|
Security Orchestration
Security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) is a group of cybersecurity technologies that allow organizations to respond to some incidents automatically. It collects inputs monitored by the Security Operations Center (computing), security operations team such as alerts from the Security information and event management, SIEM system, Threat Intelligence Platform , TIP, and other security technologies and helps define, prioritize, and drive standardized incident response activities. Organizations uses SOAR platforms to improve the efficiency of physical and digital security operations. SOAR enables administrators to handle security alerts without the need for manual intervention. When the network tool detects a security event, depending on its nature, SOAR can raise an alert to the administrator or take some other action. Components "Orchestration" connects the different security tools and systems of the Information system. It integrates custom-built applications with b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cybersecurity
Computer security, cybersecurity (cyber security), or information technology security (IT security) is the protection of computer systems and networks from attack by malicious actors that may result in unauthorized information disclosure, theft of, or damage to hardware, software, or data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. The field has become of significance due to the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, and due to the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity is one of the most significant challenges of the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societies they support. Security is of especially high importance for systems that govern large-scale systems with far-reaching physical effects, such as power distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Operations Center (computing)
An information security operations center (ISOC or SOC) is a facility where enterprise information systems (web sites, applications, databases, data centers and servers, networks, desktops and other endpoints) are monitored, assessed, and defended. Objective A SOC is related to the people, processes and technologies that provide situational awareness through the detection, containment, and remediation of IT threats in order to manage and enhance an organization's security posture. A SOC will handle, on behalf of an institution or company, any threatening IT incident, and will ensure that it is properly identified, analyzed, communicated, investigated and reported. The SOC also monitors applications to identify a possible cyber-attack or intrusion (event), and determines if it is a genuine malicious threat (incident), and if it could affect business. Regulatory requirements Establishing and operating a SOC is expensive and difficult; organisations should need a good reason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
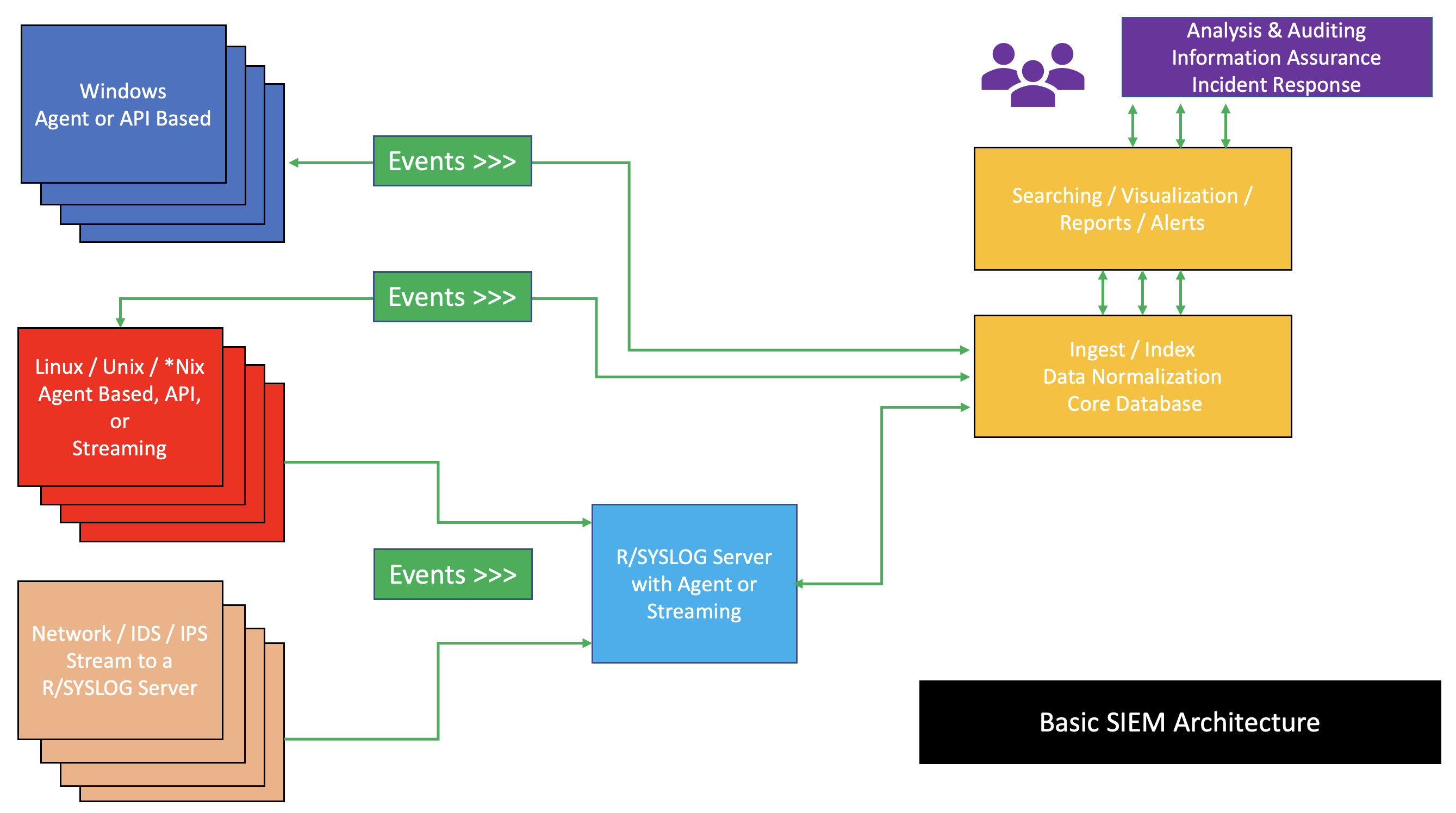
Security Information And Event Management
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a field within the field of computer security, where software products and services combine security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). They provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. Vendors sell SIEM as software, as appliances, or as managed services; these products are also used to log security data and generate reports for compliance purposes. The term and the initialism SIEM was coined by Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams of Gartner in 2005. History Monitoring system logs has grown more prevalent as complex cyber-attacks force compliance and regulatory mechanisms to mandate logging security controls within a Risk Management Framework. Logging levels of a system started with the primary function of troubleshooting system errors or debugging code compiled and run. As operating systems and networks have increased in complexity, so has the even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Threat Intelligence Platform
Threat Intelligence Platform (TIP) is an emerging technology discipline that helps organizations aggregate, correlate, and analyze threat data from multiple sources in real time to support defensive actions. TIPs have evolved to address the growing amount of data generated by a variety of internal and external resources (such as system logs and threat intelligence feeds) and help security teams identify the threats that are relevant to their organization. By importing threat data from multiple sources and formats, correlating that data, and then exporting it into an organization’s existing security systems or ticketing systems, a TIP automates proactive threat management and mitigation. A true TIP differs from typical enterprise security products in that it is a system that can be programmed by outside developers, in particular, users of the platform. TIPs can also use APIs to gather data to generate configuration analysis, Whois information, reverse IP lookup, website content an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incident Response
An incident is an event that could lead to loss of, or disruption to, an organization's operations, services or functions. Incident management (IcM) is a term describing the activities of an organization to identify, analyze, and correct hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence. These incidents within a structured organization are normally dealt with by either an incident response team (IRT), an incident management team (IMT), or Incident Command System (ICS). Without effective incident management, an incident can disrupt business operations, information security, IT systems, employees, customers, or other vital business functions. Description An incident is an event that could lead to the loss of, or disruption to, an organization's operations, services or functions. Incident management (IcM) is a term describing the activities of an organization to identify, analyze, and correct hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence. If not managed, an incident can escalate into an emerg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information System
An information system (IS) is a formal, sociotechnical, organizational system designed to collect, process, store, and distribute information. From a sociotechnical perspective, information systems are composed by four components: task, people, structure (or roles), and technology. Information systems can be defined as an integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data of which the data is used to provide information, contribute to knowledge as well as digital products that facilitate decision making. A computer information system is a system that is composed of people and computers that processes or interprets information. The term is also sometimes used to simply refer to a computer system with software installed. "Information systems" is also an academic field study about systems with a specific reference to information and the complementary networks of computer hardware and software that people and organizations use to collect, filter, process, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firewall (computing)
In computing, a firewall is a network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. A firewall typically establishes a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network, such as the Internet. History The term '' firewall'' originally referred to a wall intended to confine a fire within a line of adjacent buildings. Later uses refer to similar structures, such as the metal sheet separating the engine compartment of a vehicle or aircraft from the passenger compartment. The term was applied in the late 1980s to network technology that emerged when the Internet was fairly new in terms of its global use and connectivity. The predecessors to firewalls for network security were routers used in the late 1980s. Because they already segregated networks, routers could apply filtering to packets crossing them. Before it was used in real-life computing, the term appeared in the 1983 computer-hacking movie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Behavior Analytics
User behavior analytics (UBA) is a cybersecurity process regarding the detection of insider threats, targeted attacks, and financial fraud that tracks a system's users. UBA looks at patterns of human behavior, and then analyzes observations to detect anomalies that may indicate potential threats. Purpose The purpose of UBA, according to Johna Till Johnson of Nemertes Research, is that " Security systems provide so much information that it's tough to uncover information that truly indicates a potential for real attack. Analytics tools help make sense of the vast amount of data that SIEM, IDS/IPS, system logs, and other tools gather. UBA tools use a specialized type of security analytics that focuses on the behavior of systems and the people using them. UBA technology first evolved in the field of marketing, to help companies understand and predict consumer- buying patterns. But as it turns out, UBA can be extraordinarily useful in the security context too." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Security Operations Center
An information security operations center (ISOC or SOC) is a facility where enterprise information systems (web sites, applications, databases, data centers and servers, networks, desktops and other endpoints) are monitored, assessed, and defended. Objective A SOC is related to the people, processes and technologies that provide situational awareness through the detection, containment, and remediation of IT threats in order to manage and enhance an organization's security posture. A SOC will handle, on behalf of an institution or company, any threatening IT incident, and will ensure that it is properly identified, analyzed, communicated, investigated and reported. The SOC also monitors applications to identify a possible cyber-attack or intrusion (event), and determines if it is a genuine malicious threat (incident), and if it could affect business. Regulatory requirements Establishing and operating a SOC is expensive and difficult; organisations should need a good reason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runbook
In a computer system or network, a runbook is a compilation of routine procedures and operations that the system administrator or operator carries out. System administrators in IT departments and NOCs use runbooks as a reference. Runbooks can be in either electronic or in physical book form. Typically, a runbook contains procedures to begin, stop, supervise, and debug the system. It may also describe procedures for handling special requests and contingencies. An effective runbook allows other operators, with prerequisite expertise, to effectively manage and troubleshoot a system. Through runbook automation, these processes can be carried out using software tools in a predetermined manner. In addition to automating IT specific processes, the results of the runbook can be presented on-screen back to the user or Service Desk engineer. Multiple runbooks can be linked together using a Decision Tree to provide users with interactive troubleshooting and guided procedures. Runbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is " back up", whereas the noun and adjective form is "backup". Backups can be used to recover data after its loss from data deletion or corruption, or to recover data from an earlier time. Backups provide a simple form of disaster recovery; however not all backup systems are able to reconstitute a computer system or other complex configuration such as a computer cluster, active directory server, or database server. A backup system contains at least one copy of all data considered worth saving. The data storage requirements can be large. An information repository model may be used to provide structure to this storage. There are different types of data storage devices used for copying backups of data that is already in secondary storage onto archi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |