|
Sartidia Perrieri
''Sartidia perrieri'' is a grass species endemic to Madagascar, known from only one collected individual and now considered extinct. Henri Perrier de la Bâthie, in 1914, collected a plant in the central region of Madagascar, near Antsirabe, at an elevation of , where it grew on sandstone rocks in tapia woodland. He wrote in the description of the dried herbarium specimen that he only ever saw one individual of this species, suggesting it was already very rare at that time. Aimée Antoinette Camus named it after its collector and described it as new species in the genus '' Aristida''; Pierre Bourreil later transferred it to '' Sartidia''. ''Sartidia perrieri'' is a tuft-forming grass. The known individual is roughly high, with long leaf blades. Inflorescence is a dense, long panicle and the species has long awns extending from the lemmas in the spikelets. With its clusters of large spikelets, it is very different from the only other known ''Sartidia'' species from Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aimée Antoinette Camus
Aimée Antoinette Camus (1 May 1879 – 17 April 1965) was a French botanist. She was best known for her study of orchids and oaks. Camus also has the legacy of authoring the second highest number of land plant species among female scientists, in total naming 677 species. Camus was the daughter of Edmond Gustave Camus, also a botanist, and was born in L'Isle-Adam, about 50 kilometres north of Paris. Under her father's influence she specialized in the study of orchids and the anatomy of the plant and worked for some time with other professionals such as Paul Bergon (1863-1912) and Paul Henri Lecomte (1856-1934). Her sister was the painter Blanche-Augustine Camus (1881-1968). She also produced a major treatment of the oaks and stone oaks, providing the first comprehensive systematic treatment of the latter genus. Camus published the work ''L'Iconographie des Orchidées d´Europe et du Bassin Méditerranéen''. She gave the name of ''Neohouzeaua'' to a genus of seven tro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
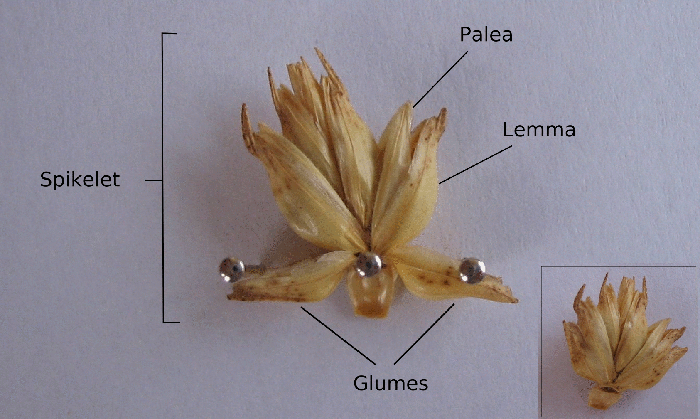
Spikelet
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Plants
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristidoideae
The Aristideae is the sole tribe of grasses in the monotypic subfamily Aristidoideae of the true grass family Poaceae. Its members are herbaceous annuals or perennials found in the tropics, subtropics and temperate zones. The tribe has over 300 species in three genera: The subfamily is a member of the PACMAD clade of grasses, the evolutionary group in which C4 photosynthesis independently evolved a number of times.Phylogeny of the Paniceae (Poaceae: Panicoideae): integrating plastid DNA sequences and morphology into a new classification Osvaldo Morrone, Lone Aagesen, Maria A. Scataglini, Diego L. Salariato, Silvia S. Denham, Maria A. Chemisquy, Silvana M. Sede, Liliana M. Giussani, Elizabeth A. Kellogg and Fernando O. Zuloag Cladistics 28 (2012) 333–356 *''Aristida ''Aristida'' is a very nearly cosmopolitan genus of plants in the grass family. ''Aristida'' is distinguished by having three awns (bristles) on each lemma of each floret. The genus includes about 300 speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C3 Carbon Fixation
carbon fixation is the most common of three metabolic pathways for carbon fixation in photosynthesis, along with and CAM. This process converts carbon dioxide and ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP, a 5-carbon sugar) into two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate through the following reaction: :CO2 + H2O + RuBP → (2) 3-phosphoglycerate This reaction was first discovered by Melvin Calvin, Andrew Benson and James Bassham in 1950. C3 carbon fixation occurs in all plants as the first step of the Calvin–Benson cycle. (In and CAM plants, carbon dioxide is drawn out of malate and into this reaction rather than directly from the air.) Plants that survive solely on fixation ( plants) tend to thrive in areas where sunlight intensity is moderate, temperatures are moderate, carbon dioxide concentrations are around 200 ppm or higher, and groundwater is plentiful. The plants, originating during Mesozoic and Paleozoic eras, predate the plants and still represent approximately 95% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C4 Carbon Fixation
carbon fixation or the Hatch–Slack pathway is one of three known photosynthetic processes of carbon fixation in plants. It owes the names to the 1960's discovery by Marshall Davidson Hatch and Charles Roger Slack that some plants, when supplied with 14, incorporate the 14C label into four-carbon molecules first. fixation is an addition to the ancestral and more common carbon fixation. The main carboxylating enzyme in photosynthesis is called RuBisCO, which catalyses two distinct reactions using either (carboxylation) or oxygen (oxygenation) as a substrate. The latter process, oxygenation, gives rise to the wasteful process of photorespiration. photosynthesis reduces photorespiration by concentrating around RuBisCO. To ensure that RuBisCO works in an environment where there is a lot of carbon dioxide and very little oxygen, leaves generally differentiate two partially isolated compartments called mesophyll cells and bundle-sheath cells. is initially fixed in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Expansion
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land ( arable land, pastures, etc.) especially in the 20th and 21st centuries. The agricultural expansion is often explained as a direct consequence of the global increase in food and energy requirements due to continuing population growth (both which in turn have been attributed to agricultural expansion itself), with an estimated expectation of 10 to 11 billion humans on Earth by end of this century. It is foreseen that most of the world's non-agrarian ecosystems ( terrestrial and aquatic) will be affected adversely, from habitat loss, land degradation, overexploitation, and other problems. The intensified food (and biofuel) production will in particular affect the tropical regions. Most modern agriculture relies on intensive methods. Further expansion of the predominant farming types that rest on a small number of highly productive crops has led to a significant loss of biodiversity on a global scale already. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct In The Wild
A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss. Examples Examples of species and subspecies that are extinct in the wild include: * Alagoas curassow (last unconfirmed sighting reported in the late 1980s, listed extinct in the wild since 1994) * Beloribitsa * Cachorrito de charco palmal (last seen in 1994, listed extinct in the wild since 1996) * Christmas Island blue-tailed skink (listed extinct in the wild since 2014) * Dabry's sturgeon (listed extinct in the wild since 2022) * Escarpment cycad (listed extinct in the wild since 2006) * Franklinia (last seen in 1803, listed extinct in the wild since 1998) * Golden skiffia (listed extinct in the wild since 1996) * Guam kingfisher (listed extinct in the wild since 1986) * Hawaiian crow or ʻalalā (last seen in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Phylogenetics
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to determine the processes by which diversity among species has been achieved. The result of a molecular phylogenetic analysis is expressed in a phylogenetic tree. Molecular phylogenetics is one aspect of molecular systematics, a broader term that also includes the use of molecular data in taxonomy and biogeography. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular evolution correlate. Molecular evolution is the process of selective changes (mutations) at a molecular level (genes, proteins, etc.) throughout various branches in the tree of life (evolution). Molecular phylogenetics makes inferences of the evolutionary relationships that arise due to molecular evolution and results in the construction of a phylogenetic tree. History The theoretical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear DNA
Nuclear DNA (nDNA), or nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid, is the DNA contained within each cell nucleus of a eukaryotic organism. It encodes for the majority of the genome in eukaryotes, with mitochondrial DNA and plastid DNA coding for the rest. It adheres to Mendelian inheritance, with information coming from two parents, one male and one female—rather than matrilineally (through the mother) as in mitochondrial DNA. Structure Nuclear DNA is a nucleic acid, a polymeric biomolecule or biopolymer, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Its structure is a double helix, with two strands wound around each other, a structure first described by Francis Crick and James D. Watson (1953) using data collected by Rosalind Franklin. Each strand is a long polymer chain of repeating nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a five-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and an organic base. Nucleotides are distinguished by their bases: purines, large bases that include adenine and gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast DNA
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, '' Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and '' Marchantia polymorpha'' (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced. Molecular structure Chloroplast DNAs are circular, and are typically 120,000–170,000 base pairs long. They can have a contour length of around 30–60 micrometers, and have a mass of about 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid speed of sequencing attained with m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



