|
Religious Policy Of The Mughals After Akbar
The Mughal Empire, which was established following the defeat of Ibrahim Lodi in 1526 at the First Battle of Panipat and consolidated over the time with expansionist policy of its rulers, derived its strength from its nobility which was hypergamous and included the Turks, Afghans, Uzbegs and even Hindu Rajputs and Khatris. The Mughal rulers were successful in reigning over a long period of time over the vast area of the subcontinent because of their administrative and religious policy, which provided for the cohesion among various sects and creeds. Both Babur and Humayun were busy throughout their regnal years in wars and conquest apart from suppression of revolt and couldn't devote enough time for the administration and policies formulation. It was Akbar (who promoted the syncretic religion called Dīn-i Ilāhī) during whose reign the religious policy of the Mughals were formulated. The later Mughals followed Akbar but violation of his policy went unabated many a times leading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth-most populous state, with a population of 60.4 million. It is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Gujarat's capital city is Gandhinagar, while its largest city is Ahmedabad. The Gujaratis are indigenous to the state and their language, Gujarati, is the state's official language. The state encompasses 23 sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation (more than any other state). The most important sites are Lothal (the world's first dry dock), Dholavira (the fifth largest site), and Gola Dhoro (where 5 uncommon seals were found). Lothal is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Arjun Dev
Guru Arjan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਅਰਜਨ, pronunciation: ; 15 April 1563 – 30 May 1606) was the first of the two Gurus martyred in the Sikh faith and the fifth of the ten total Sikh Gurus. He compiled the first official edition of the Sikh scripture called the Adi Granth, which later expanded into the Guru Granth Sahib. He was born in Goindval, in the Punjab, the youngest son of Bhai Jetha, who later became Guru Ram Das, and Mata Bhani, the daughter of Guru Amar Das. He completed the construction of Darbar Sahib at Amritsar, after the fourth Sikh Guru founded the town and built a sarovar. Guru Arjan compiled the hymns of previous Gurus and of other saints into Adi Granth, the first edition of the Sikh scripture, and installed it in the Harimandir Sahib. Guru Arjan reorganized the Masands system initiated by Guru Ram Das, by suggesting that the Sikhs donate, if possible, one-tenth of their income, goods or service to the Sikh organization (''dasvandh''). The ''Masand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
Chaitanya Mahaprabhu (; born Vishvambhar Mishra) was a 15th-century Indian saint who is considered to be the combined avatar of Radha and Krishna by his disciples and various scriptures. Chaitanya Mahaprabhu's mode of worshipping Krishna with ecstatic song and dance had a profound effect on Vaishnavism in Bengal. He was also the chief proponent of the Vedantic philosophy of Achintya Bheda Abheda Tattva. Mahaprabhu founded Gaudiya Vaishnavism ( the Brahma-Madhva-Gaudiya Sampradaya). He expounded Bhakti yoga and popularized the chanting of the Hare Krishna Maha-mantra. He composed the '' Shikshashtakam'' (eight devotional prayers). Chaitanya is sometimes called Gauranga or Gaura due to his molten gold–like complexion. His birthday is celebrated as Gaura-purnima. He is also called Nimai due to him being born underneath a Neem tree. Life '' Chaitanya'' means "one who is conscious" (derived from Chetana, which means "Consciousness"); ''Maha'' means "Great" and ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matha
A ''matha'' (; sa, मठ, ), also written as ''math'', ''muth'', ''mutth'', ''mutt'', or ''mut'', is a Sanskrit word that means 'institute or college', and it also refers to a monastery in Hinduism.Matha Encyclopædia Britannica Online 2009 An alternative term for such a monastery is ''adheenam''. The earliest epigraphical evidence for ''mathas'' related to Hindu-temples comes from the 7th to 10th century CE. The most famous Advaita Vedanta ''mathas'' or ''peethams'', which came to be affiliated with the Advaita tradition in the 14th century, are Govardhanmaṭha Pīṭhaṃ at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. In ancient times, Mathura was an economic hub, located at the junction of important caravan routes. The 2011 Census of India estimated the population of Mathura at 441,894. In Hinduism, Mathura is birthplace of Krishna, which is located at the Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex. It is one of the Sapta Puri, the seven cities considered holy by Hindus, also called Mokshyadayni Tirth. The Kesava Deo Temple was built in ancient times on the site of Krishna's birthplace (an underground prison). Mathura was the capital of the kingdom of Surasena, ruled by Kansa, the maternal uncle of Krishna. Mathura is part of the Lord Krishna circuit (Mathura,Vrindavan,Barsana, Govardhan, Kurukshetra, Dwarka and Bhalka). Janmashtami is grandly celebrated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
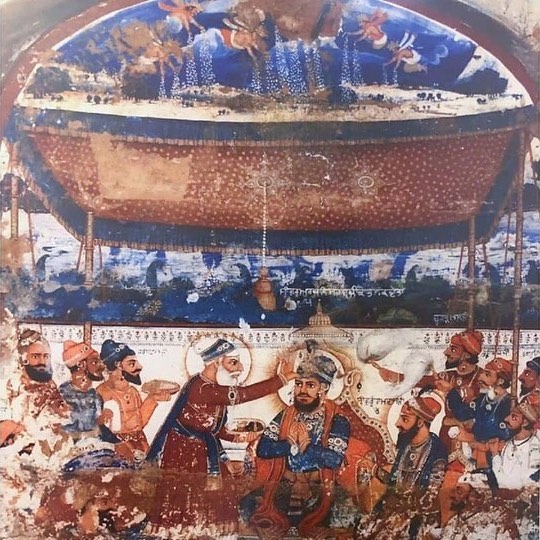
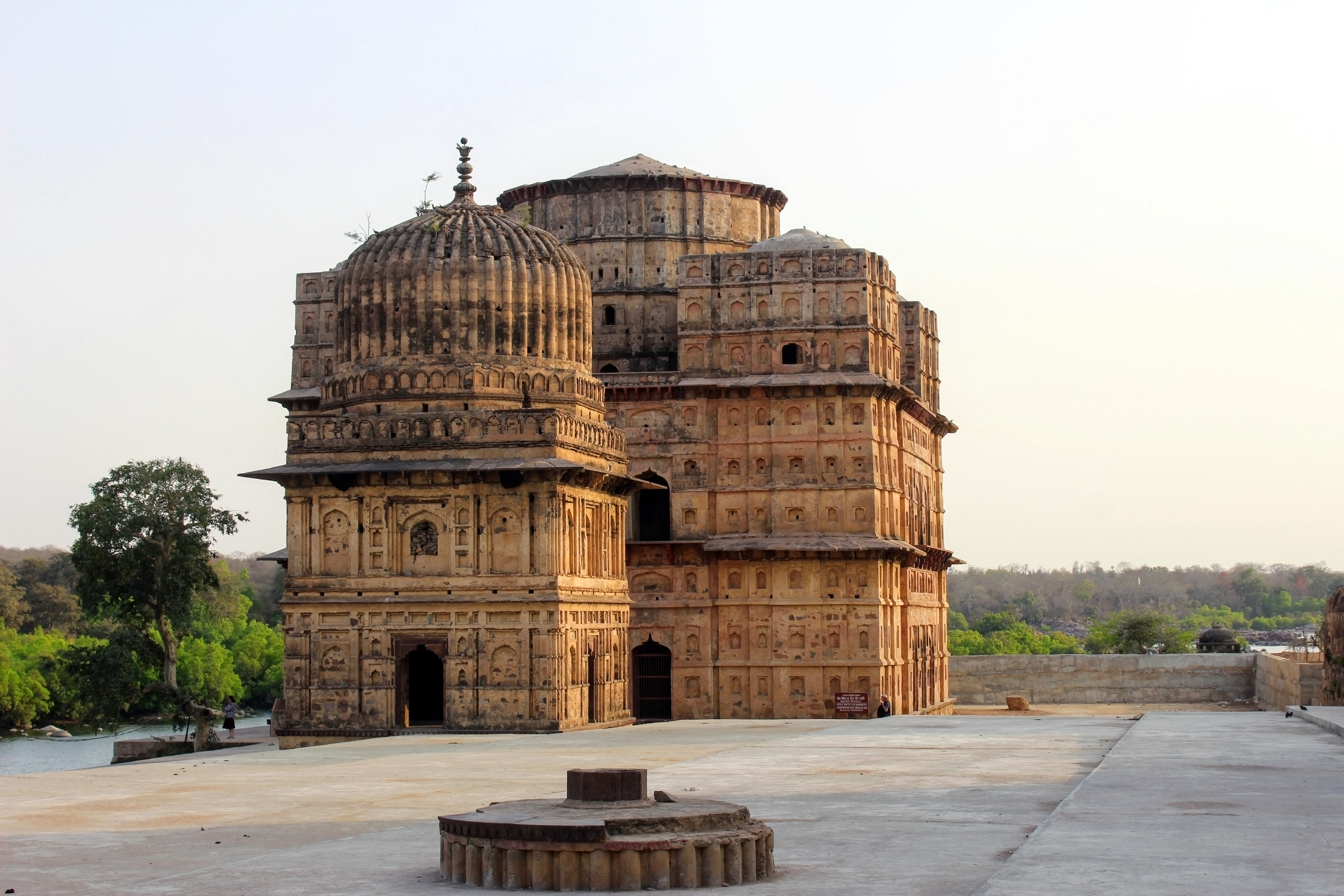
Vir Singh Bundela
Vir Singh Deo, also known as Bir Singh Dev, was a Bundela Rajput chief and the ruler of the kingdom of Orchha. He was a vassal of the Mughal Empire. and ruled between 1605 and either 1626 or 1627. Vir Singh Deo assassinated Abul Fazl who was returning from Deccan in a plot contrived by the Mughal Prince Salim. According to Aruna, he is "the most famous and most powerful of all the Orchha Chiefs. A man of dashing personality, a great warrior and no scruples, a bold and organised administrator". He was considered to built the Jhansi fort Deo was among the Rajput rulers of his era who sponsored temples in the Brajmandal area that comprised Vrindavan and Mathura. In addition, the Phool Bagh gardens, and the Lakshmi temple were all built by Deo. His mausoleum is located in Orchha, and features both Hindu and Mughal architecture. Vir Singh Deo was succeeded by Jhujhar Singh, the first-born son of the senior of his three queens. Deo was patron to the poet Keshavdas Keshavdas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism. Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within the Trimurti, the triple deity of supreme divinity that includes Brahma and Shiva. Gavin Flood, An Introduction to Hinduism' (1996), p. 17. In Vaishnavism, Vishnu is the supreme being who creates, protects, and transforms the universe. In the Shaktism tradition, the Goddess, or Adi Shakti, is described as the supreme Para Brahman, yet Vishnu is revered along with Shiva and Brahma. Tridevi is stated to be the energy and creative power ( Shakti) of each, with Lakshmi being the equal complementary partner of Vishnu. He is one of the five equivalent deities in Panchayatana puja of the Smarta tradition of Hinduism. According to Vaishnavism, the highest form of Ishvara is with qualities ( Saguna), and have certain form, but is li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varaha
Varaha ( sa, वराह, , "boar") is an avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu, in the form of a boar. Varaha is generally listed as third in the Dashavatara, the ten principal avatars of Vishnu. Varaha is most commonly associated with the legend of lifting the Earth (personified as the goddess Bhudevi) out of the cosmic ocean. When the asura Hiranyaksha stole the earth and hid her in the primordial waters, Vishnu appeared as Varaha to rescue her. Varaha slew the asura, and retrieved the Earth from the ocean, lifting it on his tusks, and restored Bhudevi to her place in the universe. Varaha may be depicted as completely a boar or in an anthropomorphic form, with a boar's head and the human body. His consort, Bhudevi, the personified Earth, is often depicted as a young woman, lifted by Varaha. Etymology and other names The deity Varaha derives its name from the Sanskrit word ''varāha'' (Devanagari: वराह, ) meaning "boar" or "wild boar". The word ''varāha'' is from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
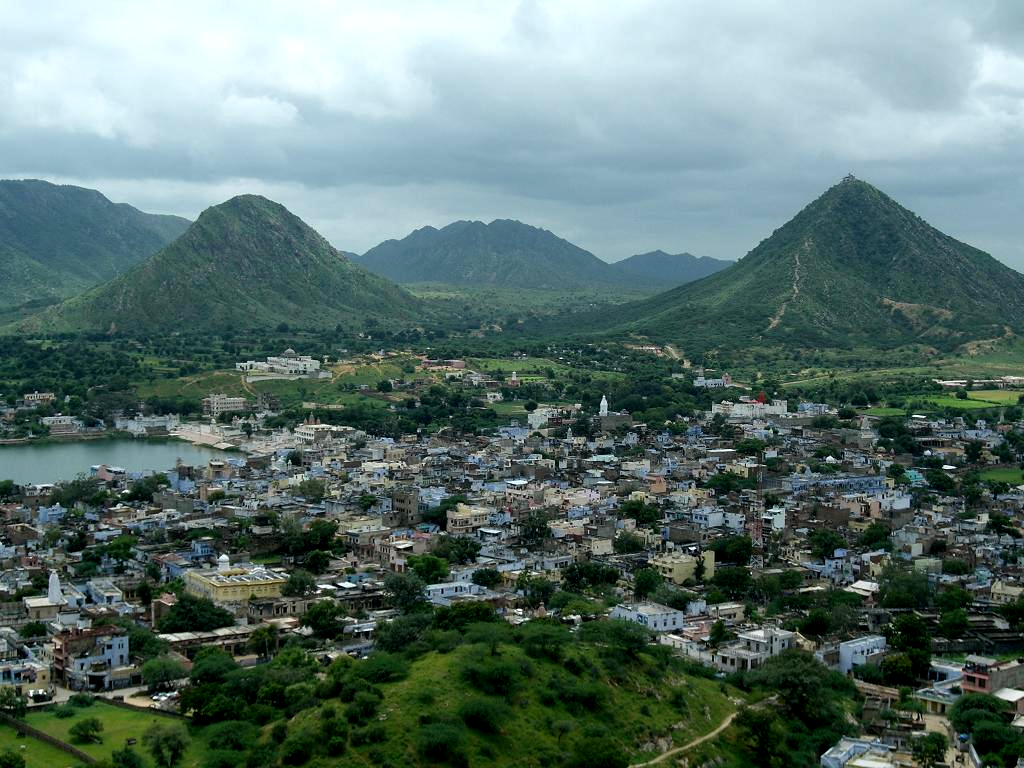
Pushkar
Pushkar is a city and headquarters of Pushkar tehsil in the Ajmer district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is situated about northwest of Ajmer and about southwest of Jaipur.Pushkar Encyclopaedia Britannica It is a pilgrimage site for s and Sikhs. Pushkar has many temples. Most of the temples and ghats in Pushkar are from the 18th century and later, because many temples were destroyed during Muslim conquests in the area. Subsequently, the destroyed temples were rebuilt. The most famous among Pushkar temples is the red spired [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "''Ajayameru''" (translated as "Invincible Hills") by a Chahamana ruler, either Ajayaraja I or Ajayaraja II, and served as their capital until the 12th century CE. Home to the dargah of Moinuddin Chishti, Ajmer is one of the most important destinations of Islamic pilgrimage in South Asia. Ajmer is surrounded by the Aravalli Mountains. Ajmer had been a municipality since 1869. Ajmer has been selected as one of the heritage cities for the HRIDAY and Smart City Mission schemes of the Government of India. History Ajmer was originally known as ''Ajayameru''. The city was founded by an 11th-century Chahamana king Ajaydeva. Historian Dasharatha Sharma notes that the earliest mention of the city's name occurs in Palha's ''Pattavali'', which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amar Singh I
Maharana Amar Singh I, the Maharana of Mewar (March 16, 1559 – January 26, 1620), was the eldest son and successor of Maharana Pratap of Mewar. He was the 16th Rana of Mewar dynasty of Sisodia Rajputs and ruler of Mewar from January 19, 1597 till his death on January 26, 1620. His capital was Udaipur. Birth and coronation Amar Singh was the eldest son of Maharana Pratap. He was born in Chittor on 16 March 1559 to Maharana Pratap and Maharani Ajabde Punwar, the same year, when foundation of Udaipur was laid by his grandfather, Udai Singh II. Amar Singh succeeded Maharana Pratap upon his death on 19 January 1597. Reign In start of his reign, Amar Singh implemented internal reforms. He defined the order of precedence for his chiefs, and their privileges. He also rehabilitated people, who were displaced due to Mughal invasions, settled them in many villages, including Kelwa, Muroli and Rampura. He appointed Hari Das Jhala as the commander of his standing army and made large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |