|
River Terraces (tectonic–climatic Interaction)
Terrace (geology), Terraces can be formed in many ways and in several geologic and environmental settings. By studying the size, shape, and age of terraces, one can determine the geologic processes that formed them. When terraces have the same age and/or shape over a region, it is often indicative that a large-scale geologic or environmental mechanism is responsible. Tectonic uplift and Climate change (general concept), climate change are viewed as dominant mechanisms that can shape the earth’s surface through erosion. River terraces can be influenced by one or both of these forcing mechanisms and therefore can be used to study variation in tectonics, climate, and erosion, and how these processes interact. River terrace formation Long-lived river (fluvial) systems can produce a series of terrace (geology), terrace surfaces over the course of their geologic lifetime. When rivers Aggradation, flood, sediment deposits in sheets across the floodplain and build up over time. Later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Series Of Paired River Terraces Plainsvg
A, or a, is the first Letter (alphabet), letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''a'' (pronounced ), plural English alphabet#Letter names, ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Greek alphabet#History, Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The Letter case, uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English grammar, "English articles, a", and its variant "English articles#Indefinite article, an", are Article (grammar)#Indefinite article, indefinite arti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmogenic Nuclide
Cosmogenic nuclides (or cosmogenic isotopes) are rare nuclides (isotopes) created when a high-energy cosmic ray interacts with the nucleus of an '' in situ'' Solar System atom, causing nucleons (protons and neutrons) to be expelled from the atom (see cosmic ray spallation). These nuclides are produced within Earth materials such as rocks or soil, in Earth's atmosphere, and in extraterrestrial items such as meteoroids. By measuring cosmogenic nuclides, scientists are able to gain insight into a range of geological and astronomical processes. There are both radioactive and stable cosmogenic nuclides. Some of these radionuclides are tritium, carbon-14 and phosphorus-32. Certain light (low atomic number) primordial nuclides (isotopes of lithium, beryllium and boron) are thought to have been created not only during the Big Bang, but also (and perhaps primarily) to have been made after the Big Bang, but before the condensation of the Solar System, by the process of cosmic ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergent Coastline
An emergent coastline is a stretch along the coast that has been exposed by the sea by a relative fall in sea levels by either isostasy or eustasy. Emergent coastline are the opposite of submergent coastlines, which have experienced a relative rise in sea levels. The emergent coastline may have several specific landforms: * Raised beach or machair * Wave cut platform * Sea cave such as King's Cave, Isle of Arran The Scottish Gaelic word ''machair'' or ''machar'' refers to a fertile low-lying raised beach found on some of the coastlines of Ireland and Scotland (especially the Outer Hebrides). Hudson Bay, in Canada's north, is an example of an emergent coastline. It is still emerging by as much as 1 cm per year. Another example of emergent coastline is the Eastern Coastal Plains of the Indian Subcontinent The Indian subcontinent is a physiographical region in Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
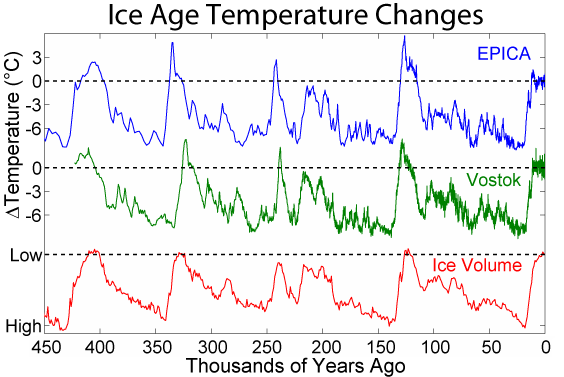
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate between glacial periods. The Last Glacial Period ended about 15,000 years ago. The Holocene is the current interglacial. A time with no glaciers on Earth is considered a greenhouse climate state. Quaternary Period Within the Quaternary, which started about 2.6 million years before present, there have been a number of glacials and interglacials. At least eight glacial cycles have occurred in the last 740,000 years alone. Penultimate Glacial Period The Penultimate Glacial Period (PGP) is the glacial period that occurred before the Last Glacial Period. It began about 194,000 years ago and ended 135,000 years ago, with the beginning of the Eemian interglacial. Last Glacial Period The last glacial period was the most recent glacial period wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milankovitch Cycles
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypothesized that variations in eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession combined to result in cyclical variations in the intra-annual and latitudinal distribution of solar radiation at the Earth's surface, and that this orbital forcing strongly influenced the Earth's climatic patterns. Earth's movements The Earth's rotation around its axis, and revolution around the Sun, evolve over time due to gravitational interactions with other bodies in the Solar System. The variations are complex, but a few cycles are dominant. The Earth's orbit varies between nearly circular and mildly elliptical (its eccentricity varies). When the orbit is more elongated, there is more variation in the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and in the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas Landsat 7
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia (Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus, the Ganges, and the Tsangpo–Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their combined drainage basin is home to some 600 million people; 53 million people live in the Himalayas. The Himalayas have pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Terrace Diagram(plain Svg)
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean. Marine or marines may refer to: Ocean * Maritime (other) * Marine art * Marine biology * Marine debris * Marine habitats * Marine life * Marine pollution Military * Marines, a naval-based infantry force ** United States Marine Corps ** Royal Marines of the UK ** Brazilian Marine Corps ** Spanish Marine Infantry ** Fusiliers marins (France) ** Indonesian Marine Corps ** Republic of China Marine Corps ** Republic of Korea Marine Corps ** Royal Thai Marine Corps *"Marine" also means "navy" in several languages: ** Austro-Hungarian Navy () ** Belgian Navy (, , ) ** Royal Canadian Navy () *** Provincial Marine (1796–1910), a predecessor to the Royal Canadian Navy ** Navy of the Democratic Republic of the Congo () ** Royal Danish Navy () ** Finnish Navy (, ) ** French Navy () ** Gabonese Navy () ** German Navy () ** Royal Moroccan Navy () ** Royal Netherlands Navy () ** Swedish Navy () Place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annum
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to help identify biozones, as they make up the basic biostratig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–thorium Dating
Uranium–thorium dating, also called thorium-230 dating, uranium-series disequilibrium dating or uranium-series dating, is a radiometric dating technique established in the 1960s which has been used since the 1970s to determine the age of calcium carbonate materials such as speleothem or coral. Unlike other commonly used radiometric dating techniques such as rubidium–strontium or uranium–lead dating, the uranium-thorium technique does not measure accumulation of a stable end-member decay product. Instead, it calculates an age from the degree to which secular equilibrium has been restored between the radioactive isotope thorium-230 and its radioactive parent uranium-234 within a sample. Background Thorium is not soluble in natural water under conditions found at or near the surface of the earth, so materials grown in or from this water do not usually contain thorium. In contrast, uranium is soluble to some extent in all natural water, so any material that precipitates o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |