|
Scalar Field Solution
In general relativity, a scalar field solution is an exact solution of the Einstein field equation in which the gravitational field is due entirely to the field energy and momentum of a scalar field. Such a field may or may not be ''massless'', and it may be taken to have ''minimal curvature coupling'', or some other choice, such as ''conformal coupling''. Definition In general relativity, the geometric setting for physical phenomena is a Lorentzian manifold, which is physically interpreted as a curved spacetime, and which is mathematically specified by defining a metric tensor g_ (or by defining a frame field). The curvature tensor R^_ of this manifold and associated quantities such as the Einstein tensor G_, are well-defined even in the absence of any physical theory, but in general relativity they acquire a physical interpretation as geometric manifestations of the gravitational field. In addition, we must specify a scalar field by giving a function \psi. This function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Relativity
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalizes special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the ' is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations. Newton's law of universal gravitation, which describes classical gravity, can be seen as a prediction of general relativity for the almost flat spacetime geometry around stationary mass distributions. Some predictions of general relativity, however, are beyond Newton's law of universal gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Field Theory
In physics, an effective field theory is a type of approximation, or effective theory, for an underlying physical theory, such as a quantum field theory or a statistical mechanics model. An effective field theory includes the appropriate degrees of freedom to describe physical phenomena occurring at a chosen length scale or energy scale, while ignoring substructure and degrees of freedom at shorter distances (or, equivalently, at higher energies). Intuitively, one averages over the behavior of the underlying theory at shorter length scales to derive what is hoped to be a simplified model at longer length scales. Effective field theories typically work best when there is a large separation between length scale of interest and the length scale of the underlying dynamics. Effective field theories have found use in particle physics, statistical mechanics, condensed matter physics, general relativity, and hydrodynamics. They simplify calculations, and allow treatment of dissipatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Group
In physics and mathematics, the Lorentz group is the group of all Lorentz transformations of Minkowski spacetime, the classical and quantum setting for all (non-gravitational) physical phenomena. The Lorentz group is named for the Dutch physicist Hendrik Lorentz. For example, the following laws, equations, and theories respect Lorentz symmetry: * The kinematical laws of special relativity * Maxwell's field equations in the theory of electromagnetism * The Dirac equation in the theory of the electron * The Standard Model of particle physics The Lorentz group expresses the fundamental symmetry of space and time of all known fundamental laws of nature. In small enough regions of spacetime where gravitational variances are negligible, physical laws are Lorentz invariant in the same manner as special relativity. Basic properties The Lorentz group is a subgroup of the Poincaré group—the group of all isometries of Minkowski spacetime. Lorentz transformations are, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Identities
In mathematics, Newton's identities, also known as the Girard–Newton formulae, give relations between two types of symmetric polynomials, namely between power sums and elementary symmetric polynomials. Evaluated at the roots of a monic polynomial ''P'' in one variable, they allow expressing the sums of the ''k''-th powers of all roots of ''P'' (counted with their multiplicity) in terms of the coefficients of ''P'', without actually finding those roots. These identities were found by Isaac Newton around 1666, apparently in ignorance of earlier work (1629) by Albert Girard. They have applications in many areas of mathematics, including Galois theory, invariant theory, group theory, combinatorics, as well as further applications outside mathematics, including general relativity. Mathematical statement Formulation in terms of symmetric polynomials Let ''x''1, ..., ''x''''n'' be variables, denote for ''k'' ≥ 1 by ''p''''k''(''x''1, ..., ''x''''n'') the ''k''-th p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gröbner Basis
In mathematics, and more specifically in computer algebra, computational algebraic geometry, and computational commutative algebra, a Gröbner basis is a particular kind of generating set of an ideal in a polynomial ring over a field . A Gröbner basis allows many important properties of the ideal and the associated algebraic variety to be deduced easily, such as the dimension and the number of zeros when it is finite. Gröbner basis computation is one of the main practical tools for solving systems of polynomial equations and computing the images of algebraic varieties under projections or rational maps. Gröbner basis computation can be seen as a multivariate, non-linear generalization of both Euclid's algorithm for computing polynomial greatest common divisors, and Gaussian elimination for linear systems. Gröbner bases were introduced in 1965, together with an algorithm to compute them ( Buchberger's algorithm), by Bruno Buchberger in his Ph.D. thesis. He named them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characteristic Polynomial
In linear algebra, the characteristic polynomial of a square matrix is a polynomial which is invariant under matrix similarity and has the eigenvalues as roots. It has the determinant and the trace of the matrix among its coefficients. The characteristic polynomial of an endomorphism of a finite-dimensional vector space is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix of that endomorphism over any base (that is, the characteristic polynomial does not depend on the choice of a basis). The characteristic equation, also known as the determinantal equation, is the equation obtained by equating the characteristic polynomial to zero. In spectral graph theory, the characteristic polynomial of a graph is the characteristic polynomial of its adjacency matrix. Motivation In linear algebra, eigenvalues and eigenvectors play a fundamental role, since, given a linear transformation, an eigenvector is a vector whose direction is not changed by the transformation, and the corresponding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
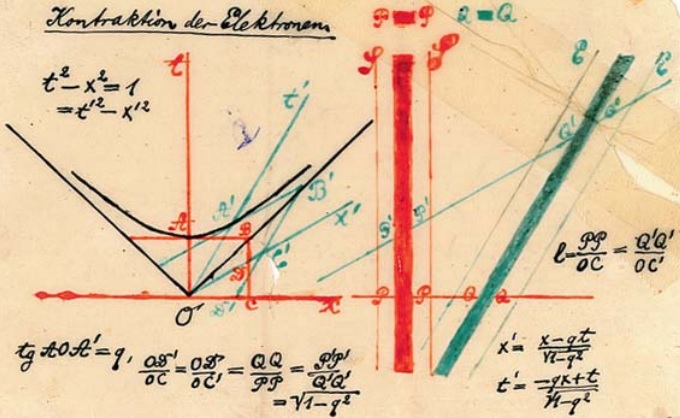
Spacelike
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timelike
In physics, spacetime is a mathematical model that combines the three dimensions of space and one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional manifold. Spacetime diagrams can be used to visualize relativistic effects, such as why different observers perceive differently where and when events occur. Until the 20th century, it was assumed that the three-dimensional geometry of the universe (its spatial expression in terms of coordinates, distances, and directions) was independent of one-dimensional time. The physicist Albert Einstein helped develop the idea of spacetime as part of his theory of relativity. Prior to his pioneering work, scientists had two separate theories to explain physical phenomena: Isaac Newton's laws of physics described the motion of massive objects, while James Clerk Maxwell's electromagnetic models explained the properties of light. However, in 1905, Einstein based a work on special relativity on two postulates: * The laws of physics are invariant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
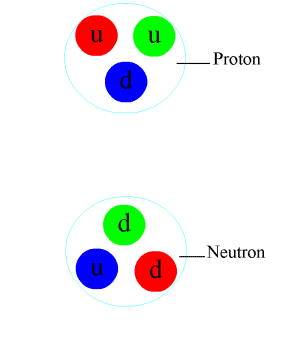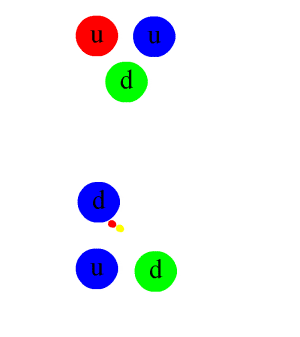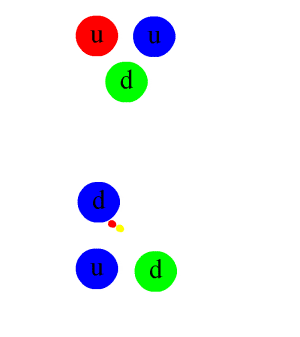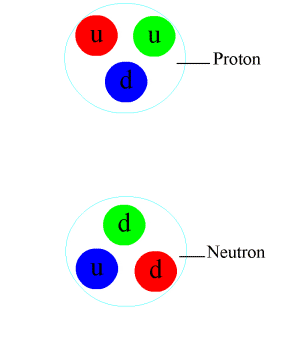
Pion
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more generally, the lightest hadrons. They are unstable, with the charged pions and decaying after a mean lifetime of 26.033 nanoseconds ( seconds), and the neutral pion decaying after a much shorter lifetime of 85 attoseconds ( seconds). Charged pions most often decay into muons and muon neutrinos, while neutral pions generally decay into gamma rays. The exchange of virtual pions, along with vector, rho and omega mesons, provides an explanation for the residual strong force between nucleons. Pions are not produced in radioactive decay, but commonly are in high-energy collisions between hadrons. Pions also result from some matter–antimatter annihilation events. All types of pions are also produced in natural pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintessence (physics)
In physics, quintessence is a hypothetical form of dark energy, more precisely a scalar field, postulated as an explanation of the observation of an accelerating rate of expansion of the universe. The first example of this scenario was proposed by Ratra and Peebles (1988) and Wetterich (1988). The concept was expanded to more general types of time-varying dark energy, and the term "quintessence" was first introduced in a 1998 paper by Robert R. Caldwell, Rahul Dave and Paul Steinhardt. It has been proposed by some physicists to be a fifth fundamental force. Quintessence differs from the cosmological constant explanation of dark energy in that it is dynamic; that is, it changes over time, unlike the cosmological constant which, by definition, does not change. Quintessence can be either attractive or repulsive depending on the ratio of its kinetic and potential energy. Those working with this postulate believe that quintessence became repulsive about ten billion years ago, ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |