|
Spizellomyces Punctatus
''Spizellomyces punctatus'' is a chytrid fungus living in soil. It is a saprotrophic fungus that colonizes decaying plant material. Being an early diverging fungus, ''S. punctatus'' retains ancestral cellular features that are also found in animals and amoebae. Its pathogenic relatives, ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'' and '' B. salamandrivorans'', infect amphibians and cause global biodiversity loss. The pure culture of ''S. punctatus'' was first obtained by Koch (named ''Phlyctochytrium punctatum''). Genome The genome of ''S. punctatus'' strain DAOM BR117 was sequenced under the Origins of Multicellularity project. Its genome size is about 24.13 Mb with a GC content of 47.6%. The genome has 9,424 predicted transcripts and 8,952 predicted protein-coding genes. The DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession number is ACOE00000000. Genetic transformation Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation Genetic transformation of ''S. punctatus'' zoospores by plant pathogen '' Agrobacterium tumefac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chytridiomycota
Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zoöspores. Chytrids are one of the early diverging fungal lineages, and their membership in kingdom Fungi is demonstrated with chitin cell walls, a posterior whiplash flagellum, absorptive nutrition, use of glycogen as an energy storage compound, and synthesis of lysine by the -amino adipic acid (AAA) pathway. Chytrids are saprobic, degrading refractory materials such as chitin and keratin, and sometimes act as parasites. There has been a significant increase in the research of chytrids since the discovery of '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'', the causal agent of chytridiomycosis. Classification Species of Chytridiomycota have traditionally been delineated and classified based on development, morphology, substrate, and method of zoöspore discharge. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nourseothricin
Nourseothricin (NTC) is a member of the streptothricin-class of aminoglycoside antibiotics produced by ''Streptomyces'' species. Chemically, NTC is a mixture of the related compounds streptothricin C, D, E, and F. NTC inhibits protein synthesis by inducing miscoding. It is used as a selection marker for a wide range of organisms including bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi, and plant cells. It is not known to have adverse side-effects on positively selected cells, a property cardinal to a selection drug. NTC can be inactivated by nourseothricin N-acetyl transferase (NAT) from '' Streptomyces noursei'', an enzyme that acetylates the beta-amino group of the beta-lysine residue of NTC. NAT can thus act as an antibiotic resistance Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. All classes of microbes can evolve resistance. Fungi evolve antifungal resistance. Viruses evolve antiviral resistanc .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Tube
A germ tube is an outgrowth produced by spores of spore-releasing fungi during germination. The germ tube differentiates, grows, and develops by mitosis to create somatic hyphae.C.J. Alexopolous, Charles W. Mims, M. Blackwell, ''Introductory Mycology, 4th ed.'' (John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken NJ, 2004) A germ tube test is a diagnostic test in which a sample of fungal spores are suspended in animal serum and examined by microscopy for the detection of any germ tubes.Chapter IV. Germ Tube Test iYEAST IDENTIFICATION document at doctorfungus.org. Retrieved July 2011 It is particularly indicated for colonies of white or cream color on fungal culture, where a positive germ tube test is strongly indicative of ''Candida albicans''. See also * Oomycota Oomycota forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage of fungus-like eukaryotic microorganisms, called oomycetes (). They are filamentous and heterotrophic, and can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction of an oospor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogels
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still diffuse through this system. A gel has been defined phenomenologically as a soft, solid or solid-like material consisting of two or more components, one of which is a liquid, present in substantial quantity. By weight, gels are mostly liquid, yet they behave like solids because of a three-dimensional cross-linked network within the liquid. It is the crosslinking within the fluid that gives a gel its structure (hardness) and contributes to the adhesive stick ( tack). In this way, gels are a dispersion of molecules of a liquid within a solid medium. The word ''gel'' was coined by 19th-century Scottish chemist Thomas Graham by clipping from '' gelatine''. The process of forming a gel is called gelation. IUPAC definition } ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
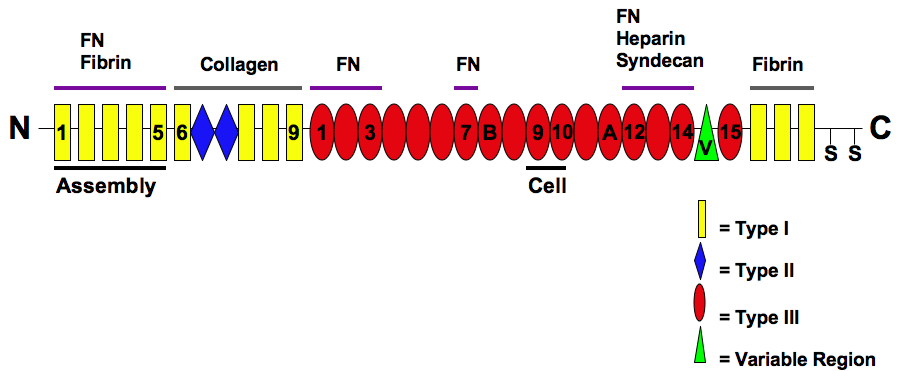
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high-molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteasome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. Proteins are tagged for degradation with a small protein called ubiquitin. The tagging reaction is catalyzed by enzymes called ubiquitin ligases. Once a protein is tagged with a single ubiquitin molecule, this is a signal to other ligases to attach additional ubiquitin molecules. The result is a ''polyubiquitin chain'' that is bound by the proteasome, allowing it to degrade the tagged protein. The degradation process yields peptides of about seven to eight amino acids long, which can then be further degraded into shorter amino acid sequences and used in synthesizing new proteins. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton. Microtubules function in many essential cellular processes, including mitosis. Tubulin-binding drugs kill cancerous cells by inhibiting microtubule dynamics, which are required for DNA segregation and therefore cell division. In eukaryotes, there are six members of the tubulin superfamily, although not all are present in all species.Turk E, Wills AA, Kwon T, Sedzinski J, Wallingford JB, Stearns "Zeta-Tubulin Is a Member of a Conserved Tubulin Module and Is a Component of the Centriolar Basal Foot in Multiciliated Cells"Current Biology (2015) 25:2177-2183. Both α and β tubulins have a mass of around 50 kDa and are thus in a similar range compared to actin (with a mass of ~42 kDa). In contrast, tubulin polymers (microtubules) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axoneme
An axoneme, also called an axial filament is the microtubule-based cytoskeletal structure that forms the core of a cilium or flagellum. Cilia and flagella are found on many cells, organisms, and microorganisms, to provide motility. The axoneme serves as the "skeleton" of these organelles, both giving support to the structure and, in some cases, the ability to bend. Though distinctions of function and length may be made between cilia and flagella, the internal structure of the axoneme is common to both. Structure Inside a cilium and a flagellum is a microtubule-based cytoskeleton called the axoneme. The axoneme of a primary cilium typically has a ring of nine outer microtubule doublets (called a 9+0 axoneme), and the axoneme of a motile cilium has two central microtubules in addition to the nine outer doublets (called a 9+2 axoneme). The axonemal cytoskeleton acts as a scaffolding for various protein complexes and provides binding sites for molecular motor proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encystment
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, usually a bacterium or a protist or rarely an invertebrate animal, that helps the organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. It can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Encystment, the formation of the cyst, also helps the microbe to disperse easily, from one host to another or to a more favorable environment. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. In excystment, the exact stimulus is unknown for most protists. Unfavorable environmental conditions such as lack of nutrients or oxygen, extreme temperatures, lack of moisture and presence of toxic chemicals, which are not conducive for the growth of the microbeEugene W. Nester, Denise G. Anderson, C. Evans Roberts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
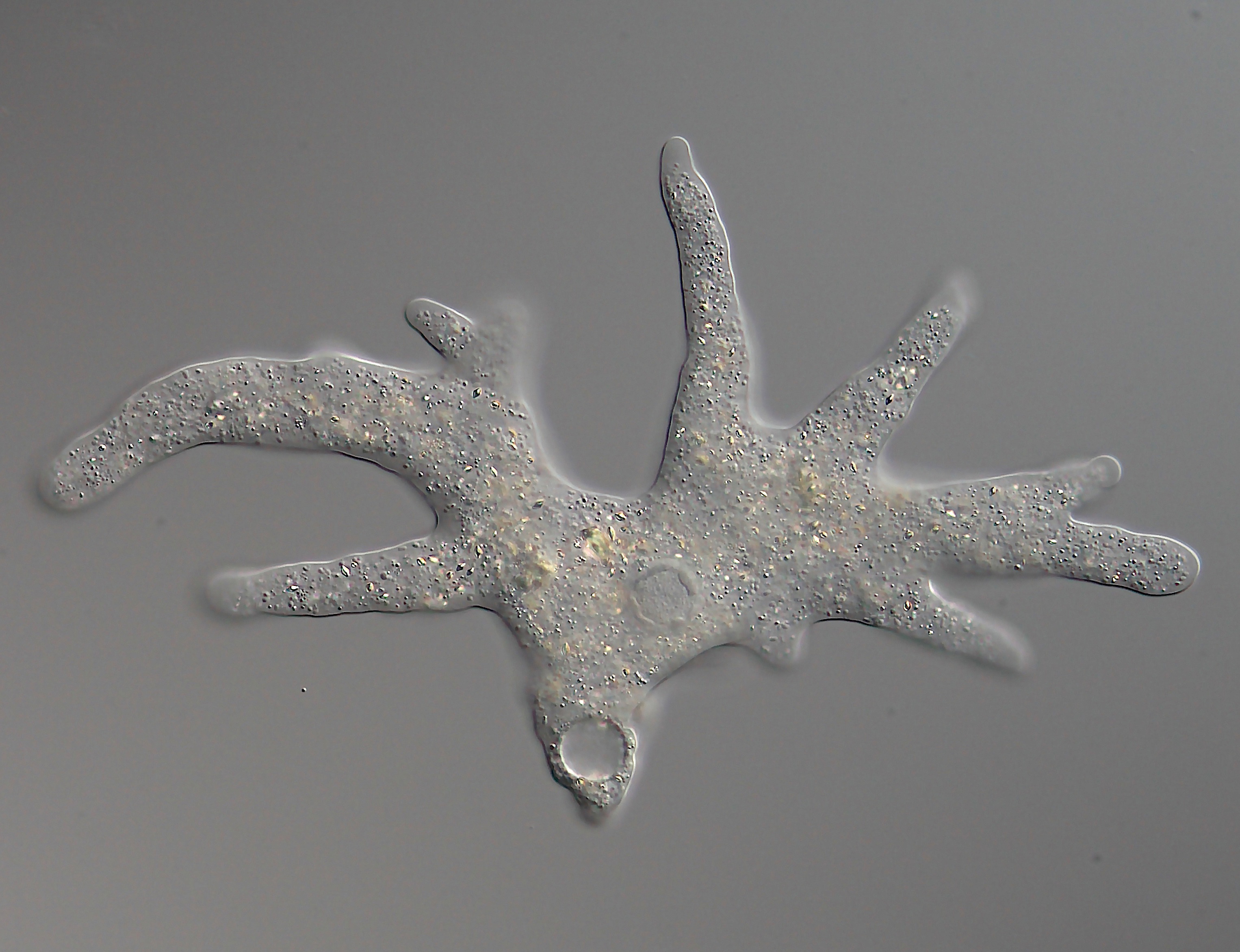
Pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actin
Actin is a protein family, family of Globular protein, globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in myofibril, muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 micromolar, μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm. An actin protein is the monomeric Protein subunit, subunit of two types of filaments in cells: microfilaments, one of the three major components of the cytoskeleton, and thin filaments, part of the Muscle contraction, contractile apparatus in muscle cells. It can be present as either a free monomer called G-actin (globular) or as part of a linear polymer microfilament called F-actin (filamentous), both of which are essential for such important cellular functions as the Motility, mobility and contraction of cell (biology), cells during cell division. Actin participates in many important cellular pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilium
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |