|
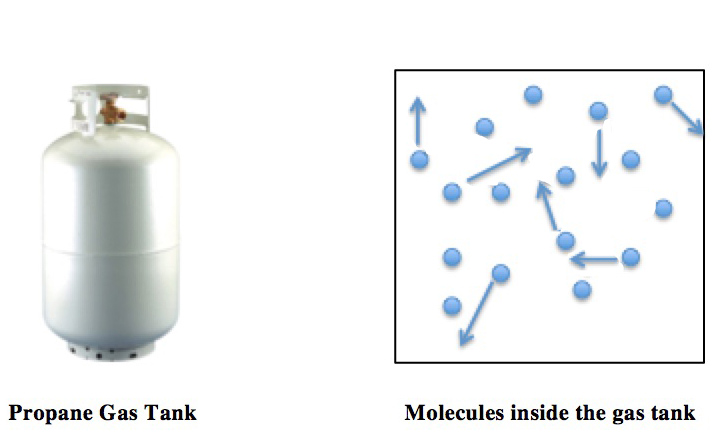
Standard Cubic Feet Per Minute
Standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM) is the molar flow rate of a gas expressed as a volumetric flow at a "standardized" temperature and pressure thus representing a fixed number of moles of gas regardless of composition and actual flow conditions. It is related to the mass flow rate of the gas by a multiplicative constant which depends only on the molecular weight of the gas. There are different standard conditions for temperature and pressure, so care is taken when choosing a particular standard value. Worldwide, the "standard" condition for pressure is variously defined as an absolute pressure of 101,325 pascals (Atmospheric pressure), 1.0 bar (i.e., 100,000 pascals), 14.73 psia, or 14.696 psia and the "standard" temperature is variously defined as 68 °F, 60 °F, 0 °C, 15 °C, 20 °C, or 25 °C. The relative humidity (e.g., 36% or 0%) is also included in some definitions of standard conditions. In Europe, the standard temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and temperature respectively; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory, as was achieved (independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature used in the equation of state is an absolute temperature: the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Million Standard Cubic Feet Per Day
Million standard cubic feet per day is a unit of measurement for gases that is predominantly used in the United States. It is frequently abbreviated MMSCFD. MMSCFD is commonly used as a measure of natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, compressed natural gas and other gases that are extracted, processed or transported in large quantities. A related measure is "mega standard cubic metres per day" (MSm3/d), which is equal to 106 Sm3/d used in many countries outside the United States. of the in the One MMSCFD equals 1177.6 Sm3/h. When converting to mass flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Cubic Foot
A standard cubic foot (scf) is a unit representing the amount of gas (such as natural gas) contained in a volume of one cubic foot at reference temperature and pressure conditions. It is the unit commonly used when following the United States customary units, customary system, a collection of standards set by the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Another unit used for the same purpose is the standard cubic metre (Sm3), derived from SI units, representing the amount of gas contained in a volume of one cubic meter at different reference conditions. The reference conditions depend on the type of gas and differ from other standard temperature and pressure conditions. Usage The scf and the scm are units of molecular quantity for gases can be used with the ideal gas law to compute the quantity per unit of volume for other pressures and temperatures. In spite of the label "standard", there is a variety of definitions, mainly depending on the type of gas. Since, for a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Conditions For Temperature And Pressure
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used standards are those of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), although these are not universally accepted. Other organizations have established a variety of other definitions. In industry and commerce, the standard conditions for temperature and pressure are often necessary for expressing the volumes of gases and liquids and related quantities such as the rate of volumetric flow (the volumes of gases vary significantly with temperature and pressure): standard cubic meters per second (Sm3/s), and normal cubic meters per second (Nm3/s). Many technical publications (books, journals, advertisements for equipment and machinery) simply state "standard cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Laws
The laws describing the behaviour of gases under fixed pressure, volume, amount of gas, and absolute temperature conditions are called gas laws. The basic gas laws were discovered by the end of the 18th century when scientists found out that relationships between pressure, volume and temperature of a sample of gas could be obtained which would hold to approximation for all gases. The combination of several empirical gas laws led to the development of the ideal gas law. The ideal gas law was later found to be consistent with atomic and kinetic theory. History In 1643, the Italian physicist and mathematician, Evangelista Torricelli, who for a few months had acted as Galileo Galilei's secretary, conducted a celebrated experiment in Florence. He demonstrated that a column of mercury in an inverted tube can be supported by the pressure of air outside of the tube, with the creation of a small section of vacuum above the mercury. This experiment essentially paved the way towards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Fan
A centrifugal fan is a mechanical device for moving air or other gases in a direction perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the fan. Centrifugal fans often contain a ducted fan, ducted housing to direct outgoing air in a specific direction or across a heat sink; such a fan is also called a blower, blower fan, or squirrel-cage fan (because it looks like a hamster wheel). Tiny ones used in computers are sometimes called biscuit blowers. These fans move air from the rotating inlet of the fan to an outlet. They are typically used in ducted applications to either draw air through ductwork/heat exchanger, or push air through similar impellers. Compared to standard axial fans, they can provide similar air movement from a smaller fan package, and overcome higher Fluid dynamics, resistance in air streams. Centrifugal fans use the kinetic energy of the impellers to move the air stream, which in turn moves against the resistance caused by ducts, dampers and other components. Centrifu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressibility
In thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, the compressibility (also known as the coefficient of compressibility or, if the temperature is held constant, the isothermal compressibility) is a measure of the instantaneous relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure (or mean stress) change. In its simple form, the compressibility \kappa (denoted in some fields) may be expressed as :\beta =-\frac\frac, where is volume and is pressure. The choice to define compressibility as the negative of the fraction makes compressibility positive in the (usual) case that an increase in pressure induces a reduction in volume. The reciprocal of compressibility at fixed temperature is called the isothermal bulk modulus. Definition The specification above is incomplete, because for any object or system the magnitude of the compressibility depends strongly on whether the process is isentropic or isothermal. Accordingly, isothermal compressibility is defined: :\beta_T=-\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Feet Per Minute
The cubic foot (symbol ft3 or cu ft) , . is an Imperial unit, imperial and (non-metric) unit of volume, used in the United States and the United Kingdom. It is defined as the volume of a with sides of one () in |
Compressibility Factor
In thermodynamics, the compressibility factor (Z), also known as the compression factor or the gas deviation factor, describes the deviation of a real gas from ideal gas behaviour. It is simply defined as the ratio of the molar volume of a gas to the molar volume of an ideal gas at the same temperature and pressure. It is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law to account for the real gas behaviour.Properties of Natural Gases . Includes a chart of compressibility factors versus reduced pressure and reduced temperature (on last page of the PDF document) In general, deviation from ideal behaviour becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the temperat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rankine Scale
The Rankine scale ( ) is an absolute scale of thermodynamic temperature named after the University of Glasgow engineer and physicist Macquorn Rankine, who proposed it in 1859. History Similar to the Kelvin scale, which was first proposed in 1848, zero on the Rankine scale is absolute zero, but a temperature difference of one Rankine degree (°R or °Ra) is defined as equal to one Fahrenheit degree, rather than the Celsius degree used on the Kelvin scale. In converting from kelvin to degrees Rankine, 1 K = °Ra or 1 K = 1.8 °Ra. A temperature of 0 K (−273.15 °C; −459.67 °F) is equal to 0 °Ra.B.8 Factors for Units Listed Alphabetically from Usage The Rankine scale is used in engineering systems where ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |