|
Solvay Public Library
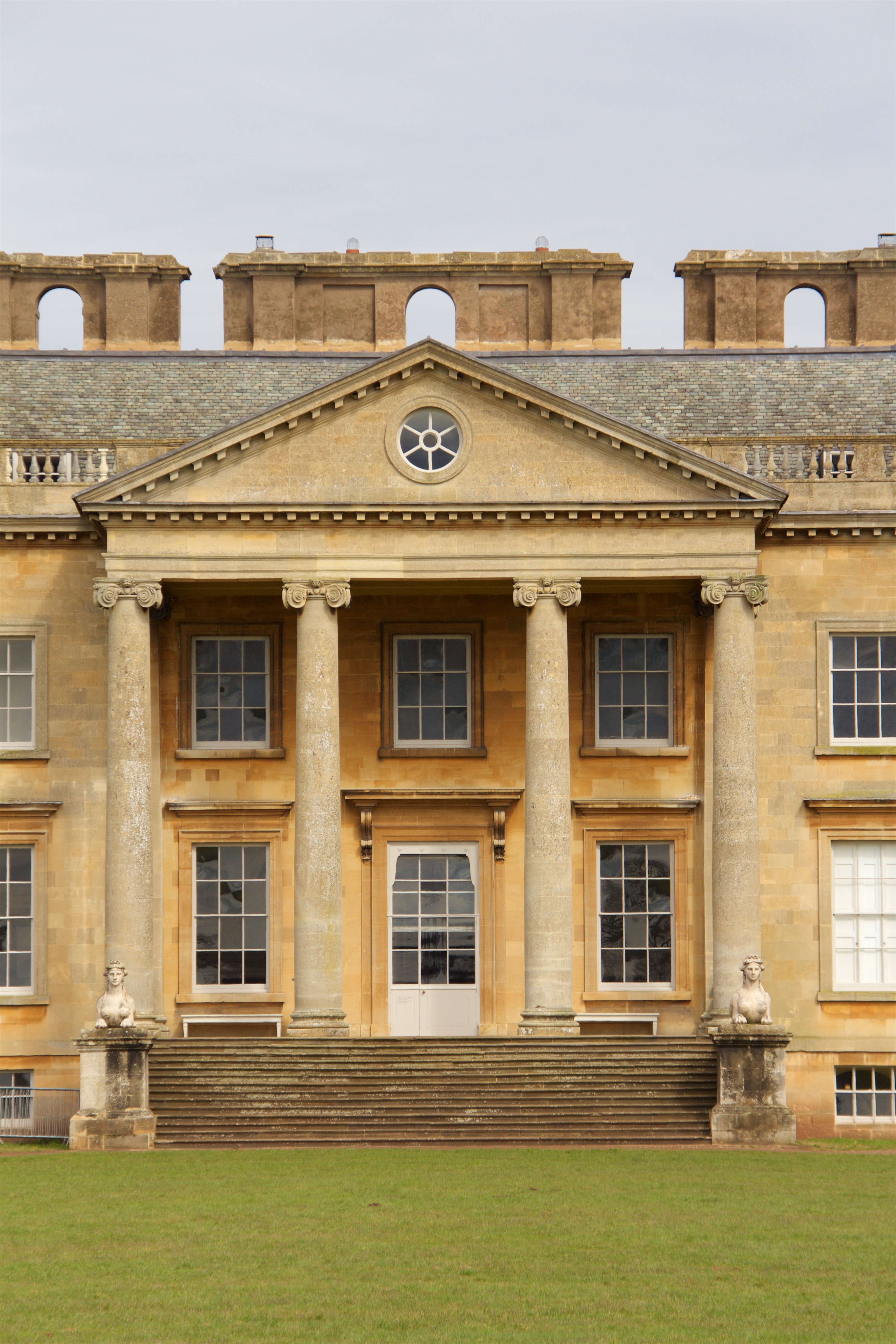
The Solvay Public Library is a historic Carnegie library building located at Solvay in Onondaga County, New York. It was built between 1903 and 1905, and is a one-story, buff-colored brick building on a high basement. It has a hipped roof and Classical Revival style design elements including a distyle-in-antis portico in the Ionic order. It was built in part with a $10,000 donation from Andrew Carnegie. ''Note:'' This includes an''Accompanying photographs''/ref> It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Hist ... in 2007. It was renovated in recent years with focus on preserving and restoring historically accurate details. References Carnegie libraries in New York (state) Libraries on the National Register of Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvay, New York
Solvay is a Administrative divisions of New York#Village, village located in the town of Geddes, New York, Geddes, Onondaga County, New York, Onondaga County, New York (state), New York, United States, and a suburb of the city of Syracuse, New York, Syracuse. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 6,645. The village is named after the Ernest Solvay, Solvay brothers, Belgium, Belgian inventors of the chemical process employed by the Solvay Process Company, formerly the major industry of the village. History The area was within the former Central New York Military Tract, but Solvay was in a location reserved for members of the Onondaga tribe. The village was initially founded in 1794 by James Geddes (engineer), James Geddes and was initially called "Geddesburgh." The first residents were mostly Ireland, Irish, subsequently joined by County of Tyrol, Tyroleans and Poland, Poles. Eventually the community became known for its population largely Italy, Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onondaga County, New York
Onondaga County ( ) is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 476,516. The county seat is Syracuse, New York, Syracuse. The county is part of the Central New York region of the state. Onondaga County is the core of the Syracuse metropolitan area, Syracuse Metropolitan Statistical Area. History The name ''Onondaga'' derives from the name of the Native American tribe (Native American), tribe indigenous to this area, one of the original Iroquois, Five Nations of the ''Haudenosaunee''. They call themselves (Endonym, autonym) Onondaga people, ''Onoda'gega'', sometimes spelled ''Onontakeka.'' The word means "People of the Hills." Sometimes the term is ''Onondagaono'' ("The People of the Hills"). The federally recognized Onondaga Nation has a Indian reservation, reservation within the county, on which they have self-government. When counties were established in New York ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of Roman architecture, ancient Rome and ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer, more complete, and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distyle-in-antis
In classical architecture, distyle in antis denotes a temple with the side walls extending to the front of the porch and terminating with two antae, the pediment being supported by two columns or sometimes caryatids. This is the earliest type of temple structure in the ancient Greek world. An example is the Siphnian Treasury in Delphi, built around 525 BCE. Smaller two-column structures without antae are called distyle. The next evolution in temple design came with amphiprostyle, where four columns stand in line on the porch in front of a naos. File:Treasury of the Siphnians by Hansen.JPG, Reconstruction of the Siphnian Treasury File:Greek temples.svg, Types of temple plan See also * Antae temple *Prostyle Prostyle and Prostylos (), literally meaning "with columns in front", is an architectural term designating temples (especially Greek and Roman) featuring a row of columns on the front. The term is often used as an adjective when referring to th ... References Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the '' cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ''cella''. The word ''pronaos'' () is Greek for "before a temple". In Latin, a pronaos is also referred to as an ''anticum'' or ''prodomus''. The pronaos of a Greek a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital (architecture), capital, which have been the subject of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie ( , ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the History of the iron and steel industry in the United States, American steel industry in the late-19th century and became one of the List of richest Americans in history, richest Americans in history. He became a leading philanthropist in the United States, Great Britain, and the British Empire. During the last 18 years of his life, he gave away around $350 million (equivalent to $ billion in ), almost 90 percent of his fortune, to charities, foundations and universities. His 1889 article proclaiming "The Gospel of Wealth" called on the rich to use their wealth to improve society, expressed support for progressive taxation and an Inheritance tax, estate tax, and stimulated a wave of philanthropy. Carnegie was born in Dunfermline, Scotland. He immigrated to what is now Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States with his parents in 1848 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York State Office Of Parks, Recreation And Historic Preservation
The New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation (NYS OPRHP) is a state agency within the New York State Executive Department Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation Law § 3.03. "The office of parks, recreation and historic preservation is hereby continued in the executive department. .. charged with the operation of state parks and historic sites within the U.S. state of New York. the NYS OPRHP manages nearly of public lands and facilities, including 180 state parks and 35 historic sites, that are visited by over 78 million visitors each year. History The agency that would become the New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation (NYS OPRHP) was created in 1970; however, the history of state parks and historic sites in New York stretches back to the latter part of the 19th century. Management of state-owned parks, and guidance for the entire state park system, was accomplished by various regional commissions, private ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Register Of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government's official United States National Register of Historic Places listings, list of sites, buildings, structures, Historic districts in the United States, districts, and objects deemed worthy of Historic preservation, preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic value". The enactment of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) in 1966 established the National Register and the process for adding properties to it. Of the more than one and a half million properties on the National Register, 95,000 are listed individually. The remainder are contributing property, contributing resources within historic district (United States), historic districts. For the most of its history, the National Register has been administered by the National Park Service (NPS), an agency within the United States Department of the Interior. Its goals are to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Libraries In New York (state)
Carnegie may refer to: People *Carnegie (surname), including a list of people with the name **Andrew Carnegie, Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist * Clan Carnegie, a lowland Scottish clan Institutions Named for Andrew Carnegie * Carnegie Building (Troy, New York), on the campus of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute * Carnegie College, in Dunfermline, Scotland, a former further education college *Carnegie Community Centre, in downtown Vancouver, British Columbia *Carnegie Council for Ethics in International Affairs *Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, a global think tank with headquarters in Washington, DC, and four other centers, including: **Carnegie Middle East Center, in Beirut ** Carnegie Europe, in Brussels ** Carnegie Moscow Center *Carnegie Foundation (other), any of several foundations *Carnegie Hall, a concert hall in New York City * Carnegie Hall, Inc., a regional cultural center in Lewisburg, West Virginia *Carnegie Hero Fund *Carnegie In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libraries On The National Register Of Historic Places In New York (state)
A library is a collection of books, and possibly other materials and media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer creation stations for makers which offer access to a 3D printing station with a 3D scanner. Libraries can vary widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |