetic order at sufficiently low temperatures. Single Electronic band structure, band models are generally considered to be enough to describe the electronic properties. The cuprate supercon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ching-Wu Chu
Paul Ching Wu Chu (; born December 2, 1941) is a Taiwanese-American physicist specializing in superconductivity, magnetism, and dielectrics. He is a professor of physics and T.L.L. Temple Chair of Science in the UH Physics Department, Physics Department at the University of Houston College of Natural Sciences and Mathematics. He was the president of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology from 2001 to 2009. In 1987, he was one of the first scientists to demonstrate high-temperature superconductor, high-temperature superconductivity. Early life and education Chu was born in Changsha, Hunan, Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China in 1941. Chu's family was from Taishan, Guangdong, Taishan, Guangdong. Chu spent his childhood in Taiwan. In 1958, Chu graduated from National Qingshui Senior High School, Taiwan Provincial Cingshuei high school. In 1962, Chu earned his Bachelor of Science degree from National Cheng Kung University in Taiwan. In 1965, he earned his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meissner Effect
In condensed-matter physics, the Meissner effect (or Meißner–Ochsenfeld effect) is the expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor during its transition to the superconducting state when it is cooled below the critical temperature. This expulsion will repel a nearby magnet. The German physicists Walther Meissner, Walther Meißner (anglicized ''Meissner'') and Robert Ochsenfeld discovered this phenomenon in 1933 by measuring the magnetic field distribution outside superconducting tin and lead samples. The samples, in the presence of an applied magnetic field, were cooled below their Superconductivity#Superconducting phase transition, superconducting transition temperature, whereupon the samples cancelled nearly all interior magnetic fields. They detected this effect only indirectly because the magnetic flux is conserved by a superconductor: when the interior field decreases, the exterior field increases. The experiment demonstrated for the first time that superconducto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and has often been classified as a "rare-earth element". Yttrium is almost always found in combination with lanthanide elements in rare-earth minerals and is never found in nature as a free element. 89Y is the only stable isotope and the only isotope found in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. The most important present-day use of yttrium is as a component of phosphors, especially those used in LEDs. Historically, it was once widely used in the red phosphors in television set cathode ray tube displays. Yttrium is also used in the production of electrodes, electrolytes, electronic filters, lasers, superconductors, various medical applications, and Trace element, tracing various materials to enhance their properties. Yttrium has no known Biology, biological role. Exposure to yttrium compounds can cause Respiratory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YBCO
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconductivity, superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen [] at about . Many YBCO compounds have the general formula (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as (Y124) or (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Alexander Müller, Karl Müller, working at IBM Research – Zurich, IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superconducting Wire
Superconducting wires are electrical wires made of superconductive material. When cooled below their transition temperatures, they have zero electrical resistance. Most commonly, conventional superconductors such as niobium–titanium are used, but high-temperature superconductors such as YBCO are entering the market. Superconducting wire's advantages over copper or aluminum include higher maximum current densities and zero power dissipation. Its disadvantages include the cost of refrigeration of the wires to superconducting temperatures (often requiring cryogens such as liquid nitrogen or liquid helium), the danger of the wire quenching (a sudden loss of superconductivity), the inferior mechanical properties of some superconductors, and the cost of wire materials and construction. Its main application is in superconducting magnets, which are used in scientific and medical equipment where high magnetic fields are necessary. Important parameters The construction and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes
Heike Kamerlingh Onnes (; 21 September 1853 – 21 February 1926) was a Dutch Experimental physics, experimental physicist. After studying in Groningen and Heidelberg, he became Professor of Experimental Physics at Leiden University, where he taught from 1882 to 1923. In 1904, he established a cryogenics laboratory where he exploited the Hampson–Linde cycle to investigate how materials behave when cooled to nearly absolute zero. In 1908, he became the first to liquefaction of gases, liquefy helium, cooling it to near 1.5 kelvin, at the time the coldest temperature achieved on earth. For this research, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1913. Using liquid helium to investigate the electrical conductivity of solid mercury (element), mercury, he found in 1911 that at 4.2 K its electrical resistance vanishes, thus discovering superconductivity. Early life Kamerlingh Onnes was born in Groningen, Netherlands. His father, Harm Kamerlingh Onnes, was a brickworks owner. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were fired clay bricks used for building house walls and other structures. Other pottery objects such as pots, vessels, vases and figurines were made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened by sintering in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial, and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as semiconductors. The word '' ceramic'' comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Zero
Absolute zero is the lowest possible temperature, a state at which a system's internal energy, and in ideal cases entropy, reach their minimum values. The absolute zero is defined as 0 K on the Kelvin scale, equivalent to −273.15 °C on the Celsius, Celsius scale, and −459.67 °F on the Fahrenheit scale. The Kelvin and Rankine temperature scales set their zero points at absolute zero by design. This limit can be estimated by extrapolating the ideal gas law to the temperature at which the volume or pressure of a classical gas becomes zero. At absolute zero, there is no thermal motion. However, due to quantum mechanics, quantum effects, the particles still exhibit minimal motion mandated by the Uncertainty principle, Heisenberg uncertainty principle and, for a system of fermions, the Pauli exclusion principle. Even if absolute zero could be achieved, this residual quantum motion would persist. Although absolute zero can be approached, it cannot be reached. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Conductor
In electrostatics, a perfect conductor is an idealized model for real conducting materials. The defining property of a perfect conductor is that static electric field and the charge density both vanish in its interior. If the conductor has excess charge, it accumulates as an infinitesimally thin layer of surface charge. An external electric field is screened from the interior of the material by rearrangement of the surface charge. Alternatively, a perfect conductor is an idealized material exhibiting infinite electrical conductivity or, equivalently, zero resistivity (cf. perfect dielectric). While perfect electrical conductors do not exist in nature, the concept is a useful model when electrical resistance is negligible compared to other effects. One example is ideal magnetohydrodynamics, the study of perfectly conductive fluids. Another example is electrical circuit diagrams, which carry the implicit assumption that the wires connecting the components have no resistance. Yet a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Superconductor
Conventional superconductors are materials that display superconductivity as described by BCS theory or its extensions. This is in contrast to unconventional superconductors, which do not. Conventional superconductors can be either type-I or type-II. Most elemental An elemental is a mythic supernatural being that is described in occult and alchemy, alchemical works from around the time of the European Renaissance, and particularly elaborated in the 16th century works of Paracelsus. According to Paracelsu ... superconductors are conventional. Niobium and vanadium are type-II, while most other elemental superconductors are type-I. Critical temperatures of some elemental superconductors: Most compound and alloy superconductors are type-II materials. The most commonly used conventional superconductor in applications is a niobium-titanium alloy - this is a type-II superconductor with a superconducting critical temperature of 11 K. The highest critical temperature so far achie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |