|
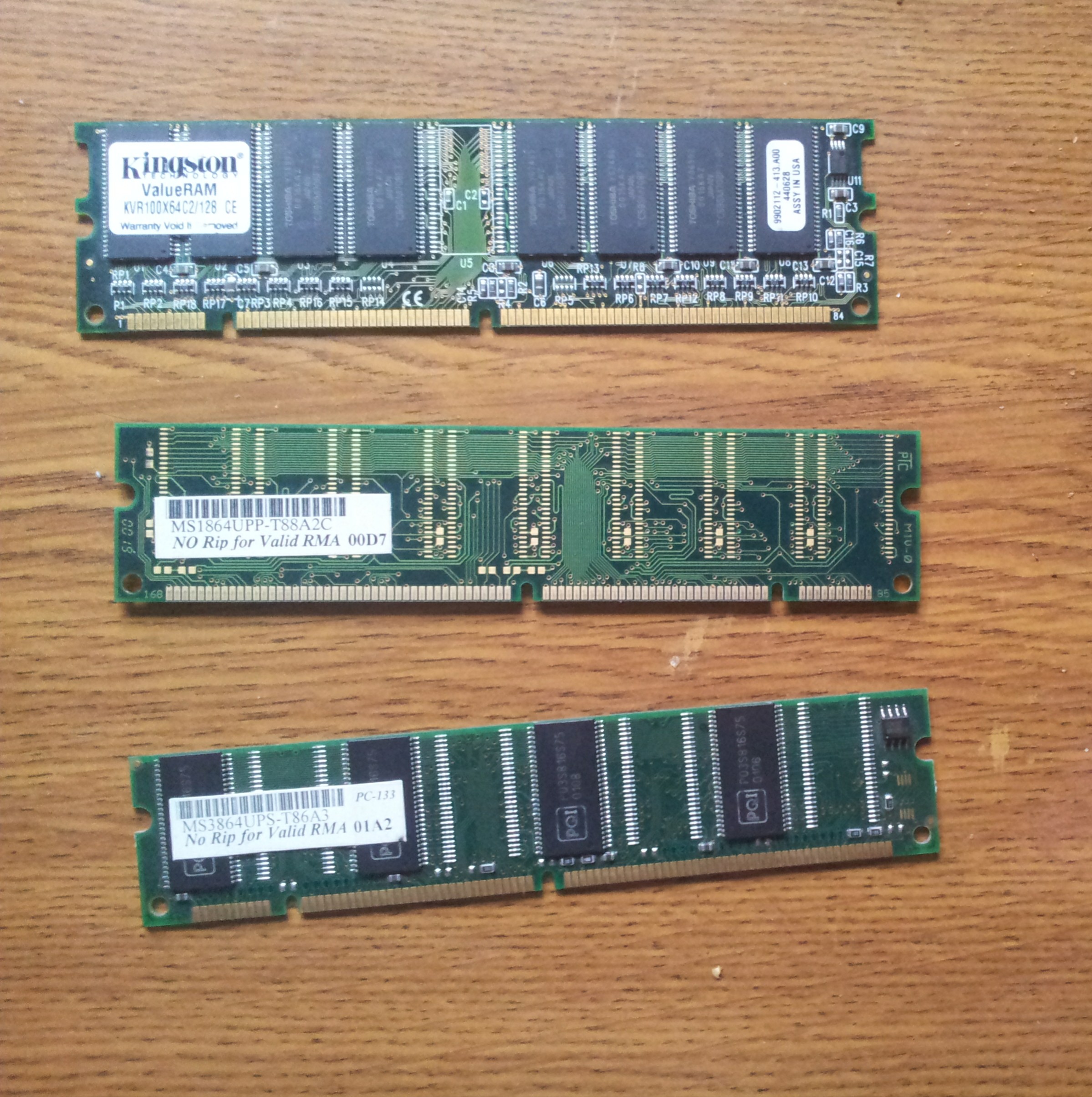
Static Random-access Memory
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed. The ''static'' qualifier differentiates SRAM from ''dynamic'' random-access memory (DRAM): * SRAM will hold its data permanently in the presence of power, while data in DRAM decays in seconds and thus must be periodically refreshed. * SRAM is faster than DRAM but it is more expensive in terms of silicon area and cost. * Typically, SRAM is used for the cache and internal registers of a CPU while DRAM is used for a computer's main memory. History Semiconductor bipolar SRAM was invented in 1963 by Robert Norman at Fairchild Semiconductor. Metal–oxide–semiconductor SRAM (MOS-SRAM) was invented in 1964 by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor. The first device was a 64-bit MOS p-channel SRAM. SRAM was the main driver behind any new CMOS-based technology fab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Dynamic Random-access Memory
Synchronous dynamic random-access memory (synchronous dynamic RAM or SDRAM) is any DRAM where the operation of its external pin interface is coordinated by an externally supplied clock signal. DRAM integrated circuits (ICs) produced from the early 1970s to the early 1990s used an ''asynchronous'' interface, in which input control signals have a direct effect on internal functions delayed only by the trip across its semiconductor pathways. SDRAM has a ''synchronous'' interface, whereby changes on control inputs are recognised after a rising edge of its clock input. In SDRAM families standardized by JEDEC, the clock signal controls the stepping of an internal finite-state machine that responds to incoming commands. These commands can be pipelined to improve performance, with previously started operations completing while new commands are received. The memory is divided into several equally sized but independent sections called ''banks'', allowing the device to operate on a memor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electronic component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-ported RAM
Dual-ported RAM (DPRAM), also called dual-port RAM, is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that can be accessed via two different buses. A simple dual-port RAM may allow only read access through one of the ports and write access through the other, in which case the same memory location cannot be accessed simultaneously through the ports since a write operation modifies the data and therefore needs to be synchronized with a read or another write operation. A dual-port RAM may be built from single-port memory cells to reduce cost or circuit complexity, and the performance penalty associated with it, which may still allow simultaneous read and write accesses to different memory locations depending on the partitioning of the memory array and having duplicate decoder paths to the partitions. A true dual-port memory has two independent ports, which means that the memory array is built from dual-port memory-cells, and the address, data, and control lines of the two ports are connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microscope
The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast. The object is placed on a stage and may be directly viewed through one or two eyepieces on the microscope. In high-power microscopes, both eyepieces typically show the same image, but with a stereo microscope, slightly different images are used to create a 3-D effect. A camera is typically used to capture the image (micrograph). The sample can be lit in a variety of ways. Transparent objects can be lit from below and solid objects can be lit with light coming through ( bright field) or around ( dark field) the objective lens. Polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Electron Microscope
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that contain information about the surface topography and composition. The electron beam is scanned in a raster scan pattern, and the position of the beam is combined with the intensity of the detected signal to produce an image. In the most common SEM mode, secondary electrons emitted by atoms excited by the electron beam are detected using a secondary electron detector ( Everhart–Thornley detector). The number of secondary electrons that can be detected, and thus the signal intensity, depends, among other things, on specimen topography. Some SEMs can achieve resolutions better than 1 nanometer. Specimens are observed in high vacuum in a conventional SEM, or in low vacuum or wet conditions in a variable pressure or environmental SEM, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometre
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling), is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth ( short scale) or one thousand million (long scale) of a meter (0.000000001 m) and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as 1 × 10−9 m and as m. History The nanometre was formerly known as the "''millimicrometre''" – or, more commonly, the "''millimicron''" for short – since it is of a micrometer. It was often denoted by the symbol ''mμ'' or, more rarely, as ''μμ'' (however, ''μμ'' should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron). Etymology The name combines the SI prefix '' nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
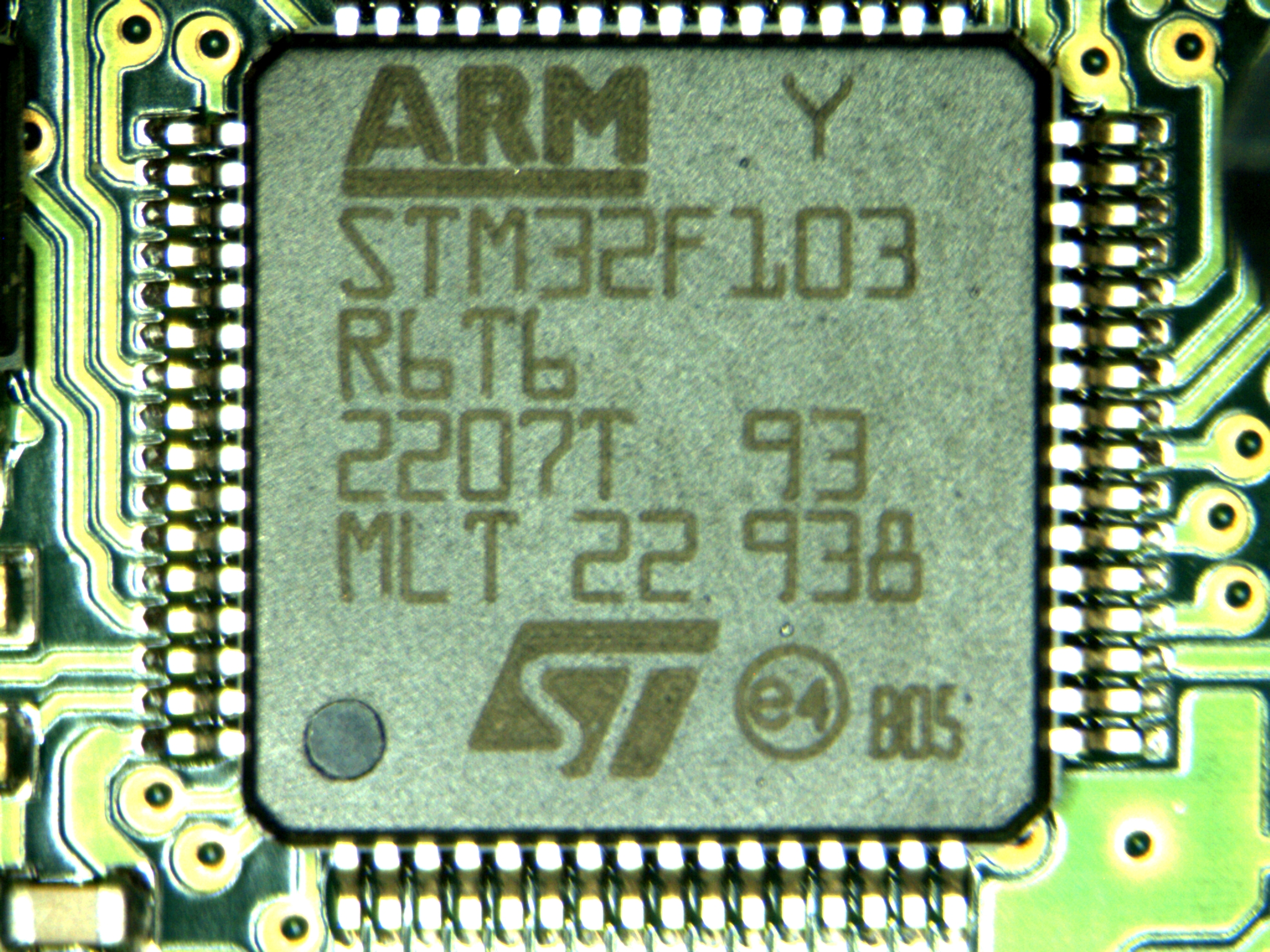
STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics Naamloze vennootschap, NV (commonly referred to as ST or STMicro) is a European multinational corporation, multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the largest of such companies in Europe. It was founded in 1987 from the merger of two state-owned semiconductor corporations: ''Thomson Semiconducteurs'' of United States/France and ''SGS Microelettronica'' of Italy. The company is incorporated in the Netherlands and headquartered in Plan-les-Ouates, Switzerland. Its shares are traded on Euronext Paris, the Borsa Italiana and the New York Stock Exchange. History ST was formed in 1987 by the merger of two government-owned semiconductor companies: Italian SGS Microelettronica (where SGS stands for ''Società Generale Semiconduttori'', "General Semiconductor Company"), and French ''Thomson Semiconducteurs'', the semiconductor arm of Thomson SA, Thomson. SGS Microelettronica originated in 1972 from a previous merger of two compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). A SoC may include a microcontroller as one of its components but usually integrates it with advanced peripherals like a graphics processing unit (GPU), a Wi-Fi module, or one or more coprocessors. Microcontrollers are used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
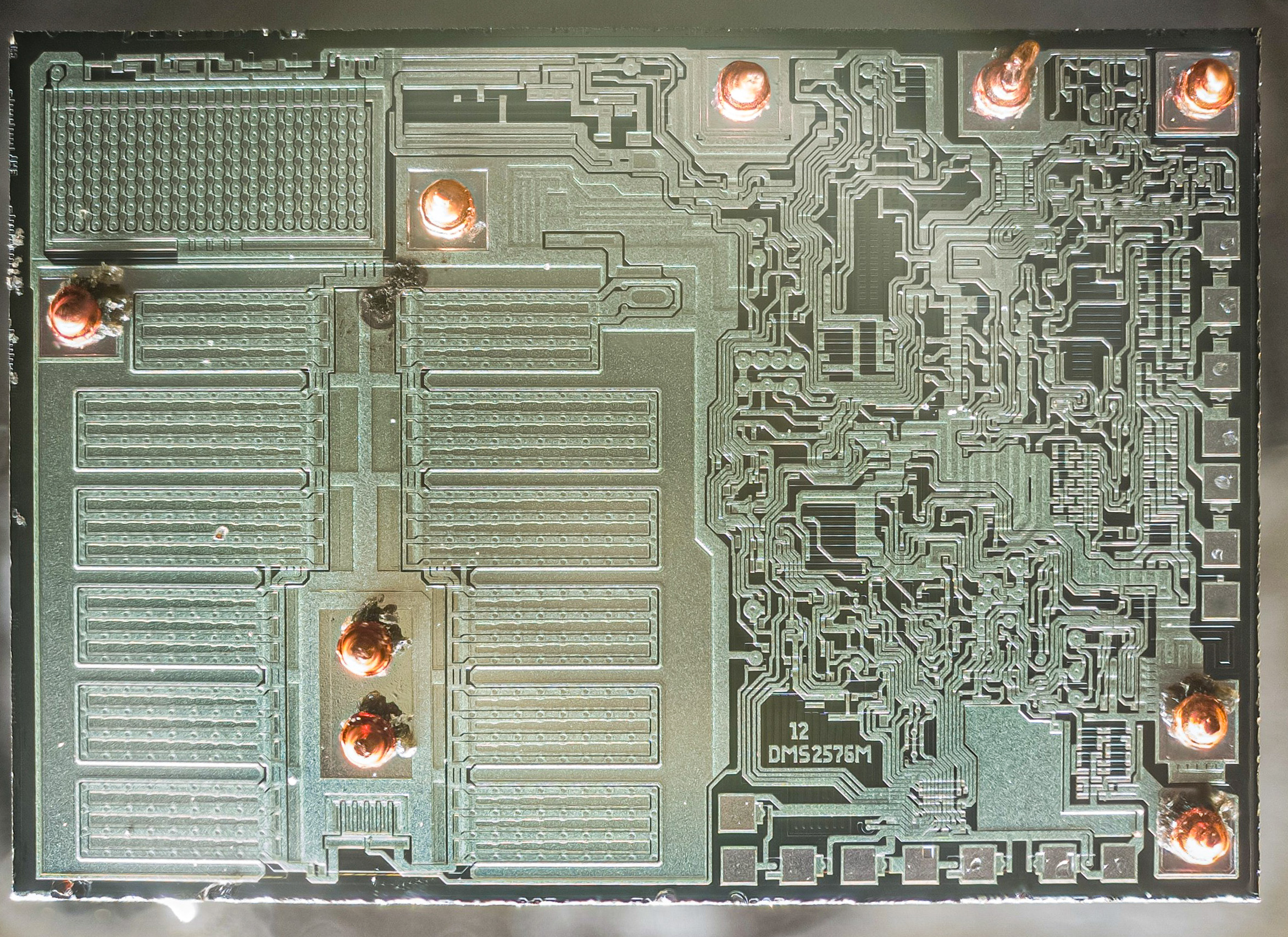
Die (integrated Circuit)
A die, in the context of integrated circuits, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is Semiconductor fabrication, fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer (electronics), wafer of electronic-grade Monocrystalline silicon, silicon (EGS) or other semiconductor (such as Gallium arsenide, GaAs) through processes such as photolithography. The wafer is cut (wafer dicing, diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die. There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board, most dies are integrated circuit packaging, packaged in List of electronic component packaging types, various forms. Manufacturing process Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of Single crystal, monocrystalline sili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Consumption
Electric energy consumption is energy consumption in the form of electrical energy. About a fifth of global energy is consumed as electricity: for residential, industrial, commercial, transportation and other purposes. The global electricity consumption in 2022 was 24,398 terawatt-hour (TWh), almost exactly three times the amount of consumption in 1981 (8,132 TWh). China, the United States, and India accounted for more than half of the global share of electricity consumption. Japan and Russia followed with nearly twice the consumption of the remaining industrialized countries. Overview Electric energy is most often measured either in joules (J), or in watt hours (W·h). : 1 W·s = 1 J : 1 W·h = 3,600 W·s = 3,600 J : 1 kWh = 3,600 kWs = 1,000 Wh = 3.6 million W·s = 3.6 million J Electric and electronic devices consume electric energy to generate desired output (light, heat, motion, etc.). During operation, some part of the energy is lost depending on the electrical efficien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Remanence
Data remanence is the residual representation of digital data that remains even after attempts have been made to remove or erase the data. This residue may result from data being left intact by a nominal file deletion operation, by reformatting of storage media that does not remove data previously written to the media, or through physical properties of the storage media that allow previously written data to be recovered. Data remanence may make inadvertent disclosure of sensitive information possible should the storage media be released into an uncontrolled environment (''e.g.'', thrown in the bin (trash) or lost). Various techniques have been developed to counter data remanence. These techniques are classified as clearing, purging/sanitizing, or destruction. Specific methods include overwriting, degaussing, encryption, and media destruction. Effective application of countermeasures can be complicated by several factors, including media that are inaccessible, media that c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |