|
Richard Hauptmann
Bruno Richard Hauptmann (November 26, 1899 – April 3, 1936) was a German-born carpenter who was convicted of the abduction and murder of the 20-month-old son of aviator Charles Lindbergh and his wife Anne Morrow Lindbergh. The Lindbergh kidnapping became known as "The Crime of the Century". Both Hauptmann and his wife, Anna Hauptmann (who later sued the State of New Jersey, various former police officers, the Hearst newspapers that had published pre-trial articles insisting on Hauptmann's guilt, and former prosecutor David T. Wilentz), proclaimed his innocence until he was executed in 1936 by electric chair at the Trenton State Prison. Background Bruno Richard Hauptmann was born in Kamenz, a town near Dresden in the Kingdom of Saxony, which was a state of the German Empire. He was the youngest of five children. Neither he nor his family or friends used the name Bruno, although prosecutors in the Lindbergh kidnapping trial insisted on referring to him by that name. At the age o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamenz
Kamenz () or Kamjenc ( Sorbian) is a town (''Große Kreisstadt'') in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany. Until 2008 it was the administrative seat of Kamenz District. The town is known as the birthplace of the philosopher and poet Gotthold Ephraim Lessing and Bruno Hauptmann, convicted kidnapper of the Lindbergh baby. It lies north-east of the major city of Dresden. Geography This small town is located in the west of the Upper Lusatia historic region (West Lusatia), about northeast of Dresden and about northwest of Bautzen. Situated on the Black Elster river, between the West Lusatian Hills and the Lusatian Highlands rising in the south, the town was built on greywacke and granite rocks which were mined here for centuries. Kamenz railway station is the terminus of Lübbenau–Kamenz and Kamenz–Pirna railway lines. It is served by '' Regionalbahn'' trains from Dresden Hauptbahnhof, operated by the Städtebahn Sachsen. The Hutberg hill west of the town centre, at an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutscher Pfadfinderverband
The Deutsche Pfadfinderverband (DPV; approximate translation: ''German Scout Association'') is an umbrella federation of sixteen German non-denominational Scouting associations. It was founded in 1970 and serves about 29,000 members. History The DPV was founded in 1970 under the name ''Deutsche Pfadfinder'' by a number of regional organizations which had left the Bund Deutscher Pfadfinder (BDP) due to the perceived loss of political neutrality within the latter. In 1971, the Deutscher Pfadfinderbund joined the ''Deutsche Pfadfinder'' and the federation was renamed to ''Deutscher Pfadfinderverband''. However, the Deutscher Pfadfinderbund left the federation after some years. In 1977, the DPV was amongst the founding members of the Deutscher Pfadfinderring (DPR); this traditional Scouting federation tried to form a counterweight to the Ring deutscher Pfadfinderverbände and the Ring Deutscher Pfadfinderinnenverbände. The DPR was disbanded in 1995. An application for membershi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highfields (Amwell And Hopewell, New Jersey)
Highfields was the home of Charles and Anne Lindbergh, the famous aviators. It was the location of the Lindbergh kidnapping, after which it was turned into a rehabilitation center. The home was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1994. Construction The Lindberghs built Highfields in 1931 on a secluded spot of the Sourland Mountain so as to escape the spotlight brought on by their celebrity status. After his pioneering solo flight from New York to Paris in 1927, four million people had attended the ticker tape parade in Charles Lindbergh's honor, and he had received two million congratulatory telegrams, making him one of the most famous Americans of the century. The Sourland Mountain location, while secluded, afforded easy access by air and automobile to the Lindberghs' offices in New York City and to the laboratories of nearby Princeton University, to which they had been granted access. Lindbergh kidnapping The home was the site of one of the most notorious ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpentry
Carpentry is a skilled trade and a craft in which the primary work performed is the cutting, shaping and installation of building materials during the construction of buildings, ships, timber bridges, concrete formwork, etc. Carpenters traditionally worked with natural wood and did rougher work such as framing, but today many other materials are also used and sometimes the finer trades of cabinetmaking and furniture building are considered carpentry. In the United States, 98.5% of carpenters are male, and it was the fourth most male-dominated occupation in the country in 1999. In 2006 in the United States, there were about 1.5 million carpentry positions. Carpenters are usually the first tradesmen on a job and the last to leave. Carpenters normally framed post-and-beam buildings until the end of the 19th century; now this old-fashioned carpentry is called timber framing. Carpenters learn this trade by being employed through an apprenticeship training—normally 4 years—an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stowaway
A stowaway or clandestine traveller is a person who secretly boards a vehicle, such as a ship, an aircraft, a train, cargo truck or bus. Sometimes, the purpose is to get from one place to another without paying for transportation. In other cases, the goal is to enter another country without first obtaining a travel visa or other permission. Stowaways differ from people smuggling in that the stowaway needs to avoid detection by the truck driver, ship crew, and others responsible for the safe and secure operation of the transportation service. Thousands of stowaways have travelled by sea or land over the last several centuries. A much smaller number of people have attempted to stowaway on aircraft. Many stowaways have died during the attempt, especially in cases of train surfing and wheel-well stowaway flights. Origin The word takes its origin with the expression ''stow away''. This ''stow away'' expression is old and was used for things (such as food), such usage is seen for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebelschütz
Nebelschütz (German) or Njebjelčicy (Upper Sorbian) is a Sorbian village in the district of Bautzen of Saxony in south-east Germany. It lies to the south-east of Kamenz. The municipality is part of the recognized Sorbian settlement area in Saxony. Upper Sorbian has an official status next to German, all villages bear names in both languages. In 2004, two thirds of the population spoke Sorbian.Walde, Martin: ''Demographisch-statistische Betrachtungen im Gemeindeverband "Am Klosterwasser".'' In: Lětopis 51 (2004), Heft 1 The town is dominated by the Baroque church of St Martin, which stands on high ground. Whilst mildly impressive from the outside the church is more noted for its magnificent interior. The church has a curious combination of both pulpit and altar, reflecting the Catholic dominance within the Sorbian area. History The village is first mentioned in 1304 in a document written in the nearby monastery of Panschwitz-Kuckau. Twin cities * Hlučín, Moravian–S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiesa (Kamenz)
Wiesa ( hsb, Brěznja) is a locality in the town of Kamenz, Saxony. It is located in the southern part of town, south of the town centre, on the Black Elster The Black Elster or Schwarze Elster () is a long river in eastern Germany, in the states Saxony, Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt, right tributary of the Elbe. Its source is in the Upper Lusatia region, near Elstra. The Black Elster flows through t ... in the district of Bautzen. History Wiesa was founded in 1238. The main job was, as in many other rural communities, agriculture. In the 19th century, several quarries were created. In 1974, Wiesa was incorporated into the neighboring town of Kamenz. References {{authority control Former municipalities in Saxony Kamenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Weapons In World War I
The use of toxic chemicals as weapons dates back thousands of years, but the first large scale use of chemical weapons was during World War I. They were primarily used to demoralize, injure, and kill entrenched defenders, against whom the indiscriminate and generally very slow-moving or static nature of gas clouds would be most effective. The types of weapons employed ranged from disabling chemicals, such as tear gas, to lethal agents like phosgene, chlorine, and mustard gas. This chemical warfare was a major component of the first global war and first total war of the 20th century. The killing capacity of gas was limited, with about 90,000 fatalities from a total of 1.3 million casualties caused by gas attacks. Gas was unlike most other weapons of the period because it was possible to develop countermeasures, such as gas masks. In the later stages of the war, as the use of gas increased, its overall effectiveness diminished. The widespread use of these agents of chemical warfar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
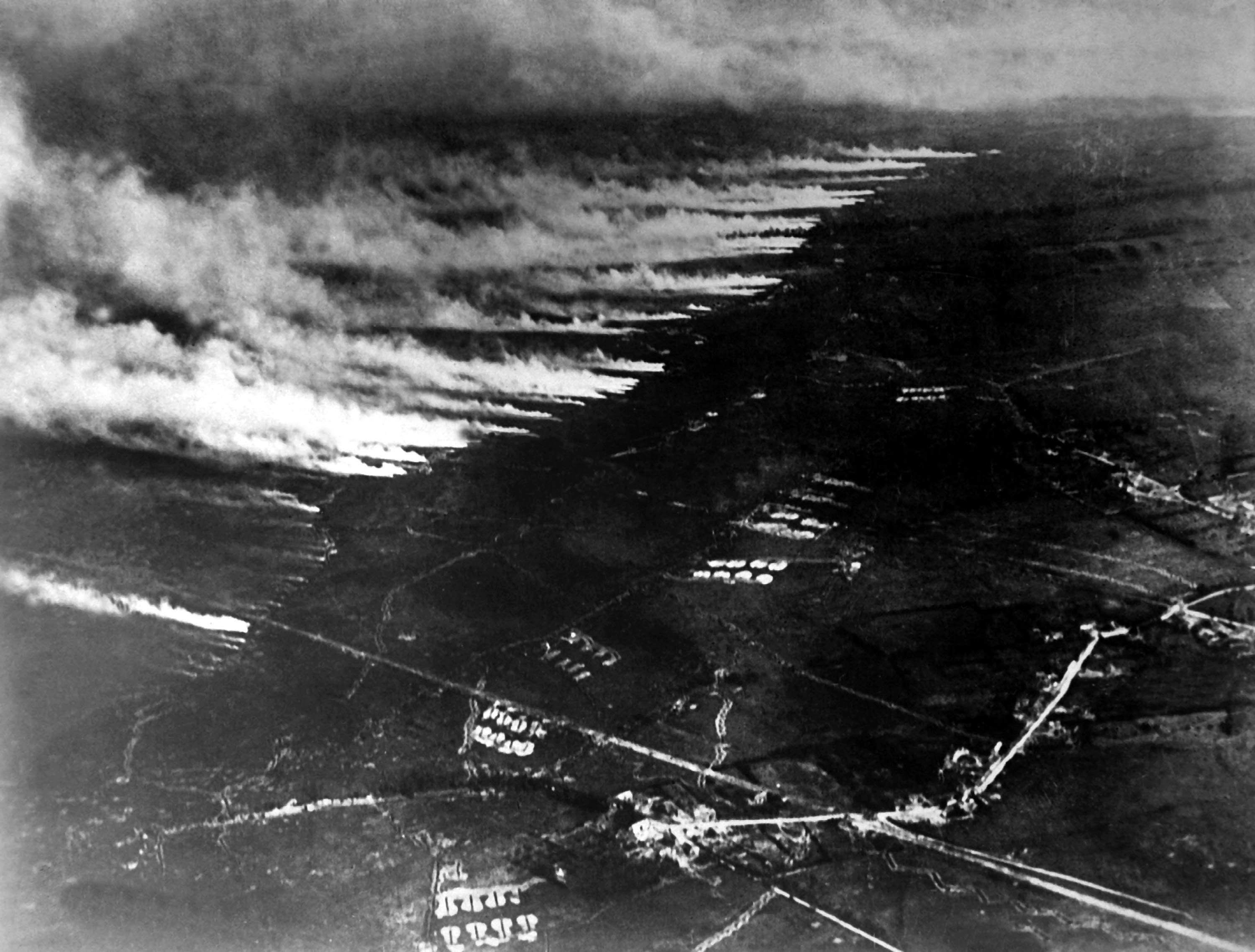
Battle Of Saint-Mihiel
The Battle of Saint-Mihiel was a major World War I battle fought from 12–15 September 1918, involving the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) and 110,000 French troops under the command of General John J. Pershing of the United States against German positions. The U.S. Army Air Service played a significant role in this action.Hanlon (1998)History of War (2007) This battle marked the first use of the terms "D-Day" and "H-Hour" by the Americans. The attack at the Saint-Mihiel salient was part of a plan by Pershing in which he hoped that the Americans would break through the German lines and capture the fortified city of Metz. It was the first large offensive launched mainly by the United States Army in World War I, and the attack caught the Germans in the process of retreating. This meant that their artillery was out of place and the American attack, coming up against disorganized German forces, proved more successful than expected. The Saint-Mihiel attack established the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Königsbrück
Königsbrück (Upper Sorbian: ''Kinspork'') is a town in the Bautzen district, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated west of Kamenz, and northeast of the Saxon capital Dresden. Königsbrück is known as the western gate of the historic Upper Lusatia region. History First mentioned in 1248 the settlement arose around a fortress in the Bohemian crown land of Upper Lusatia where the ''Via Regia'' trade route crossed the border with the Margraviate of Meissen. First mentioned as a town in 1331, Königsbrück from 1562 was the administrative centre of a Bohemian state country (''Freie Standesherrschaft''), which passed under the suzerainty of the Saxon Electorate according to the 1635 Peace of Prague. In 1906 the Kingdom of Saxony had large proving grounds laid out for the XII (1st Royal Saxon) Corps stationed at Dresden, that after World War II were used by the Soviet Army and finally closed in 1992. Transport Königsbrück railway station is located south of the town centre. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
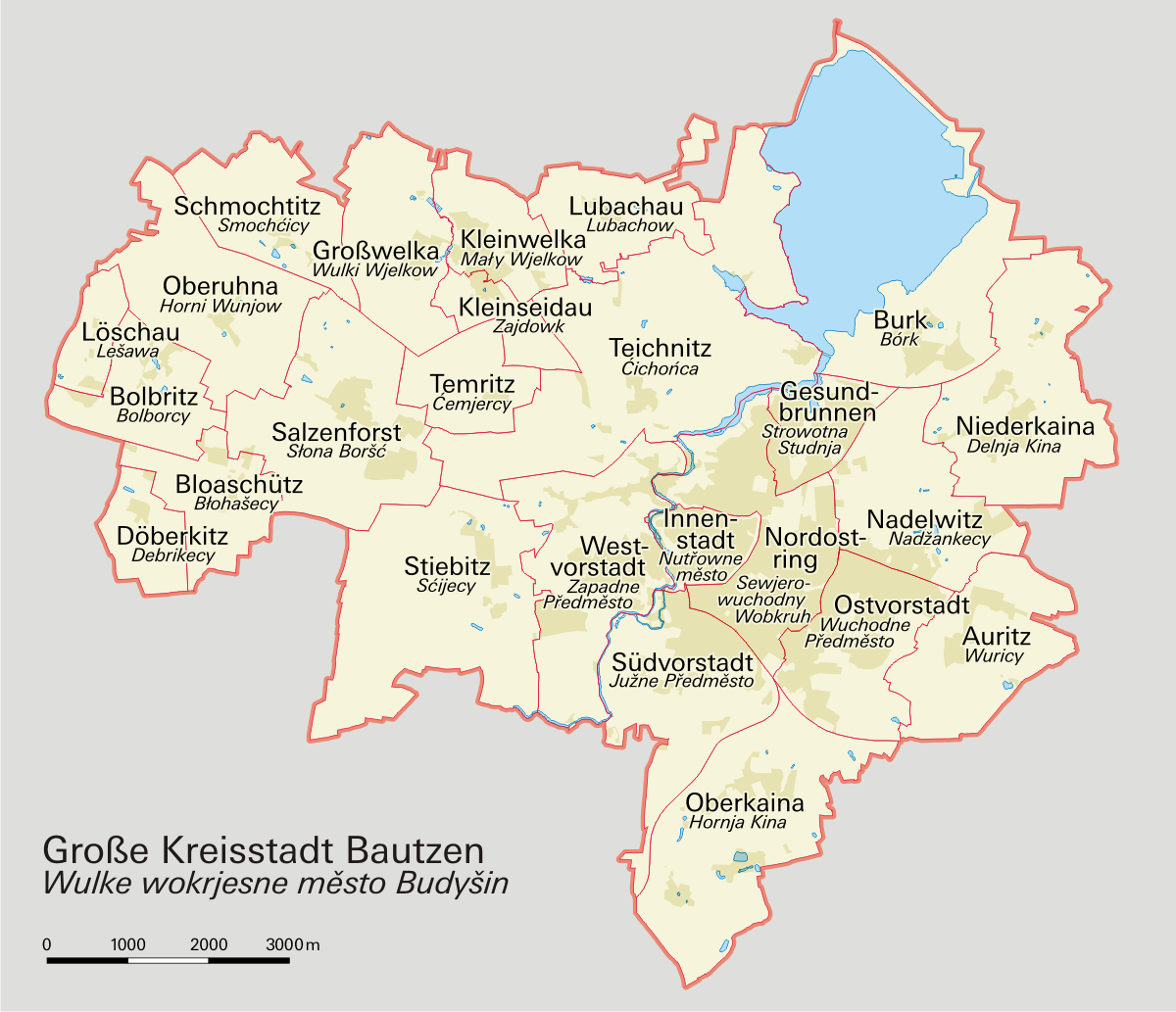
Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budissin''. In 1945 the Battle of Bautzen was Hitler’s last victory against the Soviet Union during the Battle of Berlin . Bautzen is often regarded as the unofficial, but historical capital of Upper Lusatia. The town is also the most important cultural centre of the Sorbian minority, which constitutes about 10 percent of Bautzen's population. Asteroid '' 11580 Bautzen'' is named in honour of the city. Names Like other cities and places in Lusatia, Bautzen has several different names across languages. Its German name was also officially changed in 1868. As well as ''Bautzen'' (German) and ''Budyšin'' (Upper Sorbian), the town has had the following names: * German: ''Budissin'' (variants used from c. 11th century onwards; Saxon governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1.jpg)