|
Service Network
A service network is a structure that brings together several entities to deliver a particular service. For instance, one organisation (the buyer) may sub-contract another organisation (the supplier) to deliver after-sales services to a third party (the customer). The buyer may use more than one supplier. Likewise, the supplier may participate in other networks. The rationale for a service network is that each organisation is focusing on what they do best. A service network can also be defined as a collection of people and information brought together on the internet to provide a specific service or achieve a common business objective. It is an evolving extension of service systems and applies Enterprise 2.0 technologies, also known as enterprise social software, to enable corporations to leverage the advances of the consumer internet for the benefit of business. In this case, the service network is designed to benefit from the wisdom of crowds and a human's natural tendency and des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks that consists of Private network, private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, Wireless network, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Service (economics)
A service is an act or use for which a consumer, company, or government is willing to payment, pay. Examples include work done by barbers, doctors, lawyers, mechanics, banks, insurance companies, and so on. Public services are those that society (nation state, fiscal union or region) as a whole pays for. Using resources, skill, ingenuity, and experience, service providers benefit service consumers. Services may be defined as intangible acts or performances whereby the service provider provides value to the customer. Key characteristics Services have three key characteristics: Intangibility Services are by definition intangible. They are not manufactured, transported or stocked. One cannot store services for future use. They are produced and consumed simultaneously. Perishability Services are perishable in two regards: * Service-relevant resources, processes, and systems are assigned for service delivery during a specific period in time. If the service consumer does not request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Service System
A service system (also customer service system (CSS)) is a configuration of technology and organizational networks designed to deliver services that satisfy the needs, wants, or aspirations of customers. "Service system" is a term used in the service management, service operations, services marketing, service engineering, and service design literature. While the term frequently appears, it is rarely defined. One definition of a service system is a value coproduction configuration of people, technology, internal and external service systems connected via value propositions, and shared information (language, laws, measures, etc.). The smallest service system is a single person and the largest service system is the world economy. The external service system of the global economy is considered to be ecosystem services. Service systems can be characterized by the value that results from interaction between service systems, whether the interactions are between people, businesses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Enterprise 2
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to: Business and economics Brands and enterprises * Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company * Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company * Enterprise Productions, an American film production company that operated from 1946 to 1949 * Enterprise Products, a natural gas and crude oil pipeline company * Enterprise Records, a record label * Enterprise Rent-A-Car, a car rental Provider ** Enterprise Holdings, the parent company * The Enterprise Studios, a Burbank, California music recording studio General * Business, economic activity done by a businessperson * Big business, larger corporation commonly called "enterprise" in business jargon (excluding small and medium-sized businesses) * Company, a legal entity practicing a business activity * Enterprise architecture, a strategic management discipline within an organization * Enterprise Capital Fund, a type of venture capital in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Enterprise Social Software
Enterprise social software (also known as or regarded as a major component of Enterprise 2.0), comprises social software as used in " enterprise" (business/ commercial) contexts. It includes social and networked modifications to corporate intranets and other classic software platforms used by large companies to organize their communication. In contrast to traditional enterprise software, which imposes structure prior to use, enterprise social software tends to encourage use prior to providing structure. Carl Frappaolo and Dan Keldsen defined Enterprise 2.0 in a report written for Association for Information and Image Management (AIIM) as "a system of web-based technologies that provide rapid and agile collaboration, information sharing, emergence and integration capabilities in the extended enterprise". Applications Functionality Social software for an enterprise must (according to Andrew McAfee, Associate Professor, Harvard Business School) have the following functionali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
The Wisdom Of Crowds
''The Wisdom of Crowds: Why the Many Are Smarter Than the Few and How Collective Wisdom Shapes Business, Economies, Societies and Nations'', published in 2004, is a book written by James Surowiecki about the aggregation of information in groups, resulting in decisions that, he argues, are often better than could have been made by any single member of the group. The book presents numerous case studies and anecdotes to illustrate its argument, and touches on several fields, primarily economics and psychology. The opening anecdote relates Francis Galton's surprise that the crowd at a county fair accurately guessed the weight of an ox when the median of their individual guesses was taken (the median was closer to the ox's true butchered weight than the estimates of most crowd members). The book relates to diverse collections of independently deciding individuals, rather than crowd psychology as traditionally understood. Its central thesis, that a diverse collection of independent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Mass Collaboration
Mass collaboration is a form of collective action that occurs when large numbers of people work independently on a single project, often modular in its nature. Such projects typically take place on the internet using social software and computer-supported collaboration tools such as wiki technologies, which provide a potentially infinite hypertextual substrate within which the collaboration may be situated. Open source software such as Linux was developed via mass collaboration. Factors Modularity Modularity enables a mass of experiments to proceed in parallel, with different teams working on the same modules, each proposing different solutions. Modularity allows different "blocks" to be easily assembled, facilitating decentralised innovation that all fits together. Differences Cooperation Mass collaboration differs from mass cooperation in that the creative acts taking place require the joint development of shared understandings. Conversely, group members involved in cooperati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Service Innovation
Service innovation is used to refer to many things. These include but not limited to: # Innovation in services, in ''service products'' – new or improved service products (commodities or public services). Often this is contrasted with “technological innovation”, though service products can have technological elements. This sense of service innovation is closely related to service design and "new service development". # Innovation in ''service processes'' – new or improved ways of designing and producing services. This may include innovation in service delivery systems, though often this will be regarded instead as a service product innovation. Innovation of this sort may be technological, technological - or expertise -based, or a matter of work organization (e.g. restructuring of work between professionals and paraprofessionals). # Innovation in ''service firms'', organizations, and industries – organizational innovations, as well as service product and proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Service Science, Management And Engineering
Service science, management, and engineering (SSME) is a term introduced by IBM to describe an interdisciplinary approach to the study and innovation of service systems. More precisely, SSME has been defined as the application of science, management, and engineering disciplines to tasks that one organization beneficially performs for and with another. SSME is also a proposed academic discipline and research area that would complement – rather than replace – the many disciplines that contribute to knowledge about service. The interdisciplinary nature of the field calls for a curriculum and competencies to advance the development and contribution of the field of SSME. Service systems Service systems are designed and constructed, are often very large, and, as complex systems, they have emergent properties. This makes them an engineering kind of system (in MIT's terms). For instance, large-scale service systems include major metropolitan hospitals, highway or high-rise constructio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
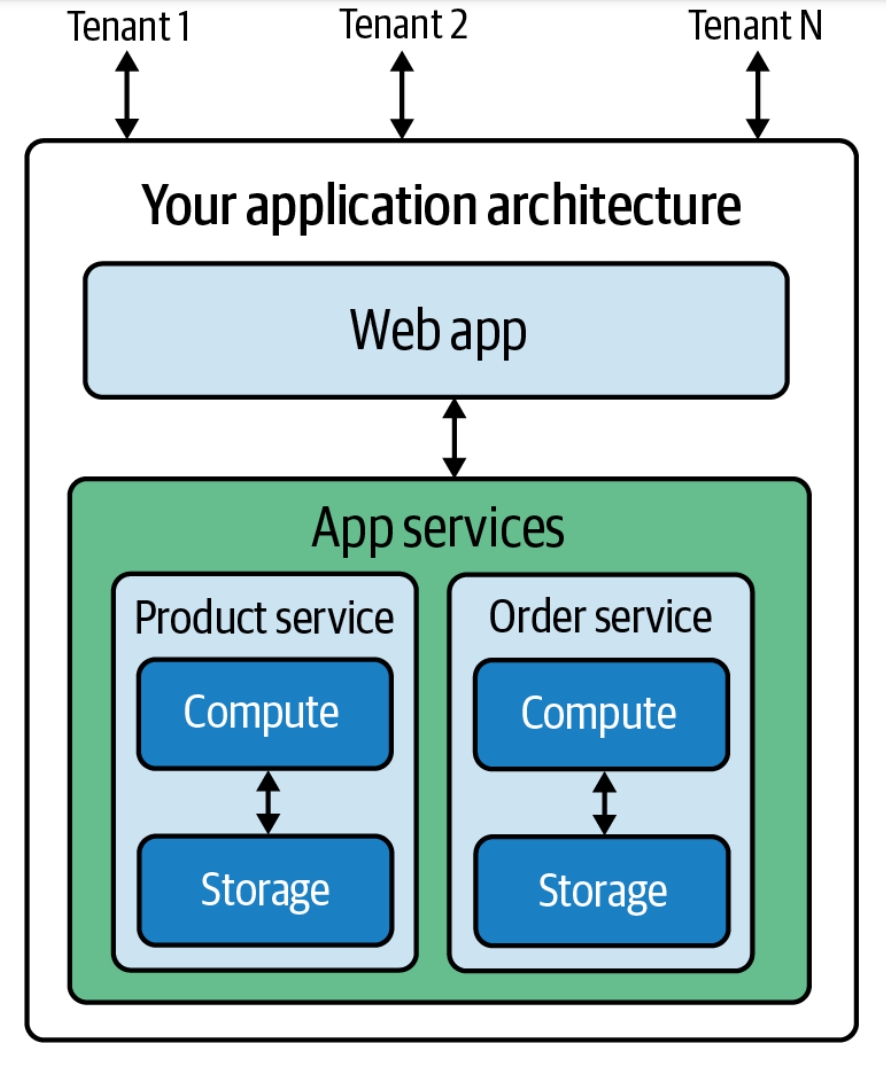 |
Software As A Service
Software as a service (SaaS ) is a cloud computing service model where the provider offers use of application software to a client and manages all needed physical and software resources. SaaS is usually accessed via a web application. Unlike other software delivery models, it separates "the possession and ownership of software from its use". SaaS use began around 2000, and by 2023 was the main form of software application deployment. Unlike most self-hosted software products, only one version of the software exists and only one operating system and configuration is supported. SaaS products typically run on rented infrastructure as a service (IaaS) or platform as a service (PaaS) systems including hardware and sometimes operating systems and middleware, to accommodate rapid increases in usage while providing instant and continuous availability to customers. SaaS customers have the abstraction of limitless computing resources, while economy of scale drives down the cost. Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Disintermediation
Disintermediation is the removal of intermediary, intermediaries in economics from a supply chain, or "cutting out the middlemen" in connection with a transaction or a series of transactions. Instead of going through traditional distribution channels, which had some type of intermediary (such as a Distribution (marketing), distributor, wholesaler, broker, or agency (law), agent), companies deal with customers directly and vice versa, for example via the Internet. History In 1967, the term was originally applied to the banking industry; disintermediation occurred when consumers avoided the intermediation of banks by investing directly in Security (finance), securities (government and private bonds, insurance companies, hedge funds, mutual funds and Share capital, stocks) rather than leaving their money in savings accounts. The original cause was a U.S. government regulation (Regulation Q) which limited the interest rate paid on interest bearing accounts which were insu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Clément Ader built the "Ader Éole" in France and made an uncontrolled, powered hop in 1890. This was the first powered aircraft, although it did not achieve controlled flight. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896. A major leap followed with the construction of the '' Wright Flyer'', the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet engine which enabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |