|
Short Bone
Short bones are designated as those bones that are more or less equal in length, width, and thickness. They include the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsals in the ankle and the Carpal bones, carpals in the wrist. They are one of five Bone#Types, types of bones: short, Long bone, long, Flat bone, flat, Irregular bone, irregular and Sesamoid bone, sesamoid. Most short bones are named according to their shape as they exhibit a variety of complex morphological features (They can be Cuboid bone, cuboid, Lunate bone, lenticular, Trapezium (bone), trapezoidal, etc.) Some authors state that short bones are only located in the carpals and tarsals. The metacarpals, metatarsals and Phalanx bone, phalanges are considered long bones as they have a shaft (tubular diaphysis), but since they're smaller than typical long bones, they're called “miniature, small or short" long bones. Nevertheless, others consider the patellae and other sesamoid bones, the Vertebra#General structure, vertebral bodies, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
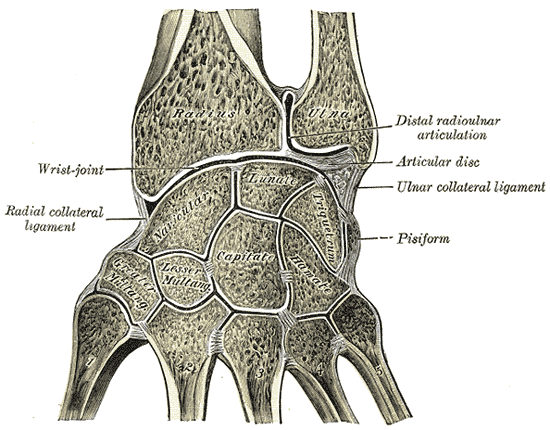
Carpal Bones
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin wikt:carpus#Latin, carpus and the Greek language, Greek wikt:καρπός#Ancient Greek, καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to joint, articulate with the radius (bone), radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint (i.e. wrist joint),Kingston 2000, pp 126-127 to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior compartment of the forearm, anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers. In tetrapods, the carpus is the sole cluster of bones in the wrist between the radius (bone), radius and ulna and the metacarpus. The bones of the carpus do not belong to individual fingers (or toes in quadrupeds), whereas those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialised connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralisation of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the resorption of bone tissue. Modified (flattened) osteoblasts become the lining cells that form a protective layer on the bone surface. The mineralised mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
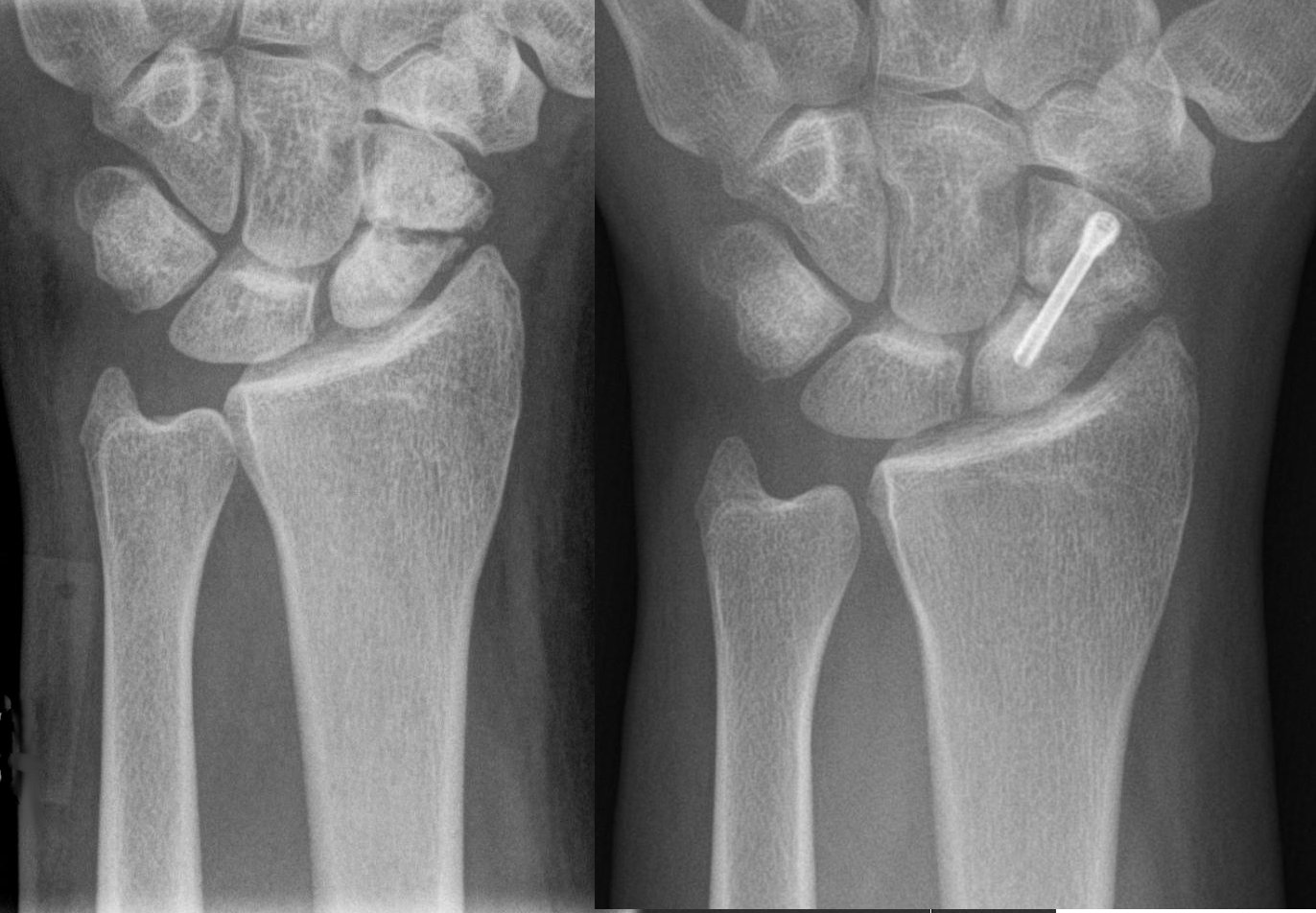
Nonunion
Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention (such as surgery) is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false joint" or pseudoarthrosis (from Greek '' pseudo-'', meaning false, , meaning joint, and '' -osis'', meaning abnormal condition). The diagnosis is generally made when there is no healing between two sets of medical imaging, such as X-ray or CT scan. This is generally after 6–8 months.Page 542 in: Nonunion is a serious complication of a fracture and may occur when the fracture moves too much, has a poor |
SOC002
SOC, SoC, Soc, may refer to: Science and technology * Information security operations center, in an organization, a centralized unit that deals with computer security issues * Selectable output control * Separation of concerns, a program design principle in computer science and software engineering * Service-oriented communications * Service-oriented computing, another term for Service-oriented architecture * Soil organic carbon, see Soil carbon * Solid Oxide Cell, an electrochemical conversion device operating either in SOFC, SOEC, or rSOC mode * spin–orbit coupling * State of charge, for batteries * Store-Operated Calcium channel * Super Optimal Broth with catabolite repression, a bacterial growth medium * Superior olivary complex * System on a chip (SoC), in electronic design * System Organ Class, an organizational division in the dictionary MedDRA Associations and societies * Society (abbr.: "soc.") * Scottish Ornithologists' Club * Scouts of China * Serbian Orthodox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossification Center
An ossification center is a point where ossification of the hyaline cartilage begins. The first step in ossification is that the chondrocytes at this point become hypertrophic and arrange themselves in rows. The matrix in which they are imbedded increases in quantity, so that the cells become further separated from each other. A deposit of calcareous material now takes place in this matrix, between the rows of cells, so that they become separated from each other by longitudinal columns of calcified matrix, presenting a granular and opaque appearance. Here and there the matrix between two cells of the same row also becomes calcified, and transverse bars of calcified substance stretch across from one calcareous column to another. Thus, there are longitudinal groups of the cartilage cells enclosed in oblong cavities, the walls of which are formed of calcified matrix which cuts off all nutrition from the cells; the cells, in consequence, atrophy, leaving spaces called the primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes (, ) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word '' chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes (which are mesenchymal stem cells) can differentiate into various cell types, including osteoblasts. Development From least- to terminally-differentiated, the chondrocytic lineage is: # Colony-forming unit-fibroblast # Mesenchymal stem cell / marrow stromal cell # Chondrocyte # Hypertrophic chondrocyte Mesenchymal (mesoderm origin) stem cells are undifferentiated, meaning they can differentiate into a variety of generative cells commonly known as osteochondrogenic (or osteogenic, chondrogenic, osteoprogenitor, etc.) cells. When referring to bone, or in this case cartilage, the originally undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells lose their pluripotency, proliferat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphyseal Plate
The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance bone remodeling, remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, but the growth plate is the place where the long bone grows longer (adds length). The plate is only found in children and adolescents; in adults, who have stopped growing, the plate is replaced by an ''epiphyseal line''. This replacement is known as epiphyseal closure or growth plate fusion. Complete fusion can occur as early as 12 for girls (with the most common being 14–15 years for girls) and as early as 14 for boys (with the most common being 15–17 years for boys). Structure Development Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage Uterus, in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endochondral Ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development and bone healing, bone repair of the mammalian skeleton, skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossification. Both endochondral and intramembranous processes initiate from a precursor mesenchymal cells, mesenchymal tissue, but their transformations into bone are different. In intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into bone. On the other hand, endochondral ossification starts with mesenchymal tissue turning into an intermediate hyaline cartilage, cartilage stage, which is eventually substituted by bone. Endochondral ossification is responsible for development of most bones including long bone, long and short bone, short bones, the bones of the axial skeleton, axial (ribs and vertebrae) and the appendicular skeleton, appendicular skeleton (e.g. upper limb, upper and lower limb, lower limbs), the bones of the Base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphysis
The metaphysis (: metaphyses) is the neck portion of a long bone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. It contains the growth plate, the part of the bone that grows during childhood, and as it grows it ossifies near the diaphysis and the epiphyses. The metaphysis contains a diverse population of cells including mesenchymal stem cells, which give rise to bone and fat cells, as well as hematopoietic stem cells which give rise to a variety of blood cells as well as bone-destroying cells called osteoclasts. Thus the metaphysis contains a highly metabolic set of tissues including trabecular (spongy) bone, blood vessels, as well as marrow adipose tissue (MAT). The metaphysis may be divided anatomically into three components based on tissue content: a cartilaginous component (epiphyseal plate), a bony component (metaphysis) and a fibrous component surrounding the periphery of the plate. The growth plate synchronizes chondrogenesis with osteogenesis or interstitial carti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphysis
The diaphysis (: diaphyses) is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat). It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a central marrow cavity which contains red or yellow marrow. In diaphysis, primary ossification Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ... occurs. Ewing sarcoma tends to occur at the diaphysis.Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Board Review, Cuccurullo Additional images Illu long bone.jpg File:EpiMetaDiaphyse.jpg, Long bone See also * Epiphysis * Metaphysis References Long bones {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |