|
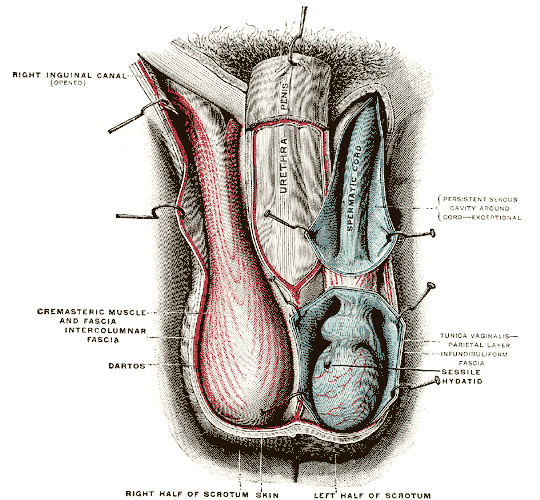
Scrotum
In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin containing the external spermatic fascia, testicles, epididymides, and vasa deferentia. The scrotum will usually tighten when exposed to cold temperatures. The scrotum is homologous to the labia majora in females. Structure In regards to humans, the scrotum is a suspended two-chambered sac of skin and muscular tissue containing the testicles and the lower part of the spermatic cords. It is located behind the penis and above the perineum. The perineal raphe is a small, vertical ridge of skin that expands from the anus and runs through the middle of the scrotum front to back. The scrotum is also a distention of the perineum and carries some abdominal tissues into its cavity including the testicular artery, testicular vein, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testicle
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring.Reproductive System 2001 Body Guide powered by Adam Animals In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external gen ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Scrotal Veins
The posterior scrotal veins are veins of the scrotum. They accompany the posterior scrotal arteries. They drain into the vesical venous plexus. They help to drain blood from part of the scrotum. Structure The posterior scrotal veins accompany the posterior scrotal arteries. They lie superficially in the scrotum. They drain into the vesical venous plexus. Function The posterior scrotal veins help to drain blood from part of the scrotum in men A man is an adult male human. Before adulthood, a male child or adolescent is referred to as a boy. Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromosome from the fa .... References External links * https://web.archive.org/web/20071024000415/http://anatomy.med.umich.edu/anatomytables/veins_pelvis_perineum.html {{circulatory-stub Veins of the torso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
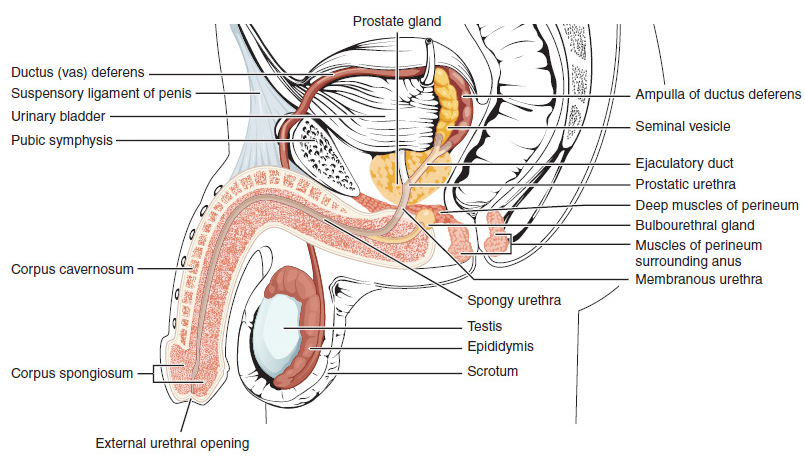
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genital Branch Of Genitofemoral Nerve
The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, also known as the external spermatic nerve in males, is a nerve in the abdomen that arises from the genitofemoral nerve. The genital branch supplies the cremaster muscle and anterior scrotal skin in males, and the skin of the mons pubis and labia majora in females. Structure The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve arises from the ventral primary divisions of L1-L2 spinal nerve roots. It passes outward on the psoas major muscle, and pierces the fascia transversalis, or passes through the deep inguinal ring. It then descends within the spermatic cord. In males, it passes through to the scrotum, where it supplies the cremaster, dartos muscle and gives a few filaments to the skin of the scrotum. In females, it accompanies the round ligament of the uterus, where it terminates as the nerve supplying the skin of the labia majora and mons pubis. Function The genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve is responsible for the motor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Related Male And Female Reproductive Organs
This list of related male and female reproductive organs shows how the male and female reproductive organs and the development of the reproductive system are related, sharing a common developmental path. This makes them biological homologues. These organs differentiate into the respective sex organs in males and females. List Internal organs External organs The external genitalia of both males and females have similar origins. They arise from the genital tubercle that forms anterior to the cloacal folds (proliferating mesenchymal cells around the cloacal membrane). The caudal aspect of the cloacal folds further subdivides into the posterior anal folds and the anterior urethral folds. Bilateral to the urethral fold, genital swellings become prominent. These structures are the future scrotum and labia majora in males and females, respectively. The genital tubercles of an eight-week-old embryo of either sex are identical. They both have a glans area, which will go on to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penis
A penis (; : penises or penes) is a sex organ through which male and hermaphrodite animals expel semen during copulation (zoology), copulation, and through which male placental mammals and marsupials also Urination, urinate. The term ''penis'' applies to many intromittent organs of vertebrates and invertebrates, but not to all. As an example, the intromittent organ of most Cephalopoda is the hectocotylus, a specialized arm, and male spiders use their pedipalps. Even within the Vertebrata, there are morphological variants with specific terminology, such as Hemipenis, hemipenes. Etymology The word "penis" is taken from the Latin word for "Latin profanity#Synonyms and metaphors, tail". Some derive that from Proto-Indo-European language, Indo-European ''*pesnis'', and the Greek word πέος = "penis" from Indo-European ''*pesos''. Prior to the adoption of the Latin word in English, the penis was referred to as a "yard". The Oxford English Dictionary cites an example of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an extension of the peritoneum that passes through the transversalis fascia. Each testicle develops in the lower thoracic and upper lumbar region and migrates into the scrotum. During its descent it carries along with it the vas deferens, its vessels, nerves etc. There is one on each side. Structure The spermatic cord is ensheathed in three layers of tissue: * '' external spermatic fascia'', an extension of the innominate fascia that overlies the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle. * '' cremasteric muscle and fascia'', formed from a continuation of the internal oblique muscle and its fascia. * '' internal spermatic fascia'', continuous with the transversalis fascia. The normal diameter of the spermatic cord is about 16 mm (range 11 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Spermatic Fascia
The external spermatic fascia (intercrural or intercolumnar fascia) is a thin membrane, prolonged downward around the surface of the spermatic cord and testis. It is separated from the dartos tunic by loose areolar tissue. It is occasionally referred to as 'Le Fascia de Webster' after an anatomist who once described it. Structure The external spermatic fascia is derived from the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle. It is acquired by the spermatic cord at the superficial inguinal ring. References External links * - "The inguinal canal and derivation of the layers of the spermatic cord The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...." * * () Scrotum Fascia {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species. Sex organs are typically differentiated into male and female types. In animals (including humans), the male sex organs include the testicles, epididymis, epididymides, and penis; the female sex organs include the clitoris, Ovary, ovaries, oviducts, and vagina. The testicle in the male and the ovary in the female are called the ''primary sex organs''. All other sex-related organs are known as ''secondary sex organs''. The outer parts are known as the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes, while the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Nerve
The perineal nerve is a nerve of the pelvis. It arises from the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. It gives superficial branches to the skin, and a deep branch to muscles. It supplies the skin and muscles of the perineum. Its latency is tested with electrodes. Structure The perineal nerve is a branch of the pudendal nerve. It lies below the internal pudendal artery. It accompanies the perineal artery. It passes through the pudendal canal for around 2 or 3 cm. Whilst still in the canal, it divides into superficial branches and a deep branch. The superficial branches of the perineal nerve become the posterior scrotal nerves in men,Essential Clinical Anatomy. K.L. Moore & A.M. Agur. Lippincott, 2 ed. 2002. Page 263 and the posterior labial nerves in women. The deep branch of the perineal nerve (also known as the "muscular" branch) travels to the muscles of the perineum. Both of these are superficial to the dorsal nerve of the penis or the dorsal nerve of the clitoris. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labioscrotal Swelling
The labioscrotal swellings (genital swellings or labioscrotal folds) are paired structures in the mammalian embryo that represent the final stage of development of the caudal end of the external genitals before sexual differentiation. In humans, the two swellings merge: * In the ''female'', they become the posterior labial commissure. The sides of the genital tubercle grow backward as the genital swellings, which ultimately form the labia majora; the tubercle itself becomes the mons pubis. * In the ''male'', they become the scrotum In most terrestrial mammals, the scrotum (: scrotums or scrota; possibly from Latin ''scortum'', meaning "hide" or "skin") or scrotal sac is a part of the external male genitalia located at the base of the penis. It consists of a sac of skin .... References External links "Development of Male External Genitalia", at mcgill.caDiagram at mhhe.com* * {{Authority control Embryology of urogenital system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |