|
Rectal Administration
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum's blood vessels,The rectum has numerous blood vessels available to absorb drugs. and flow into the body's circulatory system, which distributes the drug to the body's organs and bodily systems.The organs and systems include, depending on if the drug is able to pass the blood–brain barrier (BBB) or not, the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS), cardiovascular system (CVS), et cetera. A drug that is administered rectally will in general (depending on the drug) have a faster onset, higher bioavailability, shorter peak, and shorter duration than oral administration. Another advantage of administering a drug rectally, is that it tends to produce less nausea compared to the oral route and prevents any amount of the drug from being lost due to emesis (vomiting). In addition, the rectal route bypasses around two-thirds of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is generally lower than that of intravenous due to intestinal endothelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaporizing
Vaporization (or vaporisation) of an element or compound is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor. There are two types of vaporization: evaporation and boiling. Evaporation is a surface phenomenon, whereas boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapor (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure. Evaporation occurs ''on the surface''. Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapor of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure. For example, due to constantly decreasing pressures, vapor pumped out of a solution will eventually leave behind a cryogenic liquid. Boiling is also a phase transition from the liquid phase to gas phase, but boiling is the formation of vapor as bubbles of vapor ''below the surface'' of the liquid. Boiling occurs when the equilibrium vapor pressure of the substance is greater than or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have been rolled into a small rectangle of rolling paper to create a small, round cylinder called a cigarette. Smoking is primarily practised as a route of administration for recreational drug use because the combustion of the dried plant leaves vaporizes and delivers active substances into the lungs where they are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and reach bodily tissue. In the case of cigarette smoking, these substances are contained in a mixture of aerosol particles and gases and include the pharmacologically active alkaloid nicotine; the vaporization creates heated aerosol and gas into a form that allows inhalation and deep penetration into the lungs where absorption into the bloodstream of the active substances occurs. In some cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inhalation
Inhalation (or Inspiration) happens when air or other gases enter the lungs. Inhalation of air Inhalation of air, as part of the cycle of breathing, is a vital process for all human life. The process is autonomic (though there are exceptions in some disease states) and does not need conscious control or effort. However, breathing can be consciously controlled or interrupted (within limits). Breathing allows oxygen (which humans and a lot of other species need for survival) to enter the lungs, from where it can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Other substances – accidental Examples of accidental inhalation includes inhalation of water (e.g. in drowning), smoke, food, vomitus and less common foreign substances (e.g. tooth fragments, coins, batteries, small toy parts, needles). Other substances – deliberate Recreational use Legal – helium, nitrous oxide (" laughing gas") Illegal – various gaseous, vaporised or aerosolized recreational drugs Medical use D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Rectal Vein
The inferior mesenteric vein begins in the rectum as the superior rectal vein (superior hemorrhoidal vein), which has its origin in the hemorrhoidal plexus, and through this plexus communicates with the middle and inferior hemorrhoidal veins. The superior rectal vein leaves the lesser pelvis and crosses the left common iliac vessels with the superior rectal artery, and is continued upward as the inferior mesenteric vein In human anatomy, the inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the large intestine. It usually terminates when reaching the splenic vein, which goes on to form the portal vein with the superior mesenteric vein (SM .... References Veins of the torso Rectum {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
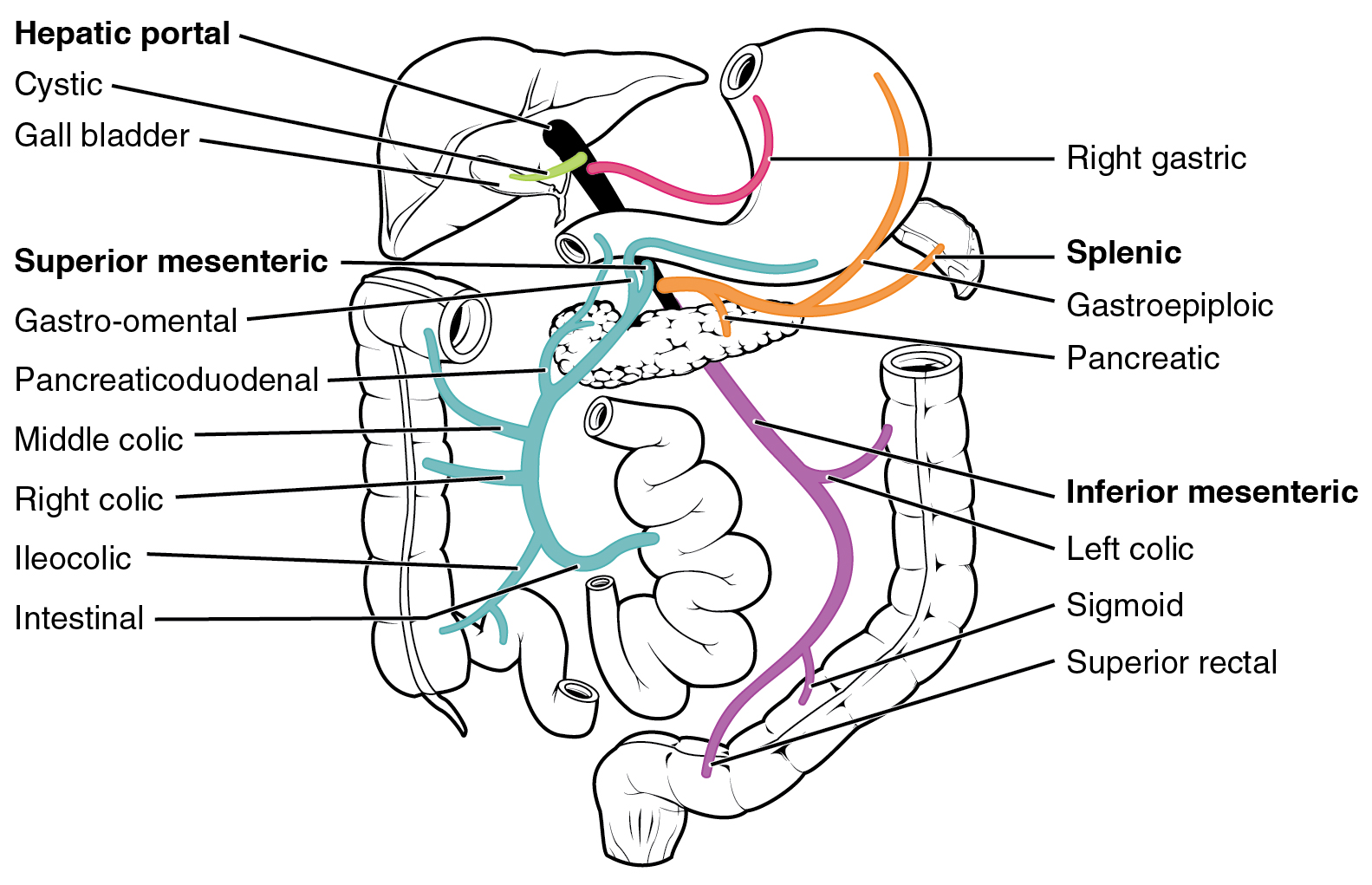
Hepatic Portal System
In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is also called the portal venous system (although it is not the only example of a portal venous system) and splanchnic veins, which is ''not'' synonymous with ''hepatic portal system'' and is imprecise (as it means ''visceral veins'' and not necessarily the ''veins of the abdominal viscera'').Splanchnic circulation. Online Medical Dictionary. URLhttp://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?splanchnic+circulation Accessed on: October 22, 2008. Structure Large veins that are considered part of the ''portal venous system'' are the: *Hepatic portal vein * Splenic vein * Superior mesenteric vein * Inferior mesenteric vein The superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein come together to form the actual hepatic portal vein. The inferior mesenteric vein connects in the majority of people on the splenic vein, but in some people, it is known to connect on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Rectal Vein
The lower part of the external hemorrhoidal plexus is drained by the inferior rectal veins (or inferior hemorrhoidal veins) into the internal pudendal vein The internal pudendal veins (internal pudic veins) are a set of veins in the pelvis. They are the venae comitantes of the internal pudendal artery. Internal pudendal veins are enclosed by pudendal canal, with internal pudendal artery and pudenda .... Pathologies involving the Inferior rectal veins may cause lower GI bleeding. Depending on the degree of inflammation, they are given a grade level ranging from 1 through 4. Additional images File:Gray405.png, The perineum. The integument and superficial layer of superficial fascia reflected. References Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Rectal Vein
The middle rectal veins (or middle hemorrhoidal vein) take origin in the hemorrhoidal plexus and receive tributaries from the bladder, prostate, and seminal vesicle. They run lateralward on the pelvic surface of the levator ani The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the ... to end in the internal iliac vein. Veins superior to the middle rectal vein in the colon and rectum drain via the portal system to the liver. Veins inferior, and including, the middle rectal vein drain into systemic circulation and are returned to the heart, bypassing the liver. References Veins of the torso {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Venous System
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels (from Greek ''kardia'' meaning ''heart'', and from Latin ''vascula'' meaning ''vessels''). The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms ''cardiovascular system'' and ''vascular system'' interchangeably with the ''circulatory system''. The network of blood vessels are the great vessels of the heart including large elastic arteries, and large veins; other arteries, smaller arterioles, capillaries that join with venules (small veins), and other veins. The circulatory system is closed in vertebrates, which means that the blood never leaves the network of blood vessels. Some invertebrates such as arth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-pass Metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the systemic circulation. It is the fraction of drug lost during the process of absorption which is generally related to the liver and gut wall. Notable drugs that experience a significant first-pass effect are buprenorphine, chlorpromazine, cimetidine, diazepam, ethanol (drinking alcohol), imipramine, insulin, lidocaine, midazolam, morphine, pethidine, propranolol, and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). First pass metabolism may occur in the liver (for propranolol, lidocaine, clomethiazole, and NTG) or in the gut (for benzylpenicillin and insulin). After a drug is swallowed, it is absorbed by the digestive system and enters the hepatic portal system. It is carried through the portal vein into the liver before it reaches the rest of the body. The liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)