|
Regret (decision Theory)
In decision theory, on making decisions under uncertainty—should information about the best course of action arrive ''after'' taking a fixed decision—the human emotional response of regret is often experienced, and can be measured as the value of difference between a made decision and the optimal decision. The theory of regret aversion or anticipated regret proposes that when facing a decision, individuals might ''anticipate'' regret and thus incorporate in their choice their desire to eliminate or reduce this possibility. Regret is a negative emotion with a powerful social and reputational component, and is central to how humans learn from experience and to the human psychology of risk aversion. Conscious anticipation of regret creates a feedback loop that transcends regret from the emotional realm—often modeled as mere human behavior—into the realm of the rational choice behavior that is modeled in decision theory. Description Regret theory is a model in theoretic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Theory
Decision theory (or the theory of choice; not to be confused with choice theory) is a branch of applied probability theory concerned with the theory of making decisions based on assigning probabilities to various factors and assigning numerical consequences to the outcome. There are three branches of decision theory: # Normative decision theory: Concerned with the identification of optimal decisions, where optimality is often determined by considering an ideal decision-maker who is able to calculate with perfect accuracy and is in some sense fully rational. # Prescriptive decision theory: Concerned with describing observed behaviors through the use of conceptual models, under the assumption that those making the decisions are behaving under some consistent rules. # Descriptive decision theory: Analyzes how individuals actually make the decisions that they do. Decision theory is closely related to the field of game theory and is an interdisciplinary topic, studied by economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Price Auction
A first-price sealed-bid auction (FPSBA) is a common type of auction. It is also known as blind auction. In this type of auction, all bidders simultaneously submit sealed bids so that no bidder knows the bid of any other participant. The highest bidder pays the price that was submitted. Strategic analysis In a FPSBA, each bidder is characterized by their monetary valuation of the item for sale. Suppose Alice is a bidder and her valuation is a. Then, if Alice is rational: *She will never bid more than a, because bidding more than a can only make her lose net value. *If she bids exactly a, then she will not lose but also not gain any positive value. *If she bids less than a, then she ''may'' have some positive gain, but the exact gain depends on the bids of the others. Alice would like to bid the smallest amount that can make her win the item, as long as this amount is less than a. For example, if there is another bidder Bob and he bids y and y [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Column Rank
In linear algebra, the rank of a matrix is the dimension of the vector space generated (or spanned) by its columns. p. 48, § 1.16 This corresponds to the maximal number of linearly independent columns of . This, in turn, is identical to the dimension of the vector space spanned by its rows. Rank is thus a measure of the " nondegenerateness" of the system of linear equations and linear transformation encoded by . There are multiple equivalent definitions of rank. A matrix's rank is one of its most fundamental characteristics. The rank is commonly denoted by or ; sometimes the parentheses are not written, as in .Alternative notation includes \rho (\Phi) from and . Main definitions In this section, we give some definitions of the rank of a matrix. Many definitions are possible; see Alternative definitions for several of these. The column rank of is the dimension of the column space of , while the row rank of is the dimension of the row space of . A fundamental result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial elli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean-squared Error
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSE) or mean squared deviation (MSD) of an estimator (of a procedure for estimating an unobserved quantity) measures the average of the squares of the errors—that is, the average squared difference between the estimated values and the actual value. MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss. The fact that MSE is almost always strictly positive (and not zero) is because of randomness or because the estimator does not account for information that could produce a more accurate estimate. In machine learning, specifically empirical risk minimization, MSE may refer to the ''empirical'' risk (the average loss on an observed data set), as an estimate of the true MSE (the true risk: the average loss on the actual population distribution). The MSE is a measure of the quality of an estimator. As it is derived from the square of Euclidean distance, it is always a positive value that decreases as the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. However, in robust statistics, statis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximin (decision Theory)
Minimax (sometimes MinMax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''mini''mizing the possible loss for a worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ Where: * is the index of the player of intere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Measurement
Level of measurement or scale of measure is a classification that describes the nature of information within the values assigned to variables. Psychologist Stanley Smith Stevens developed the best-known classification with four levels, or scales, of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. This framework of distinguishing levels of measurement originated in psychology and is widely criticized by scholars in other disciplines. Other classifications include those by Mosteller and Tukey, and by Chrisman. Stevens's typology Overview Stevens proposed his typology in a 1946 '' Science'' article titled "On the theory of scales of measurement". In that article, Stevens claimed that all measurement in science was conducted using four different types of scales that he called "nominal", "ordinal", "interval", and "ratio", unifying both " qualitative" (which are described by his "nominal" type) and "quantitative" (to a different degree, all the rest of his scales). The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prediction
A prediction (Latin ''præ-'', "before," and ''dicere'', "to say"), or forecast, is a statement about a future event or data. They are often, but not always, based upon experience or knowledge. There is no universal agreement about the exact difference from " estimation"; different authors and disciplines ascribe different connotations. Future events are necessarily uncertain, so guaranteed accurate information about the future is impossible. Prediction can be useful to assist in making plans about possible developments. Opinion In a non-statistical sense, the term "prediction" is often used to refer to an informed guess or opinion. A prediction of this kind might be informed by a predicting person's abductive reasoning, inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning, and experience; and may be useful—if the predicting person is a knowledgeable person in the field. The Delphi method is a technique for eliciting such expert-judgement-based predictions in a controlled way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
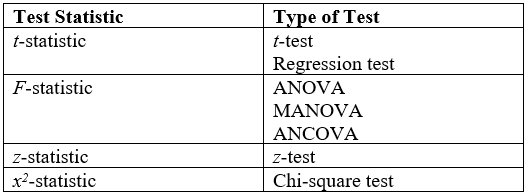
Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset (Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, " significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Savage
Leonard Jimmie Savage (born Leonard Ogashevitz; 20 November 1917 – 1 November 1971) was an American mathematician and statistician. Economist Milton Friedman said Savage was "one of the few people I have met whom I would unhesitatingly call a genius." Education and career Savage was born and grew up in Detroit. He studied at Wayne State University in Detroit before transferring to University of Michigan, where he first majored in chemical engineering, then switched to mathematics, graduating in 1938 with a Bachelor's degree. He continued at the University of Michigan with a PhD on differential geometry in 1941 under the supervision of Sumner Byron Myers. Savage subsequently worked at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, the University of Chicago, the University of Michigan, Yale University, and the Statistical Research Group at Columbia University. Though his thesis advisor was Sumner Myers, he also credited Milton Friedman and W. Allen Wallis as stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |