|
Straddle
In finance, a straddle strategy involves two transactions in options on the same underlying, with opposite positions. One holds long risk, the other short. As a result, it involves the purchase or sale of particular option derivatives that allow the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying security moves, regardless of the ''direction'' of price movement. A straddle involves buying a call and put with same strike price and expiration date. If the stock price is close to the strike price at expiration of the options, the straddle leads to a loss. However, if there is a sufficiently large move in either direction, a significant profit will result. A straddle is appropriate when an investor is expecting a large move in a stock price but does not know in which direction the move will be. A straddle made from the ''purchase'' of options is known as a long straddle, bottom straddle, or straddle purchase, while the reverse position, made from the ''sale'' of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Options Strategy
Option strategies are the simultaneous, and often mixed, buying or selling of one or more Option (finance), options that differ in one or more of the options' variables. Call options, simply known as Calls, give the buyer a right to buy a particular stock at that option's strike price. Opposite to that are Put options, simply known as Puts, which give the buyer the right to sell a particular stock at the option's strike price. This is often done to gain exposure to a specific type of opportunity or risk while eliminating other risks as part of a trading strategy. A very straightforward strategy might simply be the buying or selling of a single option; however, option strategies often refer to a combination of simultaneous buying and or selling of options. Options strategies allow traders to profit from movements in the underlying assets based on market sentiment (i.e., bullish, bearish or neutral). In the case of neutral strategies, they can be further classified into those that ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strangle (options)
In finance, a strangle is an options strategy involving the purchase or sale of two options, allowing the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying security moves, with a neutral exposure to the ''direction'' of price movement. A strangle consists of one call and one put with the same expiry and underlying but different strike prices. Typically the call has a higher strike price than the put. If the put has a higher strike price instead, the position is sometimes called a guts. If the options are purchased, the position is known as a long strangle, while if the options are sold, it is known as a short strangle. A strangle is similar to a straddle position; the difference is that in a straddle, the two options have the same strike price. Given the same underlying security, strangle positions can be constructed with a lower cost but lower probability of profit than straddles. Characteristics A strangle, requires the investor to simultaneously buy or sell b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a contract which conveys to its owner, the ''holder'', the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific quantity of an underlying asset or instrument at a specified strike price on or before a specified date, depending on the style of the option. Options are typically acquired by purchase, as a form of compensation, or as part of a complex financial transaction. Thus, they are also a form of asset (or contingent liability) and have a valuation that may depend on a complex relationship between underlying asset price, time until expiration, market volatility, the risk-free rate of interest, and the strike price of the option. Options may be traded between private parties in '' over-the-counter'' (OTC) transactions, or they may be exchange-traded in live, public markets in the form of standardized contracts. Definition and application An option is a contract that allows the holder the right to buy or sell an underlying asset or financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Leeson
Nicholas William Leeson (born 25 February 1967) is an English former derivatives trader whose fraudulent, unauthorised and speculative trades resulted in the 1995 collapse of Barings Bank, the United Kingdom's oldest existing merchant bank. He was convicted of financial crime in a Singapore court and served over four years in Changi Prison. Between 2005 and 2011, Leeson had senior management roles at League of Ireland football club Galway United. After it suffered financial difficulties, he resigned from his position as chief executive officer. He is also active on the keynote and after-dinner speaking circuit, where he advises companies about risk and corporate responsibility. Since 2023, he has been a private investigator dealing with cases of financial misconduct. Early life Nick Leeson was born in Watford, Hertfordshire, to working-class parents on a council estate. His father was a self-employed plasterer, his mother a nurse. He attended Parmiter's School in near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterfly (options)
In finance, a butterfly (or simply fly) is a limited risk, non-directional options strategy that is designed to have a high probability of earning a limited profit when the future volatility of the underlying asset is expected to be lower (when long the butterfly) or higher (when short the butterfly) than that asset's current implied volatility. Long butterfly A long butterfly position will make profit if the future volatility is lower than the implied volatility. A long butterfly options strategy consists of the following options: * Long 1 call with a strike price of (X − a) * Short 2 calls with a strike price of X * Long 1 call with a strike price of (X + a) where X = the spot price (i.e. current market price of underlying) and a > 0. Using put–call parity a long butterfly can also be created as follows: * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X + a) * Short 2 puts with a strike price of X * Long 1 put with a strike price of (X − a) where X = the spot price an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barings Bank
Barings Bank was a British merchant bank based in London. It was one of England's oldest merchant banks after Berenberg Bank, Barings' close collaborator and German representative. It was founded in 1762 by Francis Baring, a British-born member of the German–British Baring family of merchants and bankers. The bank collapsed in 1995 after suffering losses of £827 million (£ billion in ) resulting from fraudulent investments, primarily in futures contracts, conducted by its employee Nick Leeson working at its office in Singapore. History 1762–1889 Barings Bank was founded in 1762 as the John and Francis Baring Company by Sir Francis Baring, 1st Baronet, with his older brother John Baring as a mostly silent partner. They were sons of John (né Johann) Baring, wool trader of Exeter, born in Bremen, Germany. The company started business in offices off Cheapside in London, and within a few years moved to larger quarters in Mincing Lane.D. Kinaston. The City of London, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Option
In finance, the style or family of an option is the class into which the option falls, usually defined by the dates on which the option may be exercised. The vast majority of options are either European or American (style) options. These options—as well as others where the payoff is calculated similarly—are referred to as " vanilla options". Options where the payoff is calculated differently are categorized as "exotic options". Exotic options can pose challenging problems in valuation and hedging. American and European options The key difference between American and European options relates to when the options can be exercised: * A European option may be exercised only at the expiration date of the option, i.e. at a single pre-defined point in time. * An American option on the other hand may be exercised at any time before the expiration date. For both, the payoff—when it occurs—is given by * \max\, for a call option * \max\, for a put option where K is the strike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
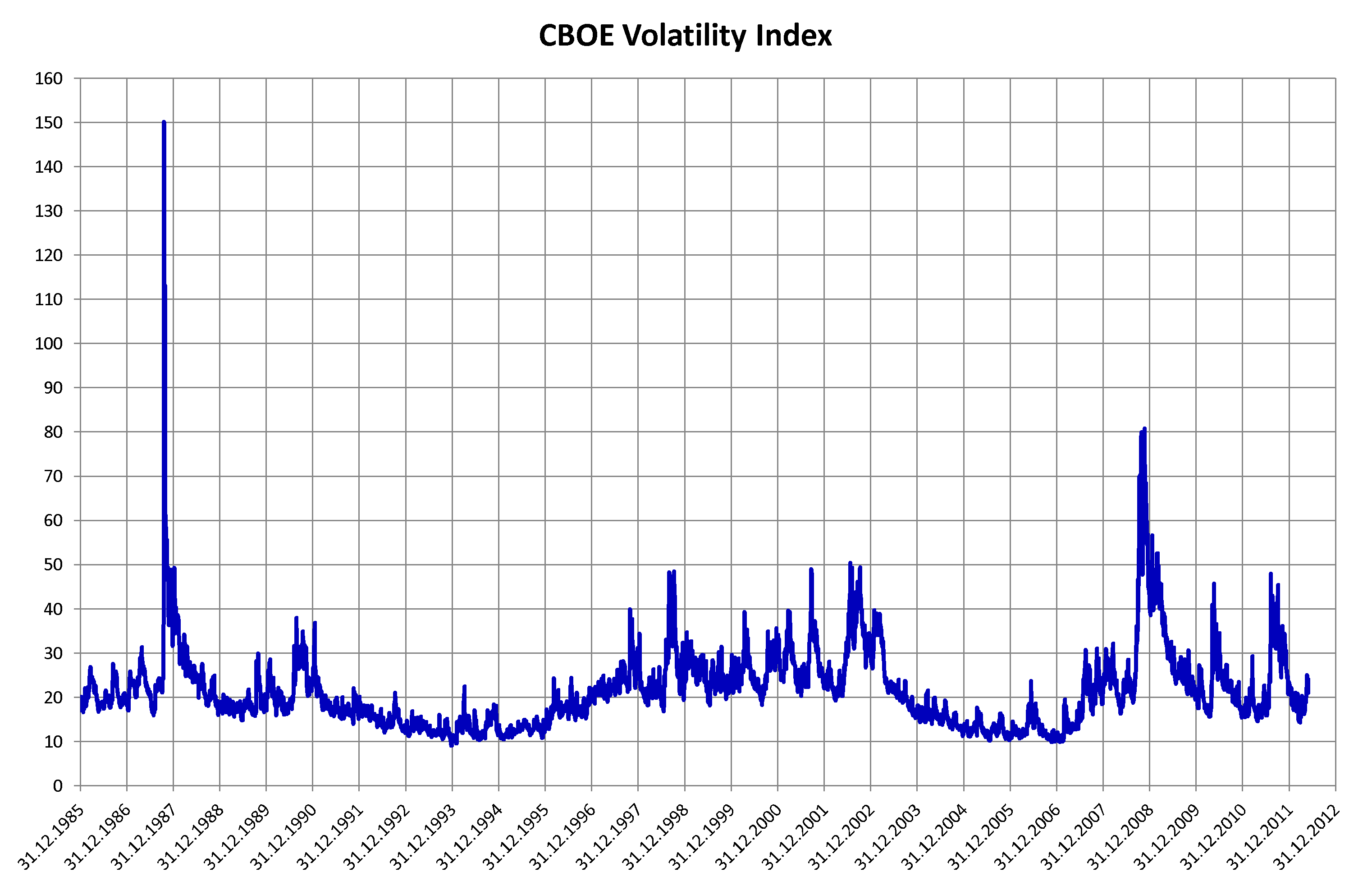
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index (economics)
In economics, statistics, and finance, an index is a number that measures how a group of related data points—like prices, company performance, productivity, or employment—changes over time to track different aspects of economic health from various sources. Consumer-focused indices include the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which shows how retail prices for goods and services shift in a fixed area, aiding adjustments to salaries, Bond (finance), bond interest rates, and tax thresholds for inflation. The cost-of-living index (COLI) compares living expenses over time or across places.Turvey, Ralph. (2004) Consumer Price Index Manual: Theory And Practice.' Page 11. Publisher: International Labour Organization. . ''The Economist''’s Big Mac Index uses a Big Mac’s cost to explore currency values and purchasing power. Market performance indices track trends like company value or employment. Stock market index, Stock market indices include the Dow Jones Industrial Average and S&P 500, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Administration wich study the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of an organization's resources to achieve its goals. Based on the scope of financial activities in financial systems, the discipline can be divided into Personal finance, personal, Corporate finance, corporate, and public finance. In these financial systems, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as Currency, currencies, loans, Bond (finance), bonds, Share (finance), shares, stocks, Option (finance), options, Futures contract, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, Investment, invested, and Insurance, insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, Financial risk, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed. The annual interest rate is the rate over a period of one year. Other interest rates apply over different periods, such as a month or a day, but they are usually annualized. The interest rate has been characterized as "an index of the preference . . . for a dollar of present ncomeover a dollar of future income". The borrower wants, or needs, to have money sooner, and is willing to pay a fee—the interest rate—for that privilege. Influencing factors Interest rates vary according to: * the government's directives to the central bank to accomplish the government's goals * the currency of the principal sum lent or borrowed * the term to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |