|
Reimer–Tiemann Reaction
The Reimer–Tiemann reaction is a chemical reaction used for the ortho-formylation of phenols; with the simplest example being the conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. The reaction was discovered by and Ferdinand Tiemann. The Reimer in question was Karl Reimer (1845-1883) not the lesser known Carl Ludwig Reimer (1856-1921). Reaction mechanism Chloroform (1) is deprotonated by a strong base (normally hydroxide) to form the chloroform carbanion (2) which will quickly alpha-eliminate to give dichlorocarbene (3); this is the principal reactive species. The hydroxide will also deprotonate the phenol (4) to give a negatively charged phenoxide (5). The negative charge is delocalised into the aromatic ring, making it far more nucleophilic. Nucleophilic attack on the dichlorocarbene gives an intermediate dichloromethyl substituted phenol (7). After basic hydrolysis, the desired product (9) is formed. Selectivity By virtue of its 2 electron-withdrawing chlorine groups, carbene (3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Tiemann
Johann Karl Wilhelm Ferdinand Tiemann (June 10, 1848 – November 14, 1899) was a German chemist and together with Karl Reimer discoverer of the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. Beginning in 1866, Tiemann studied pharmacy at the TU Braunschweig where he graduated in 1869. His professor in Brunswick wrote a letter of recommendation to August Wilhelm von Hofmann at the University of Berlin where Tiemann started as assistant of von Hofmann in 1869. In 1874 Wilhelm Haarmann and Tiemann started a company, after they discovered the synthesis of vanillin from coniferyl alcohol. The vanillin plant Holzminden was not very successful before Karl Reimer discovered the Reimer-Tiemann reaction which opened an alternative synthesis route to vanillin. In 1882 Tiemann became a professor at the University of Berlin. He was involved in the first synthesis of Jonon a compound of the sweet violet (''Viola odorata''), which became a huge success for Harmann & Reimer company. August Wilhelm von Hofma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrroles
Pyrrole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4 H4 NH. It is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air. Substituted derivatives are also called pyrroles, e.g., ''N''-methylpyrrole, C4H4NCH3. Porphobilinogen, a trisubstituted pyrrole, is the biosynthetic precursor to many natural products such as heme. Pyrroles are components of more complex macrocycles, including the porphyrinogens and products derived therefrom, including porphyrins of heme, the chlorins, bacteriochlorins, and chlorophylls. Properties Pyrrole is a colorless volatile liquid that darkens readily upon exposure to air, and is usually purified by distillation immediately before use. Pyrrole has a nutty odor. Pyrrole is a 5-membered aromatic heterocycle, like furan and thiophene. Unlike furan and thiophene, it has a dipole in which the positive end lies on the side of the heteroatom, with a dipole moment of 1.58 D. In CDCl3, it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane, is an organic compound with formula C H Cl3 and a common organic solvent. It is a colorless, strong-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to PTFE. It is also a precursor to various refrigerants. It is trihalomethane. It is a powerful anesthetic, euphoriant, anxiolytic, and sedative when inhaled or ingested. Structure The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. Natural occurrence The total global flux of chloroform through the environment is approximately tonnes per year, and about 90% of emissions are natural in origin. Many kinds of seaweed produce chloroform, and fungi are believed to produce chloroform in soil. Abiotic processes are also believed to contribute to natural chloroform productions in soils although the mechanism is still unclear. Chloroform volatilizes readily from soil and surface water and undergoes degradation in air to produce phosgene, dichloromethane, formyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenolic Acid
Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function (C6-C1 skeleton). Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively. Occurrences Phenolic acids can be found in many plant species. Their content in dried fruits can be high. Natural phenols in horse grams (''Macrotyloma uniflorum'') are mostly phenolic acids, namely 3,4-dihydroxy benzoic, ''p''-hydroxy benzoic, vanillic, caffeic, ''p''-coumaric, ferulic, syringic, and sinapinic acids. Phenolic acids can be found in several mushroom-forming species of basidiomycetes. It is also a part of the humic substances, which are the major organic constituents of soil humus. Many phenolic acids can be found in human urine. Chemistry Immobilized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (chemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achieve perfect dryness; anhydrous compounds gradually absorb water from the atmosphere so they must be stored carefully. Solids Many salts and solids can be dried using heat, or under vacuum. Desiccators can also be used to store reagents in dry conditions. Common desiccants include phosphorus pentoxide and silica gel. Chemists may also require dry glassware for sensitive reactions. This can be achieved by drying glassware in an oven, by flame, or under vacuum. Dry solids can be produced by freeze-drying, which is also known as lyophilization. Liquids or solvents In many cases, the presence of water can prevent a reaction from happening, or cause undesirable products to form. To prevent this, anhydrous solvents must be used when perform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acidic
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequence of database operations that satisfies the ACID properties (which can be perceived as a single logical operation on the data) is called a ''transaction''. For example, a transfer of funds from one bank account to another, even involving multiple changes such as debiting one account and crediting another, is a single transaction. In 1983, Andreas Reuter and Theo Härder coined the acronym ''ACID'', building on earlier work by Jim Gray who named atomicity, consistency, and durability, but not isolation, when characterizing the transaction concept. These four properties are the major guarantees of the transaction paradigm, which has influenced many aspects of development in database systems. According to Gray and Reuter, the IBM I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duff Reaction
The Duff reaction or hexamine aromatic formylation is a formylation reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of benzaldehydes with hexamine as the formyl carbon source. It is named after James Cooper Duff, who was a chemist at the College of Technology, Birmingham, around 1920–1950. The electrophilic species in this electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction is the iminium ion CH2+NR2. The initial reaction product is an iminium which is hydrolyzed to the aldehyde. See mechanism below. The reaction requires strongly electron donating substituents on the aromatic ring such as in a phenol. Formylation occurs '' ortho'' to the electron donating substituent preferentially, unless the ''ortho'' positions are blocked, in which case the formylation occurs at the ''para'' position. Examples are the synthesis of 3,5-di-''tert''-butylsalicylaldehyde: and the synthesis of syringaldehyde: If both ''ortho'' positions are vacant then a diformylation is possible, as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vilsmeier–Haack Reaction
The Vilsmeier–Haack reaction (also called the Vilsmeier reaction) is the chemical reaction of a substituted amide (1) with phosphorus oxychloride and an electron-rich arene (3) to produce an aryl aldehyde or ketone (5). The reaction is named after Anton Vilsmeier and Albrecht Haack. For example, benzanilide and dimethylaniline react with phosphorus oxychloride to produce an unsymmetrical diaryl ketone. Similarly, anthracene is formylated at the 9-position. The reaction of anthracene with ''N''-methylformanilide, also using phosphorus oxychloride, gives 9-anthracenecarboxaldehyde: : Reaction mechanism The reaction of a substituted amide with phosphorus oxychloride gives a substituted chloroiminium ion (2), also called the Vilsmeier reagent. The initial product is an iminium ion (4b), which is hydrolyzed to the corresponding ketone or aldehyde during workup. : See also * Formylation reaction A formylation reaction in organic chemistry refers to organic reactions in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
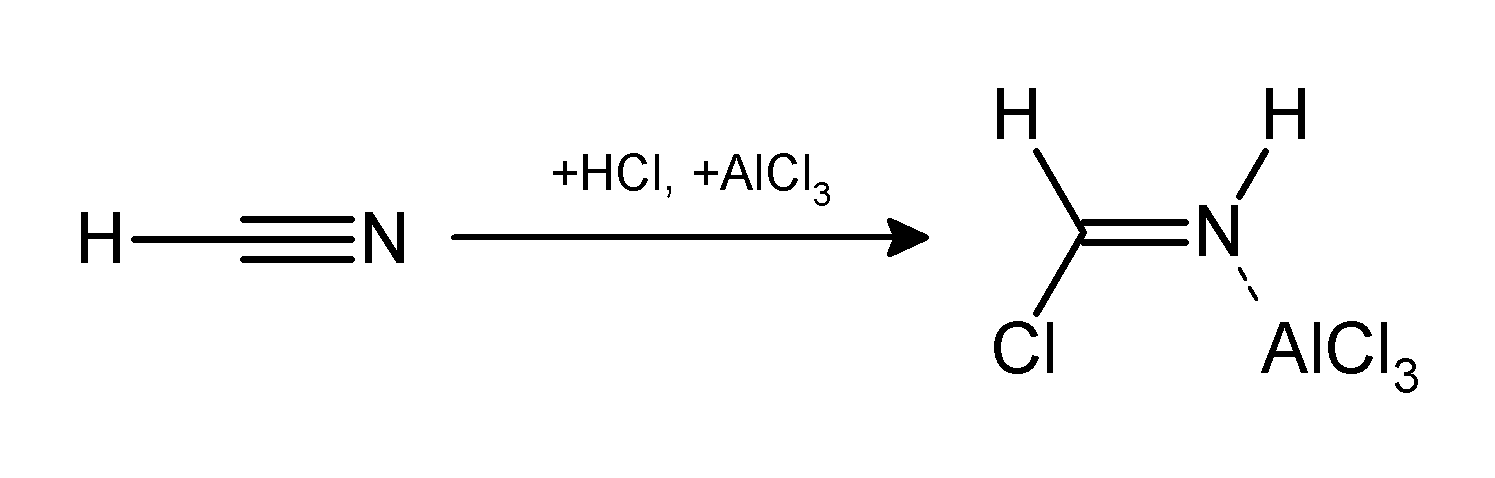
Gattermann–Koch Reaction
The Gattermann reaction, (also known as the Gattermann formylation and the Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis) is a chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds are formylated by a mixture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3. It is named for the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann and is similar to the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Modifications have shown that it is possible to use sodium cyanide or cyanogen bromide in place of hydrogen cyanide. The reaction can be simplified by replacing the HCN/AlCl3 combination with zinc cyanide. Although it is also highly toxic, Zn(CN)2 is a solid, making it safer to work with than gaseous HCN. The Zn(CN)2 reacts with the HCl to form the key HCN reactant and Zn(Cl)2 that serves as the Lewis-acid catalyst ''in-situ''. An example of the Zn(CN)2 method is the synthesis of mesitaldehyde from mesitylene. Gattermann–Koch reaction The Gattermann–Koch reaction, nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gattermann Reaction
The Gattermann reaction, (also known as the Gattermann formylation and the Gattermann salicylaldehyde synthesis) is a chemical reaction in which aromatic compounds are formylated by a mixture of hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst such as AlCl3. It is named for the German chemist Ludwig Gattermann and is similar to the Friedel–Crafts reaction. Modifications have shown that it is possible to use sodium cyanide or cyanogen bromide in place of hydrogen cyanide. The reaction can be simplified by replacing the HCN/AlCl3 combination with zinc cyanide. Although it is also highly toxic, Zn(CN)2 is a solid, making it safer to work with than gaseous HCN. The Zn(CN)2 reacts with the HCl to form the key HCN reactant and Zn(Cl)2 that serves as the Lewis-acid catalyst ''in-situ''. An example of the Zn(CN)2 method is the synthesis of mesitaldehyde from mesitylene. Gattermann–Koch reaction The Gattermann–Koch reaction, nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |