|
Static Analysis
Static analysis, static projection, or static scoring is a simplified analysis wherein the effect of an immediate change to a system is calculated without regard to the longer-term response of the system to that change. If the short-term effect is then extrapolated to the long term, such extrapolation is inappropriate. Its opposite, dynamic analysis or dynamic scoring, is an attempt to take into account how the system is likely to respond to the change over time. One common use of these terms is budget policy in the United States, although it also occurs in many other statistical disputes. Examples A famous example of extrapolation of static analysis comes from overpopulation theory. Starting with Thomas Malthus at the end of the 18th century, various commentators have projected some short-term population growth trend for years into the future, resulting in the prediction that there would be disastrous overpopulation within a generation or two. Malthus himself essentially cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
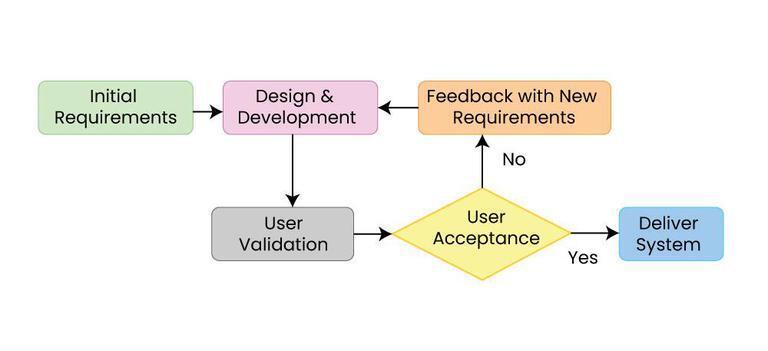 |
Software Development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, writing source code, code, in that it includes conceiving the goal, evaluating feasibility, analyzing software requirements, requirements, software design, design, software testing, testing and software release life cycle, release. The process is part of software engineering which also includes management, organizational management, Software project management, project management, configuration management and other aspects. Software development involves many skills and job specializations including software programmer, programming, software test, testing, Technical writing, documentation, graphic design, user support, marketing, and fundraising. Software development involves many software tools, tools including: compiler, integrated develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Dynamic Scoring
Dynamic scoring is a forecasting technique for government revenues, expenditures, and budget deficits that incorporates predictions about the behavior of people and organizations based on changes in fiscal policy, usually tax rates. Dynamic scoring depends on models of the behavior of economic agents which predict how they would react once the tax rate or other policy change goes into effect. This means the uncertainty induced in predictions is greater to the degree that the proposed policy is unlike current policy. Unfortunately, any such model depends heavily on judgment, and there is no evidence that it is more effective or accurate. For example, a dynamic scoring model may include econometric model of a transitional phase as the population adapts to the new policy, rather than the so-called static-scoring alternative of standard assumption about behavior of people being immediately and directly sensitive to prices. The outcome of the dynamic analysis is therefore heavily depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Fiscal Policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation and to increase employment. In modern economies, inflation is conventionally considered "healthy" in the range of 2%–3%. Add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Human Overpopulation
Human overpopulation (or human population overshoot) is the idea that human populations may become too large to be sustainability, sustained by their environment or resources in the long term. The topic is usually discussed in the context of world population, though it may concern individual nations, regions, and cities. Since 1804, the global living human population has World population milestones, increased from 1 billion to 8 billion due to Modern medicine, medical advancements and improved agricultural productivity. Annual world population growth peaked at 2.1% in 1968 and has since dropped to 1.1%. According to the most recent Projections of population growth, United Nations' projections, the global human population is expected to reach 9.7 billion in 2050 and would peak at around 10.4 billion people in the 2080s, before decreasing, noting that fertility rates are falling worldwide. Other models agree that the population will stabilize before or after 2100. Conversely, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Thomas Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English economist, cleric, and scholar influential in the fields of political economy and demography. In his 1798 book ''An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Malthus observed that an increase in a nation's food production improved the well-being of the population, but the improvement was temporary because it led to population growth, which in turn restored the original per capita production level. In other words, humans had a propensity to use abundance for population growth rather than for maintaining a high standard of living, a view and stance that has become known as the " Malthusian trap" or the "Malthusian spectre". Populations had a tendency to grow until the lower class suffered hardship, want, and greater susceptibility to war, famine, and disease, a pessimistic view that is sometimes referred to as a Malthusian catastrophe. Malthus wrote in opposition to the popular view in 18th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
The Population Bomb
''The Population Bomb'' is a 1968 book co-authored by former Stanford University professor Paul R. Ehrlich and former Stanford senior researcher in conservation biology Anne H. Ehrlich. From the opening page, it predicted worldwide famines due to overpopulation, as well as other major societal upheavals, and advocated immediate action to limit population growth. Fears of a "population explosion" existed in the mid-20th century baby boom years, but the book and its authors brought the idea to an even wider audience. The book has been criticized since its publication for an alarmist tone, and over the subsequent decades, for inaccurate assertions and failed predictions. For instance, regional famines have occurred since the publication of the book, but not world famines. The Ehrlichs themselves still stand by the book despite the flaws identified by its critics, with Paul stating in 2009 that "perhaps the most serious flaw in ''The Bomb'' was that it was much too optimistic abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Technological Singularity
The technological singularity—or simply the singularity—is a hypothetical point in time at which technological growth becomes uncontrollable and irreversible, resulting in unforeseeable consequences for human civilization. According to the most popular version of the singularity hypothesis, I. J. Good's #Intelligence explosion, intelligence explosion model of 1965, an upgradable intelligent agent could eventually enter a positive feedback loop of successive Recursive self-improvement, self-improvement cycles; more intelligent generations would appear more and more rapidly, causing a rapid increase ("explosion") in intelligence that culminates in a powerful superintelligence, far surpassing all human intelligence.Vinge, Vernor"The Coming Technological Singularity: How to Survive in the Post-Human Era", in ''Vision-21: Interdisciplinary Science and Engineering in the Era of Cyberspace'', G. A. Landis, ed., NASA Publication CP-10129, pp. 11–22, 1993. - "There may be developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Accelerating Change
In futures studies and the history of technology, accelerating change is the observed exponential nature of the rate of technological change in recent history, which may suggest faster and more profound change in the future and may or may not be accompanied by equally profound social and cultural change. Early observations Writing in 1904, Henry Brooks Adams outlined a " law of acceleration." Progress is accelerating including military progress. As coal-output of the world doubles every ten years, so will be the world output of bombs both in force and number. The bomb passage follows the "revolutionary" discovery of radium--an ore of uranium--and states that power leaps from every atom. Resistance to the law of acceleration is futile and progress might outpace the mind. "If science were to go on doubling or quadrupling its complexities every ten years, even mathematics would soon succumb. An average mind had succumbed already in 1850; it could no longer understand the prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship. It is an experience-curve law, a type of law quantifying efficiency gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel and former CEO of the latter, who in 1965 noted that the number of components per integrated circuit had been exponential growth, doubling every year, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. Moore's empirical evidence did not directly imply that the historical trend would continue, nevertheless, his prediction has held si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Exponential Growth
Exponential growth occurs when a quantity grows as an exponential function of time. The quantity grows at a rate directly proportional to its present size. For example, when it is 3 times as big as it is now, it will be growing 3 times as fast as it is now. In more technical language, its instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to an independent variable is proportional to the quantity itself. Often the independent variable is time. Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast to other types of growth, such as quadratic growth). Exponential growth is the inverse of logarithmic growth. Not all cases of growth at an always increasing rate are instances of exponential growth. For example the function f(x) = x^3 grows at an ever increasing rate, but is much slower than growing exponentially. For example, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Hyperbolic Growth
When a quantity grows towards a singularity under a finite variation (a " finite-time singularity") it is said to undergo hyperbolic growth. More precisely, the reciprocal function 1/x has a hyperbola as a graph, and has a singularity at 0, meaning that the limit as x \to 0 is infinite: any similar graph is said to exhibit hyperbolic growth. Description If the output of a function is inversely proportional to its input, or inversely proportional to the difference from a given value x_0, the function will exhibit hyperbolic growth, with a singularity at x_0. In the real world hyperbolic growth is created by certain non-linear positive feedback mechanisms. Comparisons with other growth functions Like exponential growth and logistic growth, hyperbolic growth is highly nonlinear, but differs in important respects. These functions can be confused, as exponential growth, hyperbolic growth, and the first half of logistic growth are convex functions; however their asymptotic behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Extrapolation
In mathematics Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ..., extrapolation is a type of estimation, beyond the original observation range, of the value of a variable on the basis of its relationship with another variable. It is similar to interpolation, which produces estimates between known observations, but extrapolation is subject to greater uncertainty and a higher risk of producing meaningless results. Extrapolation may also mean extension of a wikt:method, method, assuming similar methods will be applicable. Extrapolation may also apply to human experience to project, extend, or expand known experience into an area not known or previously experienced. By doing so, one makes an assumption of the unknown [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |