|
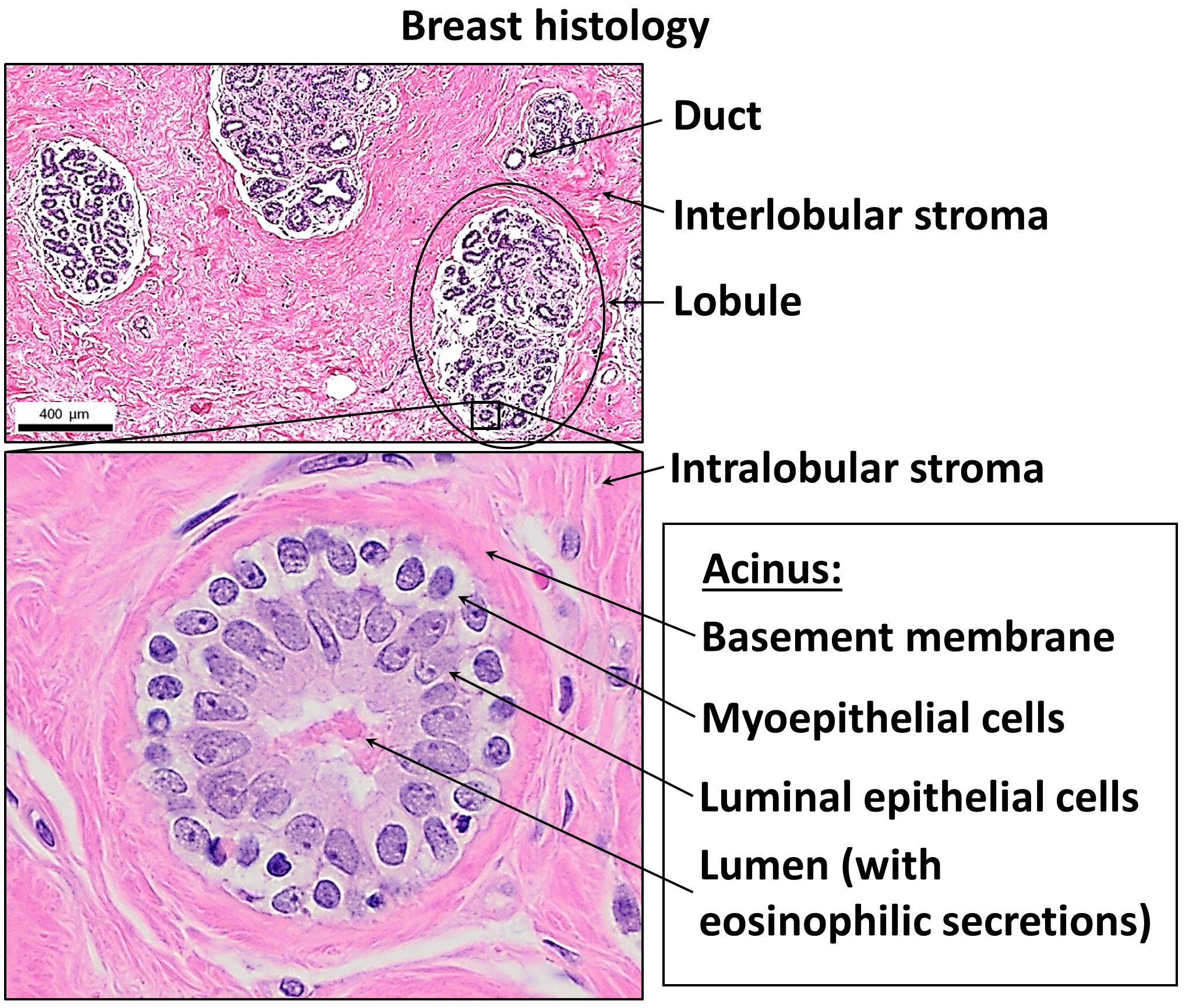
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina. In the epidermis of skin in mammals, reptiles, and birds, the layer of keratin in the outer layer of the stratified squamous epithelial surface is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of Cell (biology), cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial (Mesothelium, mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organ (anatomy), organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal Tissue (biology), tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then Histopathology, fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is composed of 15–20 layers of flattened cells with no nuclei and cell organelles. Among its properties are mechanical shear, impact resistance, water flux and hydration regulation, microbial proliferation and invasion regulation, initiation of inflammation through cytokine activation and dendritic cell activity, and selective permeability to exclude toxins, irritants, and allergens. The cytoplasm of its cells shows filamentous keratin. These corneocytes are embedded in a lipid matrix composed of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids. Desquamation is the process of cell shedding from the surface of the stratum corneum, balancing proliferating keratinocytes that form in the stratum basale. These cells migrate through the epidermis tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrett's Esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, interspersed with goblet cells that are normally only found in the small intestine and large intestine. This change is considered to be a premalignant condition because of its potential to transition into esophageal adenocarcinoma, an often-deadly cancer. The main cause of Barrett's esophagus is tissue adaptation to chronic acid exposure caused by reflux from the stomach. Barrett's esophagus is diagnosed by endoscopy to visually observe the lower esophagus, followed by a biopsy of the affected area and microscopic examination of that tissue. The cells of Barrett's esophagus are classified into four categories: nondysplastic, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia, and carcinoma. High-grade dysplasia and early stages of adenocarcinoma may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaplasia
Metaplasia () is the transformation of a cell type to another cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus. In simplistic terms, it is as if the original cells are not robust enough to withstand their environment, so they transform into another cell type better suited to their environment. If the stimulus causing metaplasia is removed or ceases, tissues return to their normal pattern of differentiation. Metaplasia is not synonymous with dysplasia, and is not considered to be an actual cancer. It is also contrasted with heteroplasia, which is the spontaneous abnormal growth of cytologic and histologic elements. Today, metaplastic changes are usually considered to be an early phase of carcinogenesis, specifically for those with a history of cancers or who are known to be susceptible to carcinogenic changes. Metaplastic change is thus often viewed as a premalignant condition th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed '' lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: * ''Lining mucosa'', nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: ** ''Alveolar mucosa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinocyte
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually being shed, which happens every 40 to 56 days in humans. Function The primary function of keratinocytes is the formation of a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, dehydration, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. Pathoge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands (Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Lymphatic vessel#Afferent vessels, Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectum
The rectum (: rectums or recta) is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. Before expulsion through the anus or cloaca, the rectum stores the feces temporarily. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the level of the third sacral vertebra or the sacral promontory depending upon what definition is used. Its diameter is similar to that of the sigmoid colon at its commencement, but it is dilated near its termination, forming the rectal ampulla. It terminates at the level of the anorectal ring (the level of the puborectalis sling) or the dentate line, again depending upon which definition is used. In humans, the rectum is followed by the anal canal, which is about long, before the gastrointestinal tract terminates at the anal verge. The word rectum comes from the Latin '' rēctum intestīnum'', meaning ''straight intestine''. Struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly Angiogenesis, vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |